Summary
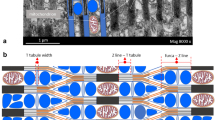
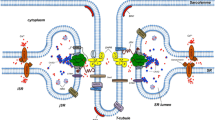
Structural details of junctional feet in triads of fish muscle are described. These feet have a less dense central core and contact both sarcoplasmic reticulum and T-tubule membranes at tetragonally disposed sites. The distribution of intramembraneous particles differs at the junctional T-membrane, and the junction is asymmetric.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BIRKS, R. I. (1965) The sarcoplasmic reticulum of twitch fibers of the frog sartorius muscle. InMuscle (edited by PAUL, W. M., DANIEL, E. E., KAY, C. M. and MONCKTON, G., pp. 199–216. New York: Pergamon Press.
CAMPBELL, K. R., FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG, C. & SHAMOO, A. E. (1980) Further characterization of light and heavy sarcoplasmic reticulum vesicles. Identification of the ‘sarcoplasmic reticulum feet’ associated with heavy sarcoplasmic reticulum.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 602, 97–116.
CASWELL, A. H., LAU, Y. H., GARCIA, M. & BRUNSWICH, J. P. (1979) Recognition and junction formation by isolated transverse tubules and terminal cisternae of skeletal muscle.J. biol. Chem. 254, 202–8.
COSTANTIN, L. L. & TAYLOR, S. R. (1973) Graded excitation in frog muscle fibers.J. gen. Physiol. 61, 424–43.
EASTWOOD, E. A. (1980) Triad structure in mammalian skeletal muscle: chemically skinned rabbit psoas.Anat. Rec. 196, 52a.
EASTWOOD, E. A., FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG, C. & PERACCHIA, C. (1982) Freeze-fracture of crayfish muscle fibres.J. Musc. Res. Cell Motility 3, 273–94.
EASTWOOD, E. A., WOOD, D. S., BOCK, K. L. & SORENSEN, M. H. (1979) Chemically skinned mammalian skeletal muscle. I. The structure of skinned rabbit psoas.Tiss. Cell 11, 553–66.
EDGE, M. B. (1970) Development of apposed sarcoplasmic reticulum at the T system and sarcolemma and the change in orientation of triads in rat skeletal muscle.Devl Biol. 28, 634–59.
EISENBERG, B. R. & EISENBERG, R. S. (1982) The T-SR junction in contracting single skeletal muscle fibers.J. gen. Physiol. 79, 1–19.
EISENBERG, B. R. & GILAI, A. (1979) Structural changes in single muscle fibers after stimulation.J. gen. Physiol. 74, 1–16.
FORBES, M. S., RENNELS, M. L. & NELSON, E. (1979) Caveolar systems and sarcoplasmic reticulum in coronary smooth muscle cells of the mouse.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 67, 325–39.
FORBES, M. S. & SPERELAKIS, N. (1977) Myocardial couplings: their structural variations in the mouse.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 58, 50–65.
FRANK, G. B. (1980) The current view of the source of trigger calcium in excitation-contraction coupling in vertebrate skeletal muscle.Biochem. Pharmacol. 29, 2399–406.
FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG, C. (1973) Studies of the triad: IV. Structure of the junction in frog slow fibers.J. Cell Biol. 56, 120–8.
FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG, C. (1974) Freeze-fracture of striated muscle from a spider. Structural differentiations of sarcoplasmic reticulum and transverse tubular system membranes.J. Cell Biol. 61, 501–15.
FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG, C. (1975) Membrane particles and transmission at the triad.Fed. Proc. 34, 1382–7.
FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG, C. (1976) The comparative structure of intracellular junctions in striated muscle fibers. InPathogenesis of Human Muscular Dystrophies (edited by ROWLAND, R.), pp. 611–625. Amsterdam: Excerpta Medica.
FRANZINI-ARMSTRONG, C. (1980) Structure of sarcoplasmic reticulum.Fed. Proc. 39, 2403–9.
GILLY, W. F. (1981) Intramembrane charge movement and excitation-contraction (E-C) coupling. InThe Regulation of Muscle Contraction E-C Coupling (edited by GRINNELL, A. D. and BRAZIER, M. A. B.), pp. 3–20. New York: Academic Press.
HEUSER, J. E. & SALPETER, S. R. (1979) Organization of acetylcholine receptors in quick frozen, deep-etched and rotary replicatedTorpedo postsynaptic membrane.J. Cell Biol. 82, 150–73.
HUXLEY, A. F. (1971) The activation of striated muscle and its mechanical response.Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 178, 1–27.
HUXLEY, H. E. (1957) The double array of filaments in cross-striated muscle.J. biophys. biochem. Cytol. 3, 631–71.
JEWETT, P. H., SOMMER, J. R. & JOHNSON, E. A. (1971) Cardiac muscle, its ultrastructure in the finch and hummingbird with special reference to the sarcoplasmic reticulum.J. Cell Biol. 49, 50–65.
KACHAR, B. & REESE, T. S. (1982) Evidence for the lipidic nature of tight junction strands.Nature 296, 464–6.
KELLY, D. E. (1969) The fine structure of skeletal muscle triad junctions.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 29, 37–49.
KELLY, D. E. & CAHILL, M. A. (1969) Skeletal muscle triad junction fine structure; new observations regarding dimples of the sarcoplasmic reticulum terminal cisternae.J. Cell Biol. 43, 66a.
KELLY, D. E. & KUDA, A. M. (1979) Subunits of the triadic junction in fast skeletal muscle as revealed by freeze-fracture.J. Ultrastruct. Res. 68, 220–33.
KOVACS, L., RIOS, E. & SCHNEIDER, M. F. (1979) Calcium transients and intramembrane charge movement in skeletal muscle fibres.Nature 279, 391–6.
MATHIAS, R. T., LEVIS, R. A. & EISENBERG, R. S. (1980) Electrical models of excitation contraction coupling and charge movement in skeletal muscle.J. gen. Physiol. 76, 1–31.
MILLER, R. G. (1980) Do ‘lipidic particles’ represent intermembrane attachment sites?Nature 287, 166–8.
PALADE, G. F. (1952) A study of fixation for electron microscopy.J. exp. Med. 95, 285–91.
RAND, R. P., REESE, T. S. & MILLER, R. G. (1981) Phospholipid deformations associated with interbilayer contact and fusion.Nature 293, 237–8.
RAKOWSKI, R. F. & BEST, P. M. (1982) Measurement of membrane charge movement and intracellular Ca2+ release in frog skeletal muscle fibers.Biophys. J. 37, 23a.
RASH, J. E. & ELLISMAN, M. H. (1974) Studies of excitable membranes. I. Macromolecular specializations of the neuromuscular junction and nonjunctional sarcolemma.J. Cell Biol. 63, 567–86.
REVEL, J. P. (1962) The sarcoplasmic reticulum of the bat crycothyroid muscle.J. Cell Biol. 12, 572–88.
SCHNEIDER, M. F. (1970) Linear electrical properties of the transverse tubules and surface membrane of skeletal muscle fibres.J. gen. Physiol. 56, 640–71.
SCHNEIDER, M. F. (1981) Membrane charge movement and depolarization-contraction coupling.Ann. Rev. Physiol. 43, 507–17.
SCHNEIDER, M. F. & CHANDLER, W. K. (1973) Voltage dependent charge movement in skeletal muscle: a possible step in excitation-contraction coupling.Nature 242, 244–6.
SCHOTLAND, D. L., BONILLA, E. & WAKAYAMA, Y. (1981) Freeze-fracture studies of muscle plasma membrane in human muscular dystrophy.Acta neuropath. 54, 189–97.
SCHULTZ, E., CLARK, A. W., SUZUKI, A. & CASSENS, R. G. (1980). Rattlesnake shaker muscle. II. Fine structure.Tiss. Cell 12, 335–51.
SHERMAN, R. G. & LUFF, A. R. (1971) Structural features of the tarsal claw muscle of the spiderEuripelma marxi Simon.Can. J. Zool. 49, 1549–61.
SOMLYO, A. P., DEVINE, C. E., SOMLYO, A. V. & NORTH, S. R. (1971) Sarcoplasmic reticulum and the temperature dependent contraction of smooth muscle in calcium-free solutions.J. Cell Biol. 51, 722–41.
SOMLYO, A. V. (1979) Bridging structures spanning the junctional gap at the triad of skeletal muscle.J. Cell Biol. 80, 743–50.
SOMLYO, A. V., SHUMAN, H. & SOMLYO, A. P. (1977) Composition of sarcoplasmic reticulumin situ by electron probe X-ray microanalysis.Nature 268, 556–8.
SOMLYO, A. V., GONZALES-SERRATOS, H., SHUMAN, H., McCLELLAN, G. & SOMLYO, A. P. (1981) Calcium release and ionic changes in sarcoplasmic reticulum of tetanized muscle: an electron probe study.J. Cell Biol. 90, 577–94.
SOMMER, J. R. & JOHNSON, E. A. (1979) Ultrastructure of cardiac muscle. InHandbook of Physiology, The Cardiovascular System I. (edited by BERNE, R. E.), pp. 113–185. The American Physiological Society.
SOMMER, J. R., WALLACE, N. R. & HASSELBACH, W. (1978) The collapse of sarcoplasmic reticulum in skeletal muscle.Z. Naturforschung. 33, 561–73.
SMITH, D. S. (1965) The organization of flight muscle in an aphidMegoura viciae (homopetra).J. Cell Biol. 27, 379–93.
VALVASSORI, R., DE EGUILEAR, M. & LANZAVECCHIA, G. (1978) Flight muscle differentiation in nymphs of dragonflyAnax imperator.Tiss. Cell 10, 167–78.
VERGARA, J., BEZANILLA, F. & SALZBERG, B. M. (1978) Nile blue fluorescence signals from cut single muscle fibers under voltage clamp conditions.J. gen. Physiol. 72, 775–800.
VERKLEIJI, A. J., MOUNBERS, A. C., LEUMISSEN-BIJVELT, J. & VERVERGAERT, P. H. J. (1979) Lipid intramembraneous particles.Nature 279, 162–3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franzini-Armstrong, C., Nunzi, G. Junctional feet and particles in the triads of a fast-twitch muscle fibre. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 4, 233–252 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00712033
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00712033