Abstract
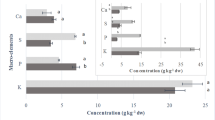
Iodine and bromine content were measured in 24 species of red (Rhodophyta), brown (Phaeophyta) and green (Chlorophyta) seaweeds and 2 species of higher water plants (Embryophyta) from the Sea of Japan, as well as in 12 species of the abovecited taxa and 1 species of flowering plant from the Sea of Okhotsk. Iodine was determined by photometric extraction with brilliant green, and bromine by neutron activation of samples. Phaeophyta and Rhodophyta were richest in iodine and bromine content. Representatives of the order Ceramiales (Rhodophyta) had high iodine and bromine contents. Thus, iodine concentrations in Ptilota filicina, Campylaephora hypnaeoides and Myriogramme yezoensis, a new iodine concentrator discovered by us, amount to 0.42, 0.094 and 0.75%, respectively. Bromine content in representatives of the family Rhodomelaceae was 3.36 and 3.74% in Japan Sea and Okhotsk Sea Rhodomela larix, respectively. Polysiphonia japonica (Rhodomelaceae) is a newly discovered concentrator of bromine (3.20%). Many species of the order Laminariales (Phaeophyta) were characterized by high iodine contents: Laminaria japonica, L. cichoriodes, L. inclinatorhiza, Cymathaere japonica and Alaria marginata. The Br:I ratio for all the species except those that concentrated iodine, was more than 1. Seaweeds that grow at greater depths showed increased iodine and bromine contents. A tendency toward increased iodine content was observed in species growing further to the North. Iodine and bromine were accumulated selectively by various organs of Sargassum pallidum.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Barashkov, G.K.: Comparative biochemistry of algae, 336 pp. Moscow: Food Industry Publishers 1972
Black, W.A.: The effect of the depth of immersion on the chemical constitution of some of the sublittoral seaweeds common to Scotland. J. Soc. chem. Ind., Lond. 69, 161–165 (1950)
Coulson, C.B.: Protein of marine algae. Chem. Ind. 38, 997–998 (1953)
Dave, H.M., D.R. Baxi and D.S. Datar: Search for source of iodine in India. Salt Res. Ind. 4 (2), 61–64 (1967)
Fedorov, A.A. and M.G. Pimenov: Chemosystematics: problems and practical significance. Communication 1. Pl. Resour. 3 (1), 3–16 (1967)
Gryzhankova, L.N., G.N. Saenko, A.V. Karyakin and N.V. Laktionova: Content of certain metals in Japan Sea algae. Okeanologija 13, 259–263 (1973)
Khromova, N.P. and T.G. Babich: Ion-exchange extraction of iodine from iodine-protein solutions following alkaline treatment of agaroid industrial wastes. Zh. prikl. Khim., Leningr. 7, 1626–1628 (1976)
Kisewetter, I.V.: Variations in chemical composition of Japanese and narrow-leaved laminarians. Izv. tikhookean. nauchno-issled. Inst. r yb. Khoz. Okeanogr. 14, 109–146 (1938)
Kongisser, R.A.: On accumulation of iodine by the algae Ptilota. R yb. Khoz. dal'n. Vost. 3–4, 43–46 (1931)
Kovalsky, V.V.: Geochemical ecology, 229 pp. Moscow: Nauka 1974
Ksenzenko, V.I. and D.S. Stasinevich: Technology of obtaining bromine and iodine, 303 pp. Moscow: Gosudarstvennoye nauchno-tekhnicheskoye izdatelstvo khimicheskoy literatury 1960
Lapin, L.N. and N.V. Reis: Method for estimating iodine in natural sodium chloride and in non-iodized common salt. Vop. Pitan., Mosk. 26 (2), 26–29 (1967)
Mastaglie, P. et J. Augier: Etude de la structure du compose phenolique contenue dans Polysiphonia fastigiata. C. r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci., Paris 229, 775–778 (1949)
Perestenko, L.P.: Rhodomela larix (Turn) C. Ag. on the Soviet Pacific coast. In: News on systematics of lower plants, Vol. 4. pp 141–150. Leningrad: Nauka 1967
Potekhina, A.V. and L.G. Paimeeva: Marine algae novel to coast of Shantar Islands, Okhotsk Sea. In: News on systematics of lower plants, Vol. 9. pp 37–39. Leningrad: Nauka 1972
Rosen, V. Ya.: Geochemistry of bromine and iodine, 143 pp. Moscow: Izdatelstvo Nedra 1970
Saenko, G.N., M.D. Korvakova, I.G. Dobrosmyslova and R.V. Masterova: On complex utilization of the agar algae Ahnfeltia tobuchiensis. In: Utilization of sea water inorganic components, Vol. 1. pp 106–110. Vladivostok: Far East Science Centre, USSR Academy of Sciences, 1975
——, V.F. Makienko and I.G. Dobrosmyslova: Concentration of polyvalent metals by seaweeds in Vostok Bay, Sea of Japan. Mar. Biol. 34, 169–176 (1976)
Saito, T. and Y. Ando: Bromine compounds in seaweeds. I. On a bromphenolic compound obtained from the red algae, Polisiphonia morrowii Harv. J. chem. Soc. Japan (Sect. Pure Chem.) 76, 478–479 (1955)
Schmid, O.J. und H.A. Hoppe: Neuere Erkenntnisse über Inhaltsstoffe der Meeresalgen. Chemikerzeitung — chem. Appar. 89, 549–553 (1965)
Scott, R.: Observations on the iodo-amino-acids of native algae using iodine-131. Nature, Lond. 173 (4414), 1098–1099 (1954)
Selivanov, L.S.: Geochemistry and biogeochemistry of scattered bromine. Trud y biogeokhim. Lab. 8, 5–72 (1946)
Trofimov, A.V.: On mineral iodine in living algae. Trud y nauchno-issled. Inst. morsk. Khoz. Okeanogr. (Trans. Res. Inst. mar. Econ. Oceanogr.) 7, 68–83 (1938)
Vernadsky, V.I.: Chemical elements and mechanisms of the Earth's crust. In: Izbranniya sochineniya, Vol. 1. pp 513–518. Moscow: Izdatelstvo Akademii Nauk SSSR 1954
—: Evolution of species and the living substance. In: Izbranniya sochieneniya, Vol. 5. pp 238–251. Moscow: Izdatelstvo Akademii Nauk SSSR 1960
—: Chemical structure of the Earth's biosphere and its surroundings, 374 pp. Moscow: Nauka 1965
Vinogradov, A.P.: The elementary chemical composition of marine organisms. Mem. Sears Fdn mar. Res. 11, 1–647 (1953)
—: Microelements and the problems facing science. Agrokhimica 8, 20–31 (1965)
Voszhinskaya, V.B., A.S. Tsapko, E.I. Blinova, A.A. Kalugina and Yu.E. Petrov: Commercial algae of the USSR, 270 pp. Moscow: Food Industry Publishers 1971
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M.E. Vinogradov, Moscow
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saenko, G.N., Kravtsova, Y.Y., Ivanenko, V.V. et al. Concentration of lodine and bromine by plants in the seas of Japan and Okhotsk. Mar. Biol. 47, 243–250 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00541002
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00541002