Abstract
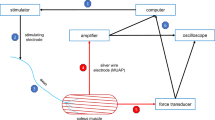
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of electrostimulation in counteracting the transformation of the unweighted rat soleus muscle. The stimulation resembled the firing patterns of normal slow motor units and was imposed during hindlimb suspension. For the 10-day hindlimb suspended rats, the transformation of the slow soleus muscle towards a faster type was characterized by a decrease in the time to peak tension and the half-relaxation time of the twitch, a reduction in the P 20/P 0 index, i. e. the ratio of the subtetanic tension at 20 Hz relative to the tetanic tension, and a decrease in the percentage distributions of type I fibres accompanied by an increase of type IIa and IIc fibres. These changes were prevented by electrostimulation since, for the parameters mentioned above, no significant difference was observed in the soleus of the suspended rats that received electrostimulation when compared with the control rats. Nevertheless, neither the loss of mass nor the decrease in force output in the suspended rats were prevented by electrostimulation. The present results suggest a positive compensation of the suspension-induced alterations in the contractile and histochemical properties of the soleus muscle by means of chronic electrostimulation, which, however, do not prevent atrophy or the loss of contractile force.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alford EK, Roy RR, Hodgson JA, Edgerton VR (1987) Electromyography of rat soleus, medial gastrocnemius and tibialis anterior during hindlimb suspension. Exp Neurol 96:635–649
Brooke MH, Kaiser KK (1970) Three “myosin adenosine triphosphatase” systems: the nature of their pH lability and sulfhydryl dependence. J Histochem Cytochem 18:670–672
Burke RE (1980) Motor unit types: functional specializations in motor control. Trends Neurosci 3:255–258
Burke RE, Levine DN, Tsairis P, Zajac FE (1973) Physiological types and histochemical profiles in motor units of the cat gastrocnemius. J Physiol (Lond) 234:723–748
Close RI (1969) Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles of the rat after cross-union. J Physiol (Lond) 204:331–346
Cotter M, Barry J, Cameron N (1988) Recovery from immobilization-induced atrophy of rabbit soleus muscles can be accelerated by chronic low-frequency stimulation. Q J Exp Physiol 73:797–800
Desplanches D, Mayet MH, Sempore B, Flandrois R (1987) Structural and functional responses to prolonged hindlimb suspension in rat muscle. J Appl Physiol 63:558–563
Diffee GM, Caiozzo VJ, Herrick RE, Baldwin KM (1991) Contractile and biochemical properties of rat soleus and plantaris after hindlimb suspension. Am J Physiol 260:528–534
Falempin M, Leclercq T, Leterme D, Mounier Y (1990) Timecourse of soleus muscle-change in and-recovery from disuse atrophy. Physiologist 33:S88-S89
Fitts RH, Metzger JM, Riley DA, Unsworth BR (1986) Models of disuse: a comparison of hindlimb suspension and immobilization. J Appl Physiol 60:1946–1953
Gardetto PR, Schluter JM, Fitts RH (1989) Contractile function of single muscle fibers after hindlimb suspension. J Appl Physiol 66:2739–2749
Grandmontagne M, Vaage O, Køpke Vøllestadn N, Hermansen L (1982) Confrontation de méthodes histochimiques et d'immunofluorescence pour le typage des fibres du muscle squelettique de rat. J Physiol (Paris) 78:14A
Gundersen K, Leberer E, Lømo T, Pette D, Staron RS (1988) Fibre-types, calcium-sequestring proteins and metabolism enzymes in denervated and chronically stimulated muscles of the rat. J Physiol (Lond) 398:177–189
Gupta RC, Misulis KE, Dettbarn WD (1989) Activity dependent characteristics of fast and slow muscle: biochemical and histochemical considerations. Neurochem Res 14:647–655
Hauschka EO, Roy RR, Edgerton VR (1988) Periodic weight support effects on rat soleus fibers after hindlimb suspension. J Appl Physiol 65:1231–1237
Hennig R, Lømo T (1985) Firing patterns of motor units in normal rats. Nature 314:164–166
Herbert ME, Roy RR, Edgerton VR (1988) Influence of oneweek hindlimb suspension and intermittent high load exercise on rat muscles. Exp Neurol 102:190–198
Jaspers SR, Fagan JM, Satarug S, Cook PH, Tischler ME (1988) Effects of immobilization on rat hindlimb muscles under non-weight bearing conditions. Muscle Nerve 11:458–466
Kirby CR, Mirellé JR, Booth FW (1992) Eccentric exercise training as a countermeasure to non-weight-bearing soleus muscle atrophy. J Appl Physiol 73:1894–4899
Lestienne FG, Gurfinkel VS (1988) Postural control in weightlessness: a dual process underlying adaptation to an unusual environment. Trends Neurosci 11:359–363
Luff AR (1974) Dynamic properties of fast and slow skeletal muscles in the cat and rat following cross-reinnervation. J Physiol (Lond) 248:83–96
Morey ER (1979) Spaceflight and bone turnover: correlation with a new rat model of weightlessness. Bioscience 29:168–172
Morrison JB (1970) The mechanics of muscle function in locomotion. J Biomech 3:431–451
Pette D, Vrbova G (1985) Neural control of phenotypic expression in mammalian muscle fibers. Muscle Nerve 8:676–689
Reiser PJ, Kasper CE, Moss RL (1987) Myosin subunits and contractile properties of single fibers from hypokinetic rat muscles. J Appl Physiol 63:2293–2300
Riley DA, Slocum GR, Bain JLW, Sedlak FR, Sowa TE, Mellender JW (1990) Rat hindlimb unloading: soleus histochemistry, ultrastructure and electromyography. J Appl Physiol 69:58–66
Specter SA, Simard CP, Fournier M, Sternlicht E, Edgerton VR (1982) Architectural alterations of rat hindlimb skeletal muscles immobilized at different lengths. Exp Neurol 76:94–110
Stevens L, Mounier Y, Holy X, Falempin M (1990) Contractile properties of rat soleus muscle after 15 days of hindlimb suspension. J Appl Physiol 68:334–340
Stump CS, Overton JM, Tipton CM (1990) Influence of single hindlimb support during simulated weightlessness in the rat. J Appl Physiol 68:627–634
Templeton GH, Padalino M, Manton J, Glasberg M, Silver CJ, Silver P, Demartino G, Leconey T, Klug G, Hagler H, Sutko JL (1984) Influence of suspension hypokinesia on rat soleus muscle. J Appl Physiol 56:278–286
Templeton GH, Sweeney L, Timson BF, Padalino M, Dudenhoefter GA (1988) Changes in fiber composition of soleus muscle during rat hindlimb suspension. J Appl Physiol 65:1191–1195
Thomason DB, Booth FW (1990) Atrophy of the soleus muscle by hindlimb unweighting. J Appl Physiol 68:1–12
Thomason DB, Herrick RE, Surdyka D, Baldwin KM (1987) Time course of soleus muscle myosin expression during hindlimb suspension and recovery. J Appl Physiol 63:130–137
Thomason DB, Herrick RE, Baldwin KM (1987) Activity influences on soleus muscle myosin during rodent hindlimb suspension. J Appl Physiol 63:138–144
Westgaard RH, Lømo T (1988) Control of contractile properties within adaptive ranges by patterns of impulse activity in the rat. J Neurosci 8:4415–4426
Winiarski AM, Roy RR, Alford EK, Chiang PC, Edgerton VR (1987) Mechanical properties of rat skeletal muscle after hindlimb suspension. Exp Neurol 96:650–660
Wronski TJ, Morey-Holton ER (1987) Skeletal response to simulated weightlessness: a comparison of suspension techniques. Aviat Space Environ Med 58:63–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leterme, D., Falempin, M. Compensatory effects of chronic electrostimulation on unweighted rat soleus muscle. Pflugers Arch. 426, 155–160 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374683
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00374683