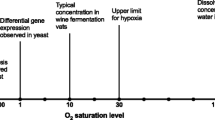
Summary
A method for the estimation of the yield on energy (Y ATP) and of the efficiency of oxidative phosphorylation, in vivo (P/O ratio) is described, which is based on the measurement of effective gas exchange values (\(Q_{O_2 }\) and \(Q_{CO_2 }\)) and of the yield coefficient Y of continuously growing populations of baker's yeast which vary in the degree of fermentation and respiration. For Y ATP a value of 12.0±0.5 \(\frac{{{\text{mg dry weight formed}}}}{{{\text{mMole ATP}}}}\) and for P/O ratio one of 1.1±0.05 \(\frac{{{\text{mMole ATP}}}}{{{\text{1/2 mMole O}}_{\text{2}} }}\) was found and seems to be independent of the type of glucose catabolism (under glucose limitation).
The gas exchange of populations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae synchronized at different growth rates was determined. The specific oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide formation rate, Q O 2, and Q CO 2, are shown to depend on the state of the cells in the budding cycle. Increase in gas metabolism and therefore increased energy generation coincides with the initiation of budding. The longer the generation time g the more expressed are these oscillations of energy formation over the budding cycle. The relationship between the course of energy generation and energy storage and the sequence of budding and single cell phase over the division cycle is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bauchop, T., and S. R. Elsden: The growth of microorganisms in relation to their energy supply. J. gen. Microbiol. 23, 457–469 (1960).
Beck, C., and H. K. von Meyenburg: Enzyme pattern and aerobic growth of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under various degress of glucose limitation. J. Bact. 96, 479–486 (1968).
Chance, B.: Phosphorylation efficiency of the intact cell. II. Crossover phenomena in baker's yeast. J. biol. Chem. 234, 3036–3040 (1959a).
—: Phosphorylation efficiency of the intact cell. III. Phosphorylation and dephosphorylation in yeast cells. J. biol. Chem. 234, 3041–3043 (1959b).
Chen, S. L.: Carbohydrate assimilation in actively growing yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Metabolic pathways for 14C-glucose utilization by yeast during aerobic fermentation. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 32, 470–479 (1959).
—: Energy requirement for microbial growth. Nature (Lond.) 202, 1135–1136 (1964).
Engelberg, J.: Measurement of degrees of synchrony in cell populations. In: Synchrony in Cell Division and Growth, ed. by E. Zeuthen, pp. 497–508, New York: Interscience Publishers 1964.
Fiechter, A.: Die kontinuierliche Züchtung von Mikroorganismen als apparatives Problem. Biotechn. Bioeng. 7, 101–128 (1965).
—, u. H. K. von Meyenburg: Wachstum und Gasstoffwechsel von Saccharomyces cerevisiae in kontinuierlicher Kultur. Path. et Microbiol. (Basel) 29, 696–704 (1966a).
Fiechter, A. u. H. K. von Meyenburg: Regulatory properties of growing cell populations of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in a continuous culture system. Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. on Yeast, p. 387–397. Bratislava 1966 b.
—— u. H. K. von Meyenburg: Automatic analysis of gasexchange in microbial systems. Biotechn. Bioeng. 10, 535–549 (1968)
Gorman, J., P. Tauro, M. LaBerge, and H. Halvorson: Timing of enzyme synthesis during synchronous division in yeast. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 15, 43–49 (1964).
Hadjipetrou, L. P., J. P. Gerrits, F. A. G. Teuflings, and A. H. Stouthamer: Relation between energy production and growth of Aerobacter aerogenes. J. gen. Microbiol. 36, 139–150 (1964).
Herbert, D.: Continuous culture of microorganisms; some theoretical aspects. Continuous cultivation of microorganisms, p. 45. A Symposium. Prague: Publ. House Czechoslov. Acad. Sci. 1958.
Hernandez, E., and M. J. Johnson: Anaerobic growth yields of Aerobacter cloacae and Escherichia coli. J. Bact. 94, 991–995 (1967a).
——: Energy supply and cell yield in aerobically grown microorganisms. J. Bact. 94, 996–1001 (1967b).
Kovachevich, R., and E. S. Guzman Barron: Comparisons of phosphogluconate oxidative pathway in normal and respiration deficient mutant yeast. Arch. Biochem. 108, 200–206 (1964).
Küenzi, M., and A. Fiechter: Changes of carbohydrate composition and trehalase activity during the budding cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch. Mikrobiol. 64, 396–407 (1969).
Lynen, F., u. R. Koenigsberger: Zum Mechanismus der Pasteurschen Reaktion: Der Phosphat-Kreislauf in der Hefe und seine Beeinflussung durch 2,4-Dinitrophenol. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 573, 60–84 (1951).
Meyenburg, H. K. von: Der Sprossungszyclus von Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Path. et Microbiol. (Basel) 31, 117–127 (1968).
Meyenburg, H. K. von: Katabolit-Repression und der Sprossungszyklus von Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Dissertation ETH, Zürich (1969).
Meyenberg, H. K. von: Stable synchrony-oscillations in continuous culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae under glucose limitation. 1 st Coll. on Short Term Biochem. Osc., Prague 1968 (in press).
Meyenburg, H. K. von, and A. Fiechter: Regulation phenomena of gaseous metabolism of aerobically growing baker's yeast. Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. on Yeast, p. 377–385. Bratislava 1966.
Monod, J.: Recherches sur la croissance des cultures bactériennes. Paris: Herrmann & Cie. 1942.
Novick, A., and L. Scilard: Experiments with the chemostat on spontaneous mutations of bacteria. Proc. natl. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 36, 708–719 (1950).
Onishi, T., K. Kawaguchi, and B. Hagihara: Preparation and some properties of yeast mitochondria. J. biol. Chem. 241, 1797–1806 (1966).
Senez, J. C.: Some considerations on the energetics of bacterial growth. Bact. Rev. 26, 95–107 (1962).
Tauro, P., and H. O. Halvorson: Effect of gene position on the timing of enzyme synthesis in synchronous cultures of yeast. J. Bact. 92, 652–661 (1966).
Whitaker, A. M., and S. R. Elsden: The relation between growth and oxygen consumption in microorganisms. J. gen. Microbiol. 31, XXII (1963).
Wiemken, A., H.K. von Meyenburg, and Ph. Matile: Properties of the vacuole in baker's yeast synchronized with a new method. Proc. 2nd Int. Symp. on Yeast Protoplasts. Brno 1968 (in press).
Williamson, D. H.: Division synchrony in yeasts. In: Synchrony in Cell Division and Growth, ed. by E. Zeuthen, pp. 351–379. New York: Interscience Publishers 1964.
—: Nuclear events in synchronously dividing yeast cultures. In: Cell Synchrony, ed. by I. L. Cameron and G. M. Padilla, pp. 81–101. New York: Academic Press 1966.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaspar von Meyenburg, H. Energetics of the budding cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae during glucose limited aerobic growth. Archiv. Mikrobiol. 66, 289–303 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00414585
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00414585