Abstract
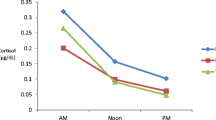
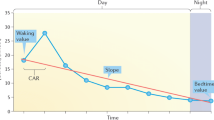
Previous research has suggested that there may be dysfunction in the control of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in autistic children. Both an abnormal cortisol circadian rhythm and failure to suppress cortisol secretion in response to dexamethasome have been reported. This study investigated the basal urinary cortisol circadian rhythm in a group of high-functioning children with autism and matched controls. No evidence was found for abnormal temporal placement of the circadian rhythm in the autistic group. There was a tendency towards cortisol hypersecretion during the day, predominantly in those autistic children who were integrated into the normal school system. While the temporal parameters of the cortisol circadian rhythm in these children with autism were probably normal, the tendency towards cortisol hypersecretion may indicate an environmental stress response in this group.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aihara, R., & Hashimoto, T. (1989). Neuroendocrinological studies on autism [In Japanese].No To Hattatsu, 21, 154–162.
Aschoff, J., Fatranska, M., Giedke, H., Doerr, P., Stamm, D., & Wisser, H. (1971). Human circadian rhythms in continuous darkness: Entrainment by social cues.Science, 171, 213–215.
Bertrand, P. V., Rudd, B. T., Weller, P. H., & Day, A. J. (1987). Free cortisol and creatinine in urine of healthy children.Clinical Chemistry, 33, 2047–2051.
Breslau, N. (1990). Does brain dysfunction increase children's vulnerability to environmental stress?Archives of General Psychiatry, 47, 15–20.
Fein, D., Pennington, B., & Waterhouse, L. (1987). Implications of social deficits in autism for neurological dysfunction. In E. Schopler & G. B. Mesibov (Eds.),Neurobiological issues in autism (pp. 127–144). New York: Plenum Press.
Fibiger, W., Singer, G., Armstrong, S., & Datar, M. (1984). Cortisol and Catecholamine changes as functions of time-of-day and self-reported mood.Neuroscience and Biobehavioural Reviews, 8, 523–530.
Halbreich, U., Zumoff, B., Kream, J., & Fukushima, D. K. (1982). The mean 1300–1600h plasma cortisol concentration as a diagnostic test for hypercortisolism.Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism, 54, 1262–1264.
Hill, S. D., Wagner, E. A., Shedlarski, J. G., Jr., & Sears, S. P. (1977). Diurnal cortisol and temperature variation of normal and autistic children.Developmental Psychobiology, 10, 579–583.
Hoshino, Y., Ohno, Y., Yamamoto, T., Murata, S., Yokoyama, F., Kaneko, M., & Kamashiro, H. (1984). Dexamethasone suppression test in autistic children.Folia Psychiatrica et Neurologica Japonica, 38, 445–449.
Hoshino, Y., Yokoyama, F., Watanabe, Murata, S., Kaneto, M., & Kumashiro, H. (1987). The diurnal variation and response to dexamethasone suppression test of saliva cortisol level in autistic children.Japanese Journal of Psychiatry & Neurology, 41, 228–235.
Inamura, K. (1984). Sleep-wake patterns in autistic children [In Japanese].Japan Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 25, 205–217.
Jensen, J. B., Realmuto, G. M., & Garfinkel, B. D. (1985). The dexamethasone suppression test in infantile autism.Journal of the American Academy of Child Psychiatry, 24, 263–265.
Maher, K. R., Harper, J. F., Macleay, A., & King, M. G. (1975). Peculiarities in the endocrine response to insulin stress in early infantile autism.Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 161, 180–184.
Minors, D. S., & Waterhouse, J. M. (1988). Mathematical and statistical analysis of circadian rhythms.Psychoneuroendocrinology, 13, 443–464.
Moore, A., Aitken, R., Burke, C., Gaskell, S., Groom, G., Holder, G., Selby, C., & Wood, P. (1985). Cortisol assays: guidelines for the provision of a clinical biochemistry service.Annals of Clinical Biochemistry, 22, 435–454.
Moore-Ede, M., Czeisler, C., & Richardson, G. (1983). Circadian time-keeping in health and disease.New England Journal of Medicine, 309, 469–476.
Moore-Ede, M. C., Sulzman, F. M., & Fuller, C. A. (1982).The clocks that time Us. Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press.
Onishi, S., Miyazawa, G., Nishimura, Y., Sugiyama, S., Yamakawa, T., Inagaki, H., Katoh, T., Itoh, S. & Isobe, K. (1983). Post-natal development of circadian rhythm in serum cortisol levels in children.Pediatrics, 72, 399–404.
Prior, M. R., (1987). Biological and neurophysiological approaches to childhood autism.British Journal of Psychiatry, 150, 8–17.
Reinberg, A., Touitou, Y., Restoin, A., Migraine, C., Levi, F. & Montagner, H. (1985). The genetic background of circadian and ultradian rhythm patterns of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids: A cross-twin study.Journal of Endocrinology, 105, 247–253.
Reinis, S., & Goldman, J. M. (1980).The development of the brain. Biological and functional perspectives. Springfield, IL: Charles C Thomas.
Riad-Fahmy, D., Read, G. F., Walker, R. F., & Griffiths, K. (1982). Steroids in saliva for assessing endocrine function.Endocrine Reviews, 3, 367–395.
Sandman, C. A., Barron, J. L., & Parker, L. (1985). Disregulation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis in the mentally retarded.Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behaviour, 23, 21–26.
Sapolsky, R. M. (1989). Hypercortisolism among socially subordinate wild baboons originates at the CNS level.Archives of General Psychiatry, 46, 1047–1051.
Segawa, M. (1985). Circadian rhythm in early infantile autism [In Japanese].Shinkei Kenkyu No Shinpo, 29, 140–153.
Touitou, Y., Sulon, J., Bogdan, A., Reinberg, A., Sodoyez, J. C., & Demey-Ponsart, E. (1983). Adrenocortical hormones, aging and mental condition: Seasonal and circadian rhythms of plasma 18-hydroxy-11-deoxycorticosterone, total and free cortisol and urinary corticosteroids.Journal of Endocrinology, 96, 53–64.
Yamazaki, K., Saito, Y., Okada, F., Fujieda, T., & Yamashita, I. (1975). An application of neuroendocrinological studies in autistic children and Heller's syndrome.Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 5, 323–332.
Yamazaki, K., Saito, Y., Shitara, M. Togashi, H., & Yamashita, K. (1971). Neuroendocrinological study on autistic children.Japan Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 12, 275–286.
Yuwiler, A., Ritvo, E. R., Bald, D., Kipper, D. & Koper, A. (1971). Examination of circadian rhythmicity of blood serotonin and platelets in autistic and non-autistic children.Journal of Autism and Childhood Schizophrenia, 1, 421–435.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
We thank Stuart Armstrong for helpful comments on an earlier draft of the manuscript, and Graham Coleman for statistical advice.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richdale, A.L., Prior, M.R. Urinary cortisol circadian rhythm in a group of high-functioning children with autism. J Autism Dev Disord 22, 433–447 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01048245
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01048245