Summary
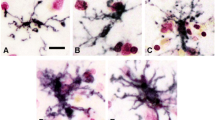
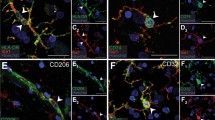
Reactive microglia or macrophages expressing the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR were detected in many neurological diseases including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, Pick's and Huntington's diseases, parkinsonism-dementia of Guam, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, Shy-Drager syndrome, multiple sclerosis and AIDS encephalopathy. Reactive astrocytes, also present in these conditions, were established as a population distinct from the HLA-DR positive microglia by double immunostaining for glial fibrillary acidic protein and HLA-DR. A distinctive pattern of HLA-DR positive cells was seen in each disease entity. Areas known to contain pathology always stained positively, and, in several cases, reactive microglia appeared in areas that would otherwise not have been suspected of being involved in the pathological process. HLA-DR staining, which outlines the surface membranes of positive cells, was so strong that lesioned areas could frequently be identified in sections with the naked eye. In adjacent sections stained with H&E or sections destained of HLA-DR and then restained with H&E, gliosis was often hard to identify except on close microscopic inspection. The results suggest that HLA-DR staining may be a valuable addition to standard neuropathological methods and might be useful in investigating diseases where pathology has not yet been identified.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antoniou AV, Baker D, El-Sady E, Turk JL, Tan BTG, Scheper RJ (1987) Identification and quantitation of the expression of T cell surface markers during the development of chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (CREAE) in the guinea pig. J Neuroimmunol 14:293–303
Barna BP, Chou SM, Jacobs B, Ransohoff RM (1987) Induction of HLA-DR antigen expression in cultured human adult nonneoplastic glial cells. Ann Neurol 22:152
Beach TG, Tago H, Nagai T, Kimura H, McGeer PL; McGeer EG (1987) Perfusion-fixation of the human brain for immunohistochemistry: comparison with immersionfixation. J Neurosci Methods 19:183–192
Boyes BE, Kim SU, Lee V, Sung SC (1986) Immunohistochemical co-localization of S-100b and the glial fibrillary acidic protein in rat brain. Neuroscience 17:857–865
Craggs RI, Webster HdeF (1985) Ia antigens in the normal rat nervous system and in lesions of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 68:263–272
DeTribolet N, Hamou MF, Mach J-P, Carrel S, Schreyer M (1984) Demonstration of HLA-DR antigens in normal human brain. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:417–418
Franks AJ, Bird CC (1986) Expression of MHC class II and lymphocyte antigens by malignant human gliomas. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 12:615
Hauser SL, Bhan AK, Gilles FH, Hoban CJ, Reinherz EL, Schlossman SF, Weiner HL (1983) Immunohistochemical staining of human brain with monoclonal antibodies that identify lymphocytes, monocytes and the Ia antigen. J Neuroimmunol 5:197–205
Hayes GM, Woodroofe MN, Cuzner ML (1987) Microglia are the major cell type expressing MHC class II in human white matter. J Neurol Sci 80:25–37
Haymaker W, Adams RD (1982) Histology and histopathology of the nervous system. Charles C. Thomas, Chicago, pp 481–547
Hickey WF, Kimura H (1987) Graft-vs.-host disease elicits expression of class I and class II histocompatibility antigens and the presence of scattered T lymphocytes in rat central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:2082–2086
Kamo H, Haebara H, Akiguchi I, Kameyama M, Kimura H, McGeer PL (1987) A distinctive distribution of reactive astroglia in the precentral cortex in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74:33–38
Lampson LA (1987) Molecular bases of the immune response to neural antigens. Trends Neurosci 10:211–216
Lampson LA, Hickey WF (1986) Monoclonal antibody analysis of MHC expression in human brain biopsies: tissue ranging from “histologically normal” to that showing different levels of glial tumor involvement. J Immunol 136:4054–4062
Ling E-A (1981) The origin and nature of microglia. In: Federoff S, Hertz L (eds) Advances in cellular neurobiology, vol 2, Academic Press, New York, pp 33–82
McGeer PL, McGeer EG, Fibiger HC (1973) Choline acetylase and glutamic acid decarboxylase in Huntington's chorea—a preliminary study. Neurology 23:912–917
McGeer PL, McGeer EG, Suzuki J, Dolman CE, Nagai T (1984) Aging, Alzheimer's disease and the cholinergic system of the basal forebrain. Neurology 34:741–745
McGeer PL, Kamo H, Harrop R, McGeer EG, Martin WRW, Pate BD, Li DKB (1986) Comparison of PET, MRI and CT with pathology in a proven case of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 36:1569–1574
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, Tago H, McGeer EG (1987) Reactive microglia in patients with senile dementia of the Alzheimer type are positive for the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR. Neurosci Lett 79:195–200
McGeer PL, McGeer EG, Itagaki S, Mizukawa K (1987) Anatomy and pathology of the basal ganglia. Can J Neurol Sci 14:363–372
McGeer PL, Itagaki S, McGeer EG, Mizukawa K (1987) Immunohistochemistry of Parkinson's disease and other basal ganglia disorders. In: Fahn S, Marsden CD, Calne DB, Goldstein M (eds) Recent developments in Parkinson's disease. Macmillan Healthcare Information. New Jersey, pp 31–45
Matsumoto Y, Fujiwara M (1986) In situ detection of class I and II major histocompatibility complex antigens in the rat central nervous system during experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuroimmunol 12:265–277
Natali PG, De Martini C, Quaranta V, Nicotra MR, Frezza F, Pellegrino MA, Ferrone S (1981) Expression of Ia-like antigens on normal human nonlymphoid tissues. Transplantation 31:75–78
Navia BA, Cho E-S, Petito CK, Price RW (1986) The AIDS dementia complex. II. Neuropathology. Ann Neurol 19: 525–535
Penfield W (1925) Microglia and the process of phagocytosis in gliomas. Am J Pathol 1:77–89
Sedgwick J, Brostoff S, Mason D (1987) Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in the absence of a classical delayedtype hypersensitivity reaction. J Exp Med 165:1058–1075
Sobel RA, Blanchette BW, Bhan AK, Colvin RB (1984) The immunopathology of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. II. Endothelial cell Ia increases prior to inflammatory cell infiltration. J Immunol 132:2402–2407
Tago H, McGeer PL, Bruce G, Hersh LB (1987) Distribution of choline acetyltransferase-containing neurons of the hypothalamus. Brain Res 415:49–62
Traugott U, Scheinberg LC, Raine CS (1985) On the presence of Ia-positive endothelial cells and astrocytes in multiple sclerosis lesions and its relevance to antigen presentation. J Neuroimmunol 8:1–14
Vazeux R, Brousse N, Jarry A, Henin D, Marche C, Vedrenne C, Mikol J, Wolff M, Michon C, Rozenbaum W, Bureau J-F, Montagnier L, Brahic M (1987) AIDS subacute encephalitis: identification of HIV-infected cells. Am J Pathol 126:403–410
Wong GHW, Bartlett PF, Clark-Lewis I, Battye F, Schrader JW (1984) Inducible expression of H-2 and Ia antigens on brain cells. Nature 310:688–691
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Medical Research Council of Canada, the Medical Services Foundation of B.C., and the Alzheimer's Association of B.C.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McGeer, P.L., Itagaki, S. & McGeer, E.G. Expression of the histocompatibility glycoprotein HLA-DR in neurological disease. Acta Neuropathol 76, 550–557 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689592
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00689592