Abstract
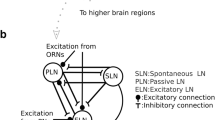
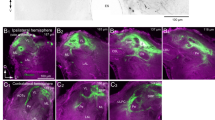
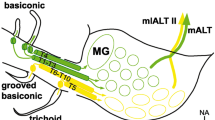
Intracellular recordings were made from the major neurites of local interneurons in the moth antennal lobe. Antennal nerve stimulation evoked 3 patterns of postsynaptic activity: (i) a short-latency compound excitatory postsynaptic potential that, based on electrical stimulation of the antennal nerve and stimulation of the antenna with odors, represents a monosynaptic input from olfactory afferent axons (71 out of 86 neurons), (ii) a delayed activation of firing in response to both electrical- and odor-driven input (11 neurons), and (iii) a delayed membrane hyperpolarization in response to antennal nerve input (4 neurons).
Simultaneous intracellular recordings from a local interneuron with short-latency responses and a projection (output) neuron revealed unidirectional synaptic interactions between these two cell types. In 20% of the 30 pairs studied, spontaneous and current-induced spiking activity in a local interneuron correlated with hyperpolarization and suppression of firing in a projection neuron. No evidence for recurrent or feedback inhibition of projection neurons was found. Furthermore, suppression of firing in an inhibitory local interneuron led to an increase in firing in the normally quiescent projection neuron, suggesting that a disinhibitory pathway may mediate excitation in projection neurons. This is the first direct evidence of an inhibitory role for local interneurons in olfactory information processing in insects. Through different types of multisynaptic interactions with projection neurons, local interneurons help to generate and shape the output from olfactory glomeruli in the antennal lobe.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AL:
-
antennal lobe
- EPSP:
-
excitatory postsynaptic potential
- GABA:
-
γ-aminobutyric acid
- IPSP:
-
inhibitory postsynaptic potential
- LN:
-
local interneuron
- MGC:
-
macroglomerular complex
- OB:
-
olfactory bulb
- PN:
-
projection neuron
- TES:
-
N-tris[hydroxymethyl]methyl-2-aminoethane-sulfonic acid
References
Alger BE, Nicoll RA (1982) Feed-forward dendritic inhibition in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells studied in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 328:105–123
Arnold G, Budharugsa S, Masson C (1988) Organization of the antennal lobe in the queen honeybee, Apis mellifera L. (Hymenoptera:Apidae). Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 17:185–195
Ashwood TJ, Lancaster B, Wheal HV (1984) In vivo and in vitro studies on putative interneurones in the rat hippocampus: possible mediators of feed-forward inhibition. Brain Res 293:279–291
Boeckh J, Boeckh V (1979) Threshold and odor specificity of phero-mone-sensitive neurons in the deutocerebrum of Antheraea pernyi and A. polyphemus. J Comp Physiol 132:235–242
Boeckh J, Ernst KD (1987) Contribution of single unit analysis in insects to an understanding of olfactory function. J Comp Physiol A 161:549–565
Boeckh J, Tolbert LP (1993) Synaptic organization and development of the antennal lobe in insects. Microsc Res Tech 24:260–280
Boeckh J, Ernst KD, Selsam P (1989) Double labelling reveals monosynaptic connection between antennal receptor cells and identified local interneurons in the deutocerebrum in the American cockroach. Zool Jb Anat 119:303–312
Boeckh J, Distler P, Ernst KD, Hösl M, Malun D (1990) Olfactory bulb and antennal lobe. In: Schild D (ed) Chemosensory information processing. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 201–227
Burrows M, Boeckh J, Esslen J (1982) Physiological and morphological properties of interneurones in the deutocerebrum of male cockroaches which respond to female pheromone. J Comp Physiol 145:447–457
Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1986) Synaptic relationships between local and projection neurons in the antennal lobe of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Soc Neurosci Abstr 12:857
Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1987a) Functions, organization, and physiology of the olfactory pathways in the lepidopteran brain. In: Gupta AP (ed) Arthropod brain: its evolution, development, structure and functions. Wiley, New York, pp 457–484
Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1987b) Male-specific, sex phero-mone-selective projection neurons in the antennal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 160:553–569
Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1988) Frequency coding by central olfactory neurons in the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Chemical Senses 13:123–130
Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1990) Representation of sexpheromonal information in the insect brain. In: Døving KB (ed) Proc Xth Internatl Symp Olfaction and Taste (ISOT X). Graphic Communication Systems, Oslo, pp 142–150
Christensen TA, Mustaparta H, Hildebrand JG (1989a) Discrimination of sex pheromone blends in the olfactory system of the moth. Chemical Senses 14:202–217
Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG, Tumlinson JH, Doolittle RE (1989b) The sex pheromone blend of Manduca sexta: responses of central olfactory interneurons to antennal stimulation in male moths. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 10:281–291
Christensen TA, Mustaparta H, Hildebrand JG (1991) Chemical communication in heliothine moths. II. Central processing of intra- and interspecific olfactory messages in the male corn earworm moth Helicoverpa zea. J Comp Physiol A 169:259–274
Distler P (1989) Histochemical demonstration of GABA-like immunoreactivity in cobalt labeled neuron individuals in the insect olfactory pathway. Histochemistry 91:245–249
Distler P (1990a) Synaptic connections of dopamine-immunoreactive neurons in the antennal lobes of Periplaneta americana. Colocalization with GABA-like immunoreactivity. Histochemistry 93:401–408
Distler P (1990b) GABA-immunocytochemistry as a label for identifying types of local interneurons and their synaptic contacts in the antennal lobes of the American cockroach. Histochemistry 93:617–626
Ernst KD, Boeckh J (1983) A neuroanatomical study on the organization of the central antennal pathways in insects. III. Neuroanatomical characterization of physiologically defined response types of deutocerebral neurons in Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 229:1–22
Flanagan D, Mercer AR (1989a) Morphology and response characteristics of neurones in the deutocerebrum of the brain in the honeybee Apis mellifera. J Comp Physiol A 164:483–494
Flanagan D, Mercer AR (1989b) An atlas and 3-D reconstruction of the antennal lobes in the worker honeybee, Apis mellifera L. (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 18:145–159
Gascuel J, Masson C (1991) A quantitative ultrastructural study of the honeybee antennal lobe. Tissue Cell 23:341–355
Getchell TV, Shepherd GM (1975a) Synaptic actions on mitral and tufted cells elicited by olfactory nerve volleys in the rabbit. J Physiol (Lond) 251:497–522
Getchell TV, Shepherd GM (1975b) Short-axon cells in the olfactory bulb: dendrodendritic synaptic interactions. J Physiol (Lond) 251:523–548
Hamilton KA, Kauer JS (1988) Responses of mitral/tufted cells to orthodromic and antidromic electrical stimulation in the olfactory bulb of the tiger salamander. J Neurophysiol 59:1736–1755
Hamilton KA, Kauer JS (1989) Patterns of intracellular potentials in salamander mitral/tufted cells in response to odor stimulation. J Neurophysiol 62:609–625
Hansson BS, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1991) Functionally distinct subdivisions of the macroglomerular complex in the antennal lobe of the male sphinx moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Neurol 312:264–278
Homberg U (1984) Processing of antennal information in extrinsic mushroom body neurons of the bee brain. J Comp Physiol A 154:825–836
Homberg U, Montague RA, Hildebrand JG (1988) Anatomy of antenno-cerebral pathways in the brain of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Cell Tissue Res 254:255–281
Homberg U, Christensen TA, Hildebrand (1989) Structure and function of the deutocerebrum in insects. Anu Rev Entomol 34:477–501
Hoskins SG, Homberg U, Kingan TG, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1986) Immunocytochemistry of GABA in the antennal lobes of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Cell Tissue Res 244:243–252
Hösl M (1990) Pheromone-sensitive neurons in the deutocerebrum of Periplaneta americana: receptive fields on the antenna. J Comp Physiol A 167:321–327
Kanzaki R, Shibuya T (1986) Identification of the deutocerebral neurons responding to the sexual pheromone in the male silk-worm moth brain. Zool Sci 3:409–418
Kanzaki R, Arbas EA, Strausfeld NJ, Hildebrand JG (1989) Physiology and morphology of projection neurons in the antennal lobe of the male moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 165:427–453
Kingan TG, Hildebrand JG (1985) γ-Aminobutyric acid in the central nervous system of metamorphosing and mature Man- duca sexta. Insect Biochem 15:667–675
Kloppenburg P, Hildebrand JG (1992) Modulatory effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on interneurons in the antennal lobe of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Soc Neurosci Abstr 18:303
Light DM (1986) Central integration of sensory signals: an exploration of processing of pheromonal and multimodal information in lepidopteran brains In: Payne TL, Birch MC, Kennedy CEJ (eds) Mechanisms in insect olfaction. Oxford Univ Press, Oxford, pp 287–301
Llinás R, Sugimori M (1980) Electrophysiological properties of in vitro Purkinje cell dendrites in mammalian cerebellar slices. J Physiol (Lond) 305:197–213
Malun D (1991a) Synaptic relationships between GABA-immunoreactive neurons and an identified uniglomerular projection neuron in the antennal lobe of Periplaneta americana: a doublelabeling electron microscopic study. Histochemistry 96:197–207
Malun D (1991b) Inventory and distribution of synapses of identified uniglomerular projection neurons in the antennal lobe of Periplaneta americana. J Comp Neurol 305:348–360
Masson C, Mustaparta H (1990) Chemical information processing in the olfactory system of insects. Physiol Rev 70:199–245
Matsumoto SG, Hildebrand JG (1981) Olfactory mechanisms in the moth Manduca sexta: response characteristics and morphology of central neurons in the antennal lobes. Proc R Soc Lond B 213:249–277
Mercer AR, Hayashi JH, Hildebrand JG (1992) Modulatory effects of 5-hydroxytryptamine on voltage-gated currents in cultured insect olfactory neurons. Soc Neurosci Abstr 18:303
Mori K (1987) Membrane and synaptic properties of identified neurons in the olfactory bulb. Prog Neurobiol 29:275–320
Newberry NR, Nicoll RA (1984) A bicuculline-resistant inhibitory post-synaptic potential in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells in vitro. J Physiol (Lond) 348:239–254
Olberg RM (1983) Interneurons sensitive to female pheromone in the deutocerebrum of the male silkworm moth, Bombyx mori. Physiol Entomol 8:419–428
Pichon Y, Sattelle DB, Lane NJ (1972) Conduction processes in the nerve cord of the moth Manduca sexta in relation to its ultrastructure and haemolymph ionic composition. J Exp Biol 56:717–734
Rospars JP (1988) Structure and development of the insect antennodeutocerebral system. Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 17:243–294
Schäfer S, Bicker G (1986) Distribution of GABA-like immuno-reactivity in the brain of the honeybee. J Comp Neurol 246:287–300
Selzer R (1979) Morphological and physiological identification of food odour specific neurones in the deutocerebrum of Periplaneta americana. J Comp Physiol 134:159–163
Starratt AN, Dahm KH, Allen N, Hildebrand JG, Payne TL, Röller H (1979) Bombykal, a sex pheromone of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. Z Naturforsch 34C:9–12
Stocker RF, Lienhard MC, Borst A, Fischbach K-F (1990) Neuronal architecture of the antennal lobe in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Tissue Res 262:9–34
Sun XJ (1991) Caractérisation électrophysiologique et morphologique des neurones olfactifs du lobe antennaire de l'abeille, Apis mellifera. D Sc thesis, Université de Paris-Sud, Centre d'Orsay, France, pp 1–184
Sun XJ, Tolbert LP, Hildebrand JG (1992) Ultrastructural characteristics of the 5HT-immunoreactive neuron in the antennal lobe of Manduca sexta. Soc Neurosci Abstr 18:303
Tauc L, Hughes GM (1963) Modes of initiation and propagation of spikes in the branching axons of molluscan central neurons. J Gen Physiol 46:533–549
Tolbert LP, Hildebrand JG (1981) Organization and synaptic ultra-structure of glomeruli in the antennal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta: a study using thin sections and freeze-fracture. Proc R Soc Lond B 213:279–301
Tumlinson JH, Brennan MM, Doolittle RE, Mitchell ER, Brabham A, Mazomenos BE, Baumhover AH, Jackson DM (1989) Identification of a pheromone blend attractive to Manduca sexta (L.) males in a wind tunnel. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 10:255–271
Waldrop B, Hildebrand JG (1989) Physiology and pharmacology of acetylcholinergic responses of interneurons in the anten- nal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 164:433–441
Waldrop B, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1987) GABA-mediated synaptic inhibition of projection neurons in the antennal lobes of the sphinx moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 161:23–32
Waxman SG (1972) Regional differentiation of the axon: A review with special reference to the concept of the multiplex neuron. Brain Res 47:269–288
Wellis DP, Scott JW (1990) Intracellular responses of identified rat olfactory bulb interneurons to electrical and odor stimulation. J Neurophysiol 64:932–947
Wellis DP, Scott JW, Harrison TA (1989) Discrimination among odorants by single neurons of the rat olfactory bulb. J Neuro-physiol 61:1161–1177
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christensen, T.A., Waldrop, B.R., Harrow, I.D. et al. Local interneurons and information processing in the olfactory glomeruli of the moth Manduca sexta . J Comp Physiol A 173, 385–399 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193512
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00193512