Summary
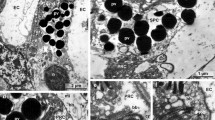
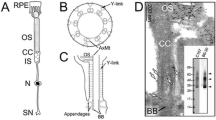
The compound eyes of the Australian tipulid fly, Ptilogyna, shed the bulk of their rhabdomeral membrane to extracellular space during turnover. The rhabdomeres of the retinulae lie in a common extracellular space (ECS), which is subdivided in the proximal retina. Before dawn, a distal region of the microvilli in each rhabdomere differentiates and becomes less electron-dense after conventional fixation. The differentiated region then dilates and develops an irregular profile. A few hours after dawn, the transformed tips break off and form a detritus in the ECS. The degraded membrane is internalised back into the retinula cells by mass endocytosis. Retinulae develop pseudopodia at sites bordering the ECS and engulf the membrane detritus, which comes to lie first of all in vacuoles within the receptor cells and then forms very large multivesicular bodies. The latter transform to multilamellar and residual bodies and are, presumably, lysed. Surrounding these secondary lysosomes are rough endoplasmic reticulum and smooth tubular systems, tentatively considered on comparative grounds to provide hydrolases. The literature concerning the ultrastructure of compound eyes offers a small number of instances where extracellular shedding can be suspected for morphological reasons. Attention is drawn to analogies with the shedding of photoreceptor membranes in vertebrate retinae.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, D.H., Fisher, S.K., Steinberg, R.H.: Mammalian cones, disc shedding, phagocytosis and renewal. Invest. Ophth. 17, 117–133 (1968)
Blest, A.D.: The rapid synthesis and destruction of photoreceptor membrane by a dinopid spider: a daily cycle. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 196, 463–483 (1978)
Blest, A.D., Day, W.A.: The rhabdomere organisation of some nocturnal pisaurid spiders in light and darkness. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 283, 1–23 (1978)
Blest, A.D., Maples, J.: Exocytotic shedding and glial uptake of photoreceptor membrane in a salticid spider. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 204, 105–112 (1979)
Blest, A.D., Kao, L., Powell, K.: Photoreceptor membrane breakdown in the spider Dinopis: The fate of rhabdomere products. Cell Tissue Res. 195, 425–444 (1978a)
Blest, A.D., Powell, K., Kao, L.: Photoreceptor membrane breakdown in the spider Dinopis: GERL differentiation in the receptors. Cell Tissue Res. 195, 277–297 (1978b)
Blest, A.D., Price, G.D., Maples, J.: Photoreceptor membrane breakdown in the spider Dinopis: localisation of acid phosphatases. Cell Tissue Res. 199, 455–472 (1979)
Blest, A.D., Stowe, S., Price, D.G.: The sources of acid hydrolases for photoreceptor membrane degradation in a grapsid crab. Cell Tissue Res. in the press (1980)
Boschek, B.C.: On the fine structure of the peripheral retina and lamina ganglionaris of the fly, Musca domestica. Z. Zellforsch. 118, 369–409 (1971)
Dobrotworski, N.V.: The Tipulidae (Diptera) of Australia. III. The genus Ptilogyna (Westwood). Aust. J. Zool. Suppl. 1, 1–41 (1971)
Eguchi, E., Waterman, T.H.: Freeze-etch and histochemical evidence for cycling in crayfish photoreceptor membranes. Cell Tissue Res. 169, 419–434 (1976)
Goldsmith, T.H., Wehner, R.: Restrictions on rotational and translational diffusion of pigment in the membranes of a rhabdomeric photoreceptor. J. Gen. Physiol. 70, 453–490 (1977)
Griffiths, G.W.: Transport of glial cell acid phosphatase by endoplasmic reticulum into damaged axons. J. Cell Sci. 36, 361–389 (1979)
Griffiths, G.W., Boschek, C.B.: Rapid degeneration of visual fibres following retinal lesions in the dipteran compound eye. Neurosci. Lett. 3, 253–258 (1976)
Hafner, G.S., Bok, D.: The distribution of 3H-leucine labelled protein in the retinula cells of the crayfish retina. J. Comp. Neurol. 174, 397–416 (1977)
Hardie, R.C., Duelli, P.: Properties of single cells in posterior lateral eyes of jumping spiders. Z. Naturforsch. 33, 156–158 (1978)
Itaya, S.K.: Rhabdom changes in the shrimp, Palaemonetes. Cell Tissue Res. 166, 265–273 (1976)
Laughlin, S.B., McGinness, S.: The structures of dorsal and ventral regions of the dragonfly retina. Cell Tissue Res. 188, 427–447 (1978)
Melamed, J., Trujillo-Cenóz, O.: The fine structure of the central cells in the ommatidium of dipterans. J. Ultrastruct. Res. 21, 313–334 (1968)
Nässel, D.R., Waterman, T.H.: Fast massive photoreceptor membrane turnover in crab eye light and dark adaptation. J. Comp. Physiol. 131, 205–216 (1979)
Perrelet, A.: Protein synthesis in the visual cells of the honeybee drone as studied with electron microscope autoradiography. J. Cell Biol. 55, 595–605 (1972)
Schneider, L., Langer, H.: Die Struktur des Rhabdoms im “Doppelauge” des Wasserläufers Gerris lacustris. Z. Zellforsch. 99, 538–559 (1969)
Sotavalta, O., Tuurala, O., Oura, A.: On the structure and photomechanical reactions of the compound eyes of crane-flies (Tipulidae; Limnobiidae). Ann. Acad. Sci. Fenn. A. 62, 1–14 (1962)
Trujillo-Cenóz, O., Bernard, G.D.: Some aspects of the retinal organisation of Sympycnus lineatus Loew (Diptera, Dolichopodidae). J. Ultrastruct. Res. 38, 149–160 (1972)
Walcott, B., Horridge, G.A.: The compound eye of Archicauloides (Megaloptera). Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B. 179, 65–72 (1971)
Wehner, R., Goldsmith, T.H.: Restrictions on translational diffusion of metarhodopsin in the membranes of rhabdomeric photoreceptors. Biol. Bull. 149, 450 (1975)
White, R.H.: The effect of light and light deprivation upon the structure of the larval mosquito eye. II. The rhabdom. J. Exp. Zool. 166, 405–425 (1967)
White, R.H.: The effect of light and light deprivation upon the structure of the mosquito larval eye. III. Multivesicular bodies and protein uptake. J. Exp. Zool. 169, 261–278 (1968)
Williams, D.S.: Ca++-induced structural changes in photoreceptor microvilli of Diptera. Cell Tissue Res. in the press (1980)
Yamamoto, M., Yoshida, M.: Fine structure of the ocelli of a synaptid holothurian, Ophiodesoma spectabilis, and the effects of light and darkness. Zoomorphologie 90, 1–17 (1978)
Young, R.W.: Visual cells, daily rhythms and vision research. Vision Res. 18, 573–578 (1978)
Zinkler, D.: Zum Lipidmuster der Photoreceptoren von Insekten. Verh. Dtsch. Zool. Ges. 67, 28–32 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Williams, D.S., Blest, A.D. Extracellular shedding of photoreceptor membrane in the open rhabdom of a tipulid fly. Cell Tissue Res. 205, 423–438 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232283
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00232283