Summary
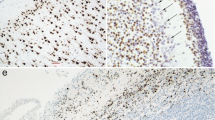
The expression of vimentin and keratins is analysed in the early postimplantation embryo of the rabbit at 11 days post conceptionem (d.p.c.) using a panel of monoclonal antibodies specific for single intermediate filament polypeptides (keratins 7, 8, 18, 19 and vimentin) and a “pan-epithelial” monoclonal keratin antibody. Electrophoretic separation of cytoskeletal preparations obtained from embryonic tissues, in combination with immunoblotting of the resulting polypeptide bands, demonstrates the presence of the rabbit equivalents of human keratins 8, 18, and vimentin in 11-day-old rabbit embryonic tissues. Immunohistochemical staining shows that several embryonic epithelia such as notochord, surface ectoderm, primitive intestinal tube, and mesonephric duct, express keratins, while others (neural tube, dermomyotome) express vimentin, and a third group (coelomic epithelia) can express both. Similarly, of the mesenchymal tissues sclerotomal mesenchyme expresses vimentin, while somatopleuric mesenchyme (abdominal wall) expresses keratins, and splanchnopleuric mesenchyme (dorsal mesentery) expresses both keratins and vimentin. While these results are in accordance with most results of keratin and vimentin expression in embryos of other species, they stand against the common concept of keratin and vimentin specificity in adult vertebrate tissues. Furthermore, keratin and vimentin are not expressed in accordance with germ layer origin of tissues in the mammalian embryo; rather the expression of these proteins seems to be related to cellular function during embryonic development.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Hasani S (1980) In-vitro Befruchtungsversuche mit präovulatorischen Kanincheneizellen. Dissertation, Universität Hannover
Broers JLV, Carney DN, Klein Rot M, Schaart G, Lane EB, Vooijs GP, Ramaekers FCS (1986) Intermediate filament proteins in classic and variant types of small cell lung carcinoma cell lines: a biochemical and immunochemical analysis using a panel of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. J Cell Sci 83:37–60
Byskov AG (1986) Differentiation of the mammalian embryonic gonad. Physiol Rev 66:71–117
Danto SI, Fishmann DA (1984) Immunocytochemical analysis of intermediate filaments in embryonic heart cells with monoclonal antibodies to desmin. J Cell Biol 98:2179–2191
Ede DA, El-Gadi AOA (1986) Genetic modifications of developmental acts in chick and mouse somite development. In: Bellairs R, Ede DA, Lash JW (eds) Somites in developing embryos. Plenum, New York, p 209–224
Erickson CA, Tucker RP, Edwards BF (1987) Changes in the distribution of intermediate-filament types in Japanese quail embryos during morphogenesis. Differentiation 34:88–97
Gruenwald P (1942) Common traits in development and structure of the organs originating from the coelomic wall. J Morphol 70:353–387
Heukeshoven J, Dernick R (1985) Simplified method for silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels and mechanism of silver staining. Electrophoresis 5:103–112
Holthöfer H, Miettinen A, Lehto VP, Lehtonen E, Virtanen I (1984) Expression of vimentin and cytokeratin types of intermediate filament proteins in developing and adult human kidneys. Lab Invest 50:552–559
Holtzer H, Marshall JM Jr, Finck H (1957) An analysis of myogenesis by the use of fluorescent antimyosin. J Biophys Biochem Cytol 3:705–724
Jackson BW, Grund C, Winter S, Franke WW, Illmensee K (1981) Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. II. Epithelial differentiation and intermediate-sized filaments in early postimplantation embryos. Differentiation 20:203–216
Kemler R, Brulet P, Schnebelen MT, Gaillard J, Jacob F (1981) Reactivity of monoclonal antibodies against intermediate filament proteins during embryonic development. J Embryol Exp Morphol 64:45–60
Keynes RJ, Stern CD (1984) Segmentation in the vertebrate nervous system. Nature 310:786–789
Kyhse-Andersen I (1984) Electroblotting of multiple gels: a simple apparatus without buffer tank for rapid transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide to nitrocellulose. J Biochem Biophys Methods 10:203–209
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lane EB (1982) Monoclonal antibodies provide specific intramolecular markers for the study of epithelial tonofilament organization. J Cell Biol 92:665–673
Lane EB, Hogan BLM, Kurkinen M, Garrels JI (1983) Co-expression of vimentin and cytokeratins in parietal endoderm cells of early mouse embryo. Nature 303:701–704
Lane EB, Bartek J, Purkis PE, Leigh IM (1985) Keratin antigens in differentiating systems. Ann N Y Acad Sci 455:241–258
Lehtonen E, Virtanen I, Saxén L (1985) Reorganization of the intermediate filament cytoskeleton in induced metanephric mesenchyme is independent of tubule morphogenesis. Dev Biol 108:481–490
Levitt P, Cooper ML, Rakic P (1983) Early divergence and changing proportions of neuronal and glial precursor cells in the primate cerebral ventricular zone. Dev Biol 96:472–484
Matsudaira PT, Burgess DR (1978) SDS microslab linear gradient polyacrylamid gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem 87:386–396
Mestres P, Hinrichsen K (1976) Zur Histogenese des Somiten beim Hühnchen. J Embryol Exp Morphol 36:669–683
Miki A, Mizoguti H (1982) Acetylcholinesterase activity in the myotome of the early chick embryo. Cell Tissue Res 227:23–40
Minot CS, Taylor E (1905) Normal plates of the development of the rabbit (Lepus cuniculus L.). In: Keibel F (ed) Normentafeln zur Entwicklungsgeschichte der Wirbelthiere. Fischer, Jena, Fünftes Heft
Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller DL, Geiger B, Krepler R (1982a) The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell 31:11–24
Moll R, Franke WW, Volc-Platzer B, Krepler B (1982b) Different keratin polypeptides in epidermis and other epithelia of human skin: a specific cytokeratin of molecular weight 46000 in epithelia of the pilosebaceous tract and basal cell epitheliomas. J Cell Biol 95:285–295
Osborn M, Debus E, Weber K (1984) Monoclonal antibodies specific for vimentin. Eur J Cell Biol 34:137–146
Page M (1988) Changing patterns of cytokeratin and vimentin in the early chick embryo. Development (in press)
Paranko J, Virtanen I (1986) Epithelial and mesenchymal cell differentiation in the fetal rat genital ducts: changes in the expression of cytokeratin and vimentin type of intermediate filaments and desmosomal plaque proteins. Dev Biol 117:135–145
Paranko J, Kallajoki M, Pelliniemi LJ, Lehto VP, Virtanen I (1986) Transient coexpression of cytokeratin and vimentin in differentiating rat Sertoli cells. Dev Biol 117:35–44
Paulin D, Babinet C, Weber K, Osborn M (1980) Antibodies as probes of cellular differentiation and cytoskeletal organization in the mouse blastocyst. Exp Cell Res 130:297–304
Quinlan RA, Schiller DL, Hatzfeld M, Achtstätter T, Moll R, Jorcano JL, Magin TM, Franke WW (1985) Patterns of expression and organization of cytokeratin intermediate filaments. Ann N Y Acad Sci 455:282–306
Ramaekers F, Huijsmans A, Moesker O, Kant A, Jap P, Herman C, Vooijs P (1983) Monoclonal antibody to keratin filaments specific for glandular epithelia and their tumors: use in surgical pathology. Lab Invest 49:353–361
Ramaekers FCS, Huijsmans A, Schaart G, Moesker O, Vooijs P (1987) Tissue distribution of keratin 7 as monitored by a monoclonal antibody. Exp Cell Res 170:235–249
Regauer S, Franke WW, Virtanen I (1985) Intermediate filament cytoskeleton of amnion epithelium and cultured amnion epithelial cells: expression of epidermal cytokeratins in cells of a simple epithelium. J Cell Biol 100:997–1009
Schermer A, Galvin S, Sun TT (1986) Differentiation-related expression of a major 64K corneal keratin in vivo and in culture suggests limbal location of corneal epithelial stem cells. J Cell Biol 103:49–62
Schmid E, Tapscott S, Bennett GS, Croop JK, Fellini SA, Holtzer H, Franke WW (1979) Differential location of different types of intermediate-sized filaments in various tissues of the chicken embryo. Differentiation 15:27–40
Solursh, M, Meier S (1986) The distribution of somite-derived myogenic cells during early development in the wing bud. In: Bellairs R, Ede DA, Lash JW (eds) Somites in developing embryos. Plenum, New York, p 261–275
Steinert PM, Steven AC, Roop DR (1985) The molecular biology of intermediate filaments. Cell 42:411–419
Tapscott SJ, Bennett GS, Toyama Y, Kleinbart F, Holtzer H (1981) Intermediate filament proteins in the developing chick spinal cord. Dev Biol 86:40–54
Tennyson VM, Brzin M, Slotwiner P (1971) The appearance of acetylcholinesterase in the myotome of the embryonic rabbit. An electron microscope cytochemical and biochemical study. J Cell Biol 51:703–721
Torrey TW (1954) The early development of the human nephros. Contrib Embryol Carnegie Inst 35:175–198
Van Muijen GNP, Ruiter DJ, Warnaar SO (1987) Coexpression of intermediate filament polypeptides in human fetal and adult tissues. Lab Invest 57:359–369
Viebahn C, Lane EB, Ramaekers FCS (1987) The mesonephric (Wolffian) and paramesonephric (Müllerian) ducts of golden hamsters express different intermediate-filament proteins during development. Differentiation 34:175–188
Wachtler F, Christ B, Jacob HJ (1982) Grafting experiments on determination and migratory behaviour of presomitic, somitic and somatopleural cells in avian embryos. Anat Embryol 164:369–378
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft and by the Netherlands Cancer Foundation
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viebahn, C., Lane, E.B. & Ramaekers, F.C.S. Keratin and vimentin expression in early organogenesis of the rabbit embryo. Cell Tissue Res. 253, 553–562 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219746
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00219746