Summary
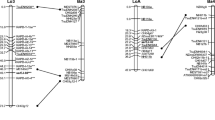
A composite linkage map of Brassica oleracea was developed from maps of four different populations, derived from 108 DNA, isozyme and morphological loci covering over 747 centimorgans in 11 linkage groups. Of these linkage groups, 8 were assigned to their respective chromosomes by alignment with gene synteny groups of B. oleracea. Distortions in segregation ratios increased with the level of divergence of the parents and were attributed to differentiation of parental chromosomes. Comparison of the individual maps demonstrates that the B. oleracea genome undergoes frequent chromosomal rearrangement, even at the subspecies level. Small inversions were the most frequent form of aberration followed by translocations. The former type of aberration could occur without a noticeable effect on meiotic behavior of chromosomes or on pollen fertility. The obvious deduction from the composite map is that a large fraction of the B. oleracea genome is duplicated, falling into three classes: randomly dispersed, linked-gene families, and blocks duplicated in non-homologous chromosomes. The genealogy of chromosomes sharing duplicated segments was formulated and indicates that B. oleracea is a secondary polyploid species derived from ancestral genome(s) of fewer chromosomes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arus P (1989) Linkage analysis of isozyme genes in Brassica Oleracea. In: Quiros CF, McGuire PE (eds) Proc 5th Crucifer Genet Workshop. Davis, Calif, pp 45.
Bernatzky R, Tanksley SD (1986) Toward a saturated linkage map in tomato based on isozymes and random cDNA sequences. Genetics 112:887–898.
Bonierbale MW, Plaisted RL, Tanksley SD (1988) RFLP maps based on a common set of clones reveal modes of chromosomal evolution in potato and tomato. Genetics 120:1095–1103.
Burnham CR (1962) Discussions in cytogenetics. Burgess Publ Co, Minneapolis Minn.
Douches DS, Quiros CF (1988) Genetic recombination in diploid synaptic mutant and a Solanum tuberosum x S. chacoense diploid hybrid. J Hered 60:183–191.
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabelling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13.
Figdore SS, Kennard WC, Song KM, Slocum MK, Osborn TC (1988) Assessment of the degree of restriction fragment length polymorphism in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 75:833–840.
Fisher RL, Goldberg RB (1982) Structure and flanking regions of soybean seed protein genes. Cell 13:277–284.
Gottlieb LD (1983) Isozyme number and phylogeny. In: Jensen U, Fairbrothers DE (eds) Proteins and nucleic acids in plant systematics. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 209–221.
Grant V (1975) Genetics of flowering plants. Columbia University Press, New York.
Gustafsson M, Bentzer B, Von Bothmer R, Snogerap S (1976) Meiosis in Greek Brassica oleracea group. Bot Not 129:73–84.
Haga T (1983) Relationship of genome to secondary pairing in Brassica (a preliminary note). Jpn J Genet 13:277–284.
Harada JJ, Baden CS, Comai L (1988) Spatially regulated genes expressed during seed germination and postgerminative development are activated during embryogeny. Mol Gen Genet 212:466–473.
Havey MJ, Muehlbauer FJ (1989) Linkages between restriction fragment length, isozyme, and morphological markers in lentil. Theor Appl Genet 77:395–401.
Helentjaris T, Slocum M, Wright S, Schaefer A, Nienhuis J (1986) Construction of genetic linkage maps in maize and tomato using restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Theor Appl Gent 72:761–769.
Helentjaris T, Weber D, Wright S (1988) Identification of the genomic locations of duplicate nucleotide sequences in maize by analysis of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Genetics 118:353–363.
Hosaka K, Kianian SF, McGrath JM, Quiros CF (1990) Development and chromosomal localization of genome-specific DNA markers of Brassica and the evolution of amphidiploids and n=9 diploid species. Genome 33:131–142.
Hu J, Quiros CF (1991) Molecular and cytological evidence of deletions in alien chromosomes for two monosomic addition lines of Brassica campestris-oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 81:221–226.
Kianian SF (1990) Evolutionary trends in the Brassica oleracea-cytodeme: chromosomal and linkage relationships. Ph. D. thesis, University of California, Davis Calif.
Kianian SF, Quiros CF (1992) Genetic analysis of major multigene families in Brassica oleracea and related species. Genome 35.
Maniatis TE, Fritsch F, Sambrook J (1982) Molecular cloning, a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD (1988) Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76:815–829.
McGrath JM, Quiros CF (1990) Generation of alien chromosome addition lines from synthetic Brassica oleracea monosomic alien chromosome addition lines with molecular markers reveals extensive gene duplication. Mol Gen Genet 223:198–204.
Ohno S (1970) Evolution by gene duplication. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York.
Paterson AH, De Verna JW, Lanini B, Tanksley SD (1990) Fine mapping of quantitative trait loci using selected overlapping recombinant chromosomes, in an interspecies cross of tomato. Genetics 124:735–742.
Pichersky E (1990) Nomad DNA-A model for movement and duplication of DNA sequences in plant genomes. Plant Mol Biol 15:437–448.
Prakash S, Hinata K (1980) Taxonomy, cytogenetics and origin of crop Brassica, a review. Opera Bot 55:1–59.
Quiros CF, Ochoa O, Kianian SF, Douches D (1987) Analysis of the Brassica oleracea genome by the generation of B. campestris-oleracea addition lines: characterization by isozymes and rRNA genes. Theor Appl Genet 74:758–766.
Quiros CF, Ochoa O, Douches DS (1988) Brassica evolution: exploring the role of X=7 species in hybridization with B. nigra and B. oleracea. J Hered 79:351–358.
Richharia RH (1937a) Cytological investigations of Raphanus Sativus, Brassica oleracea and their F1 and F2 hybrids. J Genet 34:19–44.
Richharia RH (1937b) Cytological investigation of 10-chromosome species of Brassica and their F1 hybrids. J Genet 34:45–55.
Rick CM (1969) Controlled introgression of chromosomes of Solanum pennellii into Lycopersicon esculentum: segregation and recombination. Genetics 62:753–768.
Rick CM (1972) Further studies on segregation and recombination in backcross derivatives of a tomato species hybrid. Biol Zbl 91:209–220.
Robbelen G (1960) Beitrage zur analyse des Brassica genome. Chromosoma 11:205–228.
Sampson DR (1966) Genetic analysis of Brassica oleracea using nine genes from sprouting broccoli. Can J Genet Cytol 8:404–413.
Slocum MK, Figdore SS, Kennard WC, Suzuki JY, Osborn TC (1990) Linkage arrangement of restriction fragment length polymorphism loci in Brassica oleracea. Theor Appl Genet 80:57–64.
Suzuki DT, Griffiths AJF, Miller JH, Lewontin RC (1989) An introduction to genetic analysis, 4th edn. W. H. Freeman and Co, New York.
Suiter KA, Wendel JF, Case JS (1983) Linkage-1: a pascal computer program for the detection and analysis of genetic linkage. J Hered 74:203–204.
Tanksley SD, Miller J, Paterson A, Bernatzky R (1987) Molecular mapping of plant chromosomes. In: Gustafson JP, Appels R (eds) Chromosome structure and function. Plenum Press, New York, pp 157–173.
Yarnell SH (1956) Cytogenetics of the vegetable crops. II. Crucifers. Bot Rev 22:81–166.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. Wenzel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kianian, S.F., Quiros, C.F. Generation of a Brassica oleracea composite RFLP map: linkage arrangements among various populations and evolutionary implications. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 84, 544–554 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224150
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00224150