Summary
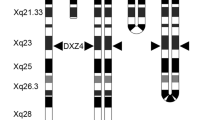
Early replication of prometaphasic human sex chromosomes was studied with the bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU)-replication technique. The studies reveal that two distal segments of Xp, including bands Xp 22.13 and Xp 22.3, replicate early in S-phase and therefore may not be subject to random inactivation. Furthermore, the replication of these distal segments of Xp occurs synchronously with those of the short arm of the Y chromosome including bands Yp 11.2 and Yp 11.32. These segments of Xp and Yp correspond well to the pairing segment of the X and Y chromosomes where a synaptonemal complex forms at early pachytene of human spermatogenesis. The homologous early replication of Yp and the distal portion of Xp may be interpreted as a remnant left untouched by the differentiation of heteromorphic sex chromosomes from originally homomorphic autosomes. A third early replicating segment is situated on the long arm of the X chromosome and corresponds to band Xq 13.1. This segment may be correlated with the X-inactivation center postulated by Therman et al. (1979).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burgoyne PS (1982) Genetic homology and crossing over in the X and Y chromosomes of mammals. Hum Genet 61:85–90
Epstein CJ (1981) Inactivation of the X chromosome.In: Ritzén M(ed) The biology of normal human growth. Raven Press, New York
Fellous M, Pearson PL, van der Linden AGJM, Meera Kahn P, Hagemeijer A (1975) Mapping the Xga red blood cell antigen in human-Chinese hamster cell hybrids: the Xg locus is possibly located on the short arm of the X chromosome. Cytogenet Cell Genet 14:293–295
Gartler SM, Andina RJ (1976) Mammalian X-chromosome inactivation. Adv Hum Genet 7:99–140
Goodfellow PN, Tippett P (1981) A human quantitative polymorphism related to Xg blood groups. Nature 289:404–405
ISCN (1981) An international system for human cytogenetic nomenclature high resolution banding. Report of the standing committee on human cytogenetic nomenclature. Cytogenet Cell Genet 31:1–32
Latt SA (1973) Microfluorometric detection of deoxyribonucleic acid replication in human metaphase chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 70:3395–3399
Lyon MF (1961) Gene action in the X-chromosome of the mouse (Mus musculus L.). Nature 190:372–373
Lyon MF (1962) Sex chromatin and gene action in the mammalian X chromosome. Am J Hum Genet 14:135–148
Lyon MF (1970) Genetic activity of sex chromosomes in somatic cells of mammals. Philos R Soc Lond [Biol] 259:41–52
Lyon MF (1972) X-chromosome inactivation and developmental patterns in mammals. Biol Rev 47:1–35
McKusick VA (1978) Mendelian inheritance in man, 5th ed. The Johns Hopkins University Press, Baltimore
McKusick VA (1982) The human genome through the eyes of a clinical geneticist. In: Human gene mapping 6, Oslo conference (1981). Cytogenet Cell Genet 32:7–23
Mohandas T, Shapiro LJ, Sparkes RS, Sparkes MC (1979) Regional assignment of the steroid sulfatase-X-linked ichthyosis locus: Implications for a noninactivated region on the short arm of human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:5779–5783
Moses MJ, Counce SJ, Paulson DF (1975) Synaptonemal complex complement of man in spreads of spermatocytes, with details of the sex chromosome pair. Science 187:363–365
Müller U, Schempp W (1982) Homologous early replication patterns of the distal short arms of prometaphasic X and Y chromosomes. Hum Genet 60:274–275
Müller CR, Migl B, Traupe H, Ropers HH (1980) X-linked steroid sulfatase: Evidence for different gene-dosage in males and females. Hum Genet 54:197–199
Ohno S (1967) Chromosomes and sex-linked genes. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Perry P, Wolff S (1974) New Giemsa method for the differential staining of sister chromatids. Nature 251:156–158
Polani PE (1982) Pairing of X and Y chromosomes, non-inactivation of X-linked genes, and the maleness factor. Hum Genet 60:207–211
Race RR,Sanger R (1975) Blood groups in man, 6th edn. Blackwell, London
Ropers HH, Migl B, Zimmer J, Müller CR(1981) Steroid sulfatase activity in cultured fibroblasts of XX males. Cytogenet Cell Genet 30:168–173
Schempp W, Müller U (1982) High resolution replication patterns of the human Y chromosome. Intra- and interindividual variation. Chromosoma 86:229–237
Schempp W, Schmid M (1981) Chromosome banding in amphibia. VI. BrdU-replication patterns in Anura and demonstration of XX/XY sex chromosomes in Rana esculenta. Chromosoma 83:697–710
Solari AJ (1980) Synaptonemal complexes and associated structures in microspread human spermatocytes. Chromosoma 81:315–337
Therman E, Sarto GE, Palmer CG, Kallio H, Denniston C (1979) Position of the human X inactivation center on Xq. Hum Genet 50: 59–64
Tiepolo L, Zuffardi O, Fraccaro M. di Natale D, Gargantini L, Müller CR Ropers HH (1980) Assignment by deletion mapping of the steroid sulfatase X-linked ichthyosis locus to Xp 223. Hum Genet 54:205–206
Wolf U (1981) Genetic aspects of H-Y antigen.Hum Genet 58:25–28
Zuffardi O, Maraschio P, Curto Lo F, üller U, Giarola A, Perotti L (1982) The role of Yp in sex determination: new evidence from X/Y translocations. Am J Med Genet 12:175–184
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schempp, W., Meer, B. Cytologic evidence for three human X-chromosomal segments escaping inactivation. Hum Genet 63, 171–174 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291539
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00291539