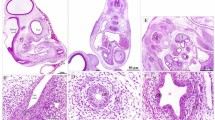
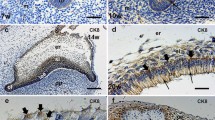
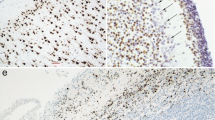
Abstract
In order to characterize human notochordal tissue we investigated notochords from 32 human embryos and fetuses ranging between the 5th and 13th gestational week, using immunohistochemistry to detect intermediate filament proteins cytokeratin, vimentin and desmin, the cytokeratin subtypes 7, 8, 18, 19 and 20, epithelial membrane antigen (EMA), and adhesion molecules pan-cadherin and E-cadherin. Strong immunoreactions could be demonstrated for pan-cytokeratin, but not for desmin or EMA. Staining for pan-cadherin and weak staining for E-cadherin was found on cell membranes of notochordal cells. Also it was demonstrated that notochordal cells of all developmental stages contain the cytokeratins 8, 18 and19, but not 7 or 20. Some cells in the embryonic notochord also contained some vimentin. Vimentin reactivity increased between the 8th and 13th gestational week parallel to morphological changes leading from an epithelial phenotype to the chorda reticulum which represents a mesenchymal tissue within the intervertebral disc anlagen. This coexpression reflects the epithelial-mesenchymal transformation of the notochord, which also loses E-cadherin expression during later stages. Our findings cannot elucidate a histogenetic germ layer origin of the human notochord but demonstrate its epithelial character. Thus, morphogenetic inductive processes between the human notochord and its surrounding vertebral column anlagen can be classified as epithelial-mesenchymal interactions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albelda SM (1993) Role of integrins and other cell adhesion molecules in tumor progression and metastasis. Lab Inv 68:4–17
Albers K, Fuchs E (1992) The molecular biology of intermediate filament proteins. Int Rev Cytol 134:243–279
Bader BL, Jahn L, Franke WW (1988) Low level expression of cytokeratins 8, 18 and 19 in vascular smooth muscle cells of human umbilical cord and in cultured cells derived therefrom, with an analysis of the chromosomal locus containing the cytokeratin 19 gene. Europ J Cell Biol 47:300–319
Balling R, Ebensperger C, Hoffmann I, Imai K, Koseki H, Mizutani Y, Wallin J (1993) The genetics of skeletal development. Ann Génét 36:56–62
Behrens J (1994) Cadherins as determinants of tissue morphology and suppressors of invasion. Act Anat 149:165–169
Ben-Ze'ev A (1984) Differential control of cytokeratins and vimentin synthesis by cell-cell contact and cell spreading in cultured epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 99:1424–1433
Bosman FT (1993) Integrins: cell adhesives and modulators of cell function. Histochem J 25:469–477
Bouropoulou V, Bosse A, Roessner A, Vollmer E, Edel G, Wusimann P, Härle A (1989) Immunohistochemical investigation of chordomas: histogenetic and differential diagnostic aspects. Curr Top Pathol 80:183–203
Broers JLV, Leij L de, Klein Rot M, Haar A ter, Lane EB, Leigh IM, Wagenaar SS, Vooijs GP, Ramaekers CS (1989) Expression of intermediate filament proteins in fetal and adult human lung tissues. Differentiation 40:119–128
Bronner-Fraser M (1993) Mechanisms of neural crest cell migration. BioEssays 15:221–230
Burger PC, Makek M, Kleihues P (1986) Tissue polypeptide staining of the chordoma and notochordal remnants. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 70:269–272
Carlson EC (1973) Intercellular connective tissue fibrils in the notochordal epithelium of the early chick embro. Am J Anat 136:77–90
Coggi G, Dell'Orto P, Braidotti P, Coggi A, Viale G (1989) Coexpression of intermediate filaments in normal and neoplastic human tissues: a reappraisal. Ultrastruct Pathol 13:501–514
Erickson CA, Perris R (1993) The role of cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions in the morphogenesis of the neural crest. Dev Biol 159:60–74
Erickson CA, Tucker RP, Edwards BF (1987) Changes in the distribution of intermediate-filament types in Japanese quail embryos during morphogenesis. Differentiation 34:88–97
Franke WW, Grund C, Kuhn C, Jackson BW, Ilmensee K (1982) Formation of cytoskeletal elements during mouse embryogenesis. III. Primary mesenchymal cells and the first appearance of vimentin filaments. Differentiation 23:43–59
Fuchs E, Weber K (1994) Intermediate filaments: structure, dynamics, function and disease. Annu Rev Biochem 63:345–382
Geiger B, Ayalon O (1992) Cadherins. Ann Rev Cell Biol 8:307–332
Geiger B, Volberg T, Ginsberg D, Bitzur S, Sabanay J, Hynes RO (1991) Broad spectrum of pan-cadherin antibodies, reactive with the C-terminal 24 amino acid residues of N-Cadherins. J Cell Sci 97:607–614
Godsave SF, Anderton BH, Wlie CC (1986) The appearance and distribution of intermediate filament proteins during differentiation of the central nervous system, skin and notochord of Xenopus laevis. J Embryol Exp Morphol 97:201–223
Götz W, Osmers R, Herken R (1995) Localization of extracellular matrix components in the embryonic human notochord and axial mesenchyme. J Anat (in press)
Goldman RD, Steinert PM (1990) Cellular and molecular biology of intermediate filaments. Plenum Press, New York London
Hall BK (1977) Chondrogenesis of the somitic mesoderm. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 53:4–53
Hay ED (1991) Collagen and other matrix glycoproteins in embryogenesis. In: Hay ED (ed) Cell biology of the extracellular matrix, 2nd edn. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 419–462
Herrmann H, Fouquet B, Franke WW (1989) Expression of intermediate filament proteins during development of Xenopus laevis. I. cDNA clones encoding different forms of vimentin. Development 105:279–298
Heyderman E, Strudley J, Powell G, Richardson TC, Cordell JC, Mason DY (1985) A new monoclonal antibody to epithelial membrane antigen (EMA)-E29. Comparison of its immunocytochemical reactivity with polyclonal ant-EMA antibodies and with another monoclonal antibody, HMFG-2. Br J Cancer 52:355–361
Jurand A (1962) The development of the notochord in chick embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol 10:602–621
Jurand A (1974) Some aspects of the development of the notochord in mouse embryos. J Embrol Exp Morphol 32:1–33
Karsten U, Papsdorf G, Roloff G, Stolley P, Abel H, Walther I, Weiss H (1985) Monoclonal anti-cytokeratin antibody from a hybridoma clone generated by electrofusion. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol 21:733–740
Kasper M (1992) Cytokeratins in intracranial and intraspinal tissues. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 126:1–82
Kasper M, Stosiek P (1990) The expression of vimentin in epithelial cells from human nasal mucosa. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 248:53–56
Kasper M, Karsten U, Stosiek P, Moll R (1989) Distribution of intermediate-filament proteins in the human enamel organ: unusual complex pattern of coexpression of cytokeratin polypeptides and vimentin. Differentiation 40:207–214
Koseki H, Wallin J, Wilting J, Mizutani Y, Kispert A, Ebensperger C, Herrmann BG, Christ B, Balling R (1993) A role for Pax-1 as a mediator of notochordal signals during the dorsoventral specification of vertebrae. Development 119:649–660
Koskull H von, Virtanen I (1987) Induction of cytokeratin expression in human mesenchymal cells. J Cell Physiol 133:321–329
Krech R, Loy V, Iglesias JR, Gerdes J, Stein H (1987) Immunhistologische Charakterisierung von Chordomen. Pathologe 8:207–212
Kuruc N, Franke WW (1988) Transient coexpression of desmin and cytokeratins 8 and 18 in developing myocardial cells of some vertebrate species. Differentiation 38:177–193
Lane EB (1993) Keratins. In: Royce PM, Steinmann B (eds) Connective tissue and its heritable disorders. Molecular, genetic, and medical aspects. Wiley-Liss, New York Chichester Brisbane, pp 237–248
Larsen WJ (1993) Human Embryology. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, London
Laucrova L, Kovarik J, Bartek J, Rejthar A, Vojtesek B (1988) Novel monoclonal antibodies defining epitope of human cytokeratin 18 molecule. Hybridoma 7:495–504
Makin C, Babrov LG, Bodmer WF (1984) Monoclonal antibody to cytokeratin for use in routine histopathology. J Clin Pathol 37:975–983
Markl J (1991) Cytokeratins in mesenchymal cells: impact on functional concepts of the diversity of intermediate filament proteins. J Cell Sci 98:261–164
Miettinen M (1993) Keratin immunohistochemistry: update of applications and pitfalls. Pathol Annu 28:113–143
Minor RR (1973) Somite chondrogenesis. A structural analysis. J Cell Biol 56:27–50
Moll R (1986) Epitheliale Tumormarker. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol 70:28–50
Moll R (1993) Cytokeratine als Differenzierungsmarker. Expressionsprofile von Epithelien und epithelialen Tumoren. Veröff Pathol 142:1–191
Moll R, Franke WW, Schiller DL, Geiger B, Krepler R (1982) The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell 31:11–24
Moll R, Hage C, Thoenes W (1991) Expression of intermediate filament proteins in fetal and adult human kidney: modulations of intermediate filament patterns during development and in damaged tissue. Lab Inv 65:74–86
Moll R, Löwe A, Laufer J, Franke WW (1992) Cytokeratin 20 in human carcinomas: a new histodiagnostic marker detected by monoclonal antibodies. Am J Pathol 140:427–447
Müller F, O'Rahilly R (1985) The first appearance of the neural tube and optic primordium in the human embryo at stage 10. Anat Embryol 172:157–169
Müller F, O'Rahilly R (1987) The development of the human brain, the closure of the caudal neuropore, and the beginning of secondary neurulation at stage 12. Anat Embryol 176:413–430
Murakami T, Wakamutsu E, Tamahashi N, Takahashi T (1985) The functional significance of human notochord in the development of vertebral column. An electron microscopic study. Tohoku J Exp Med 146:321–336
Öbrink R (1993) Cell adhesion and cell-cell contact proteins. In: Kreis T, Vale R (eds) Guidebook to the extracellular matrix and adhesion proteins. Oxford University Press, Oxford New York Tokyo, pp 109–114
Oosterwijk E, Van Muijen GNP, Oosterwijk-Wakka JC, Warnaar SO (1990) Expression of intermediate-sized filaments in developing and adult human kidney and in renal cell carcinoma. J Histochem Cytochem 38:385–392
O'Rahilly R, Müller F (1987) Developmental stages in human embryos. Including a revision of streeter's “horizons” and a survey of the Carnegic collection (Carnegie Institution of Washington, Publication 637). Carnegie Institution, Washington
Page M (1989) Changing patterns of cytokeratins and vimentin in the early chick embryo. Development 105:97–107
Paranko J, Virtanen I (1986) Epithelial and mesenchymal cell differentiation in the fetal rat genital ducts: changes in the expression of cytokeratin and vimentin type of intermediate filaments and desmosomal plaque proteins. Dev Biol 117:135–145
Petrali JP, Hinton DM, Moriaty GC, Sternberger LA (1974) The unlabeled antibody enzyme method of immunocytochemistry. J Histochem Cytochem 22:782–801
Raju T, Adelman LS, Dahl D, Bignami A (1983) Localization of keratin in the notochord and in notochord-derived tumors —immunohistochemical study of rat embryo and human chordoma. Int J Dev Neurosci 1:375–382
Ramaekers FCS, Feitz W, Moesker O, Schaart G, Herman C, Debruyne F, Vooijs P (1985) Antibodies to cytokeratin and vimentin in testicular tumour diagnosis. Virchows Arch [A] 408:127–142
Salisbury JR, Isaacson PG (1985) Demonstration of cytokeratins and an epithelial membrane antigen in chordomas and human fetal notochord. Am J Surg Pathol 9:791–797
Schaffer J (1930) Die Stützgewebe. In: Möllendorff W von (ed) Handbuch der mikroskopischen Anatomie des Menschen, Vol 2. Die Gewebe, 2nd part. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–390
Sensenig EC (1949) The early development of the human vertebral column. Contrib Embryol 33:23–41
Shimoyama Y, Hirohashi S, Hirano S, Noguchi M, Shimosato Y, Takeichi M, Abe O (1989) Cadherin cell adhesion molecules in human epithelial tissues and carcinomas. Cancer Res 49:2128–2133
Shinohara H, Tanaka O (1988) Development of the notochord in human embryos: ultrastructural, histochemical, and immunohistochemical studies. Anat Rec 220:171–178
Smedts F, Ramaekers F, Troyanovsky S, Prvszczynski M, Link M, Lane B, Leigh J, Schijf C, Voorijs P (1992) Keratin expression in cervical cancer. Am J Pathol 141:497–511
Springer M (1972) Der Canalis neurentericus beim Menschen. Z Kinderchir 11:183–189
Staagard M, Møllgård K (1989) The developing neuroepithelium in human embryonic and fetal brain studied with vimentin-immunocytochemistry. Anat Embryol 180:17–28
Starck D (1979) Vergleichende Anatomie der Wirbeltiere auf entwicklungsbiologischer Grundlage. Vol. 2: Das Skeletsystem. Allgemeines, Skeletsubstanzen, Skelet der Wirbeltiere einschließlich Lokomotionstypen. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Steinert PM (1993) Structure, function, and dynamics of keratin intermediate filaments. J Invest Dermatol 100:729–734
Stern CD (1990) Two distinct mechanisms for segmentation. Semin Dev Biol 1:109–116
Stosiek P, Kasper M, Karsten U (1988) Expression of cytokeratin and vimentin in nucleus pulposus cells. Differentiation 39:78–81
Takeichi M (1991) Cadherin cell adhesion receptors as a morphogenetic regulator. Science 251:1451–1455
Takeichi M (1993) Cadherins. In: Kreis T, Vale R (eds) Guidebook to the extracellular matrix and adhesion proteins. Oxford University Press, Oxford New York Tokyo, pp 116–118
Taylor JR, Twomey LT (1988) The development of the human intervertebral disc. In: Ghosh P (ed) The biology of the intervertebral disc, vol 1. CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 39–82
Töndury G, Theiler K (1990) Entwicklungsgeschichte und Fehlbildungen der Wirbelsäule (Die Wirbelsäule in Forschung and Praxis, Vol 98). Hippokrates, Stuttgart
Van de Klundert FAJM, Raats JMH, Bloemendal H (1993) Intermediate filaments: regulation of gene expression and assembly. Eur J Biochem 214:351–366
Van Muijen GNP, Ruiter DJ, Warnaar SO (1987) Coexpression of intermediate filament polypeptides in human fetal and adult tissues. Lab Inv 57:359–369
Vasan NS (1987) Somite chondrogenesis: the role of the microenvironment. Cell Diff 21:147–159
Viebahn C, Lane EB, Ramaekers CS (1992) Intermediate filament protein expression and mesoderm formation in the rabbit embryo. A double-labelling immunofluorescence study. Roux's Arch Dev Biol 201:45–60
Voitesek B, Staskova Z, Nenutil R, Bartkova J, Kovarik J, Rejthar A, Bartek J (1989) A panel of monoclonal antibodies to keratin no 7: characterization and value in tumor diagnosis. Neoplasma 37:333–342
Walmsley R (1953) The development and growth of the intervertebral disc. Edinburgh Med J 66:341–364
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Götz, W., Kasper, M., Fischer, G. et al. Intermediate filament typing of the human embryonic and fetal notochord. Cell Tissue Res 280, 455–462 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307819
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00307819