Abstract
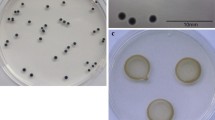
Bacteria associated with phony disease of peach (PDP) and plum leaf scald (PLS) were consistently isolated from diseased trees but not from healthy trees. Colonies of the bacteria grew slowly on PW agar, reaching 0.2 mm to 0.7 mm in diameter in 2 to 3 weeks. The bacteria did not grow on nutrient agar or other general-purpose media. Cells of the bacteria were 0.3 μm to 0.4 μm in width and 2.6 μm to 20.0 μm in length. The topography of the cell walls revealed numerous ridges and furrows. Cells extracted from diseased plants and those from culture gave a strong fluorescence when stained with immunoglobulin G to cells and purified membranes of the bacteria extracted from peach and plum in earlier studies. Immunoglobulin G to cells of the Pierce's disease bacterium from culture also reacted with the bacteria. No discernible differences were observed between strains associated with PDP and PLS in the United States and PLS in Brazil.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Davis, M. J. 1978. Pierce's disease and almond leaf scorch disease: Isolation and pathogenicity of the causal bacterium. Ph.D. Thesis. University of California, Berkeley, California.
Davis, M. J., Gillaspie, A. G., Jr., Harris, R. W., Lawson, R. H. 1980. Ratoon stunting disease of sugarcane: Isolation of the causal bacterium. Science210:1365–1367.
Davis, M. J., Purcell, A. H., Thomson, S. V. 1978. Pierce's disease of grapevine: Isolation of the causal bacterium. Science199:75–77.
Davis, M. J., Purcell, A. H., Thomson, S. V. 1980. Isolation media for the Pierce's disease bacterium. Phytopathology70:425–429.
Davis, M. J., Stassi, D. L., French, W. J., Thomson, S. V. 1979. Antigenic relationship of rickettsia-like bacteria involved in plant diseases. Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Plant Pathogenic Bacteria, Angers, Institut National de le Recherche Agronomique1979:311–315.
Davis, M. J., Thomson, S. V., Purcell, A. H. 1980. Etiological role of the xylem-limited bacterium causing pierce's disease in almond leaf scorch. Phytopathology70:472–475.
Davis, M. J., Whitcomb, R. F., Gillaspie, A. G., Jr. 1981. Fastidious bacteria of plant vascular tissue and invertebrates (including so-called rickettsia-like bacteria), pp. 2172–2188. In: Starr, M. P., Stolp, H. G., Trüper, H. G., Balows, A., Schlegel, H. G. (eds.), The prokaryotes: A handbook on habitats, isolation, and identification of bacteria. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York: Springer-Verlag.
Dedman, R. E., Holmes, A. W., Deinhardt, F. 1965. Preparation of fluorescein isothiocyanate-labeled globulin by dialysis, gel filtration and ion exchange chromatography in combination. Journal of Bacteriology89:734–739.
Fernandez-Valiela, M. V., Bakaracic, M. 1954. Nevas enfermedades del ciruelo en el delta del Parana, Argentina, pp. 2–6. In: Informaciónes de Investigaciónes Agricolas No. 84, Instituto Nacional de Tecnologia Agropecuarias. Buenos Aires, Argentina.
French, W. J., Christie, R. G., Stassi, D. L. 1977. Recovery of rickettsia-like bacteria by vacuum infiltration of peach tissues affected with phony disease. Phytopathology67:945–948.
French, W. J., Kitajima, E. W. 1978. Occurrence of plum leaf scald in Brazil and Paraguay. Plant Disease Reporter62:1035–1038.
French, W. J., Latham, A. J., Stassi, D. L. 1977. Phony peach bacterium associated with leaf scald of plum trees. Proceedings of the American Phytopathological Society4:223.
French, W. J., Stassi, D. L., Schaad, N. W. 1978. The use of immunofluorescence in the identification of phony peach bacterium. Phytopathology68:1106–1108.
Goheen, A. C., Nyland, G., Lowe, S. K. 1973. Association of rickettsia-like organisms with Pierce's disease of grapevines and alfalfa dwarf and heat therapy of the disease in grapevines. Phytopathology63:341–345.
Goldman, M. 1968. pp. 157–158. In: Fluorescent antibody methods. New York: Academic Press.
Hearon, S. S., Sherald, J. L., Kostka, S. J. 1980. Association of xylem-limited bacteria with elm, sycamore, and oak leaf scorch. Canadian Journal of Botany58:1986–1993.
Hopkins, D. L. 1977. Diseases caused by leafhopper-borne rickettsia-like bacteria. Annual Review of Phytopathology15:277–294.
Hopkins, D. L., Mollenhauer, H. H. 1973. Rickettsia-like bacterium associated with Pierce's disease of grapes. Science179:298–300.
Hopkins, D. L., Mollenhauer, H. H., French, W. J. 1973. Occurrence of a rickettsia-like bacterium in the xylem of peach trees with phony disease. Phytopathology63:1422–1423.
Hutchins, L. M. 1933. Identification and control of the phony disease of peach. Georgia Office of State Entomologist, Bulletin 78.
Hutchins, L. M., Rue, J. L. 1949. Natural spread of phony disease to apricot and plum. Phytopathology39:661–667.
Hutchins, L. M., Cochran, L. C., Turner, W. F., Weinberger, J. H. 1953. Transmission of phony disease virus from tops of certain affected peach and plum trees. Phytopathology43:691–696.
Kitajima, E. W., Bakaracic, M., Fernandez-Valiela, M. V. 1975. Association of rickettsia-like bacteria with plum leaf scald disease. Phytopathology65:476–479.
Kuriger, W. E., Schaad, N. W. 1981. Membrane proteins from the rickettsia-like bacterium of Pierce's disease of grape, pp. 483–491. In: Burgdorfer, W., Anaker, R. (eds.), RML Conference on rickettsiae and rickettsial diseases. New York: Academic Press.
Kuriger, W. E., Schaad, N. W., French, W. J. 1981. Comparison of Renografin density gradient centrifugation and ion exchange chromatography for purification of phony peach bacterium from plant extracts. Current Microbiology5:293–296.
Latham, A. J., Norton, J. D., Folsom, M. W. 1980. Leaf scald on plum shoots growing from disease-free buds. Plant Disease64:995–996.
McCoy, R. E., Thomas, D. L., Tsai, J. H., French, W. J. 1978. Periwinkle wilt, a new disease associated with xylem delimited rickettsialike bacteria transmitted by a sharpshooter. Plant Disease Reporter62:1022–1026.
Mircetich, S. M., Lowe, S. K., Moller, W. J., Nyland, G. 1976. Etiology of almond leaf scorch disease and transmission of the causal agent. Phytopathology66:17–24.
Nomé, S. F., Raju, B. C., Goheen, A. C., Nyland, G., Docampo, D. 1980. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for Pierce's disease bacteria in plant tissues. Phytopathology70:746–749.
Nyland, G., Goheen, A. C., Lowe, S. K., Kirkpatrick, H. C. 1973. The ultrastructure of a rickettsialike organism from a peach tree affected with phony disease. Phytopathology63:1275–1278.
Schaad, N. W. 1978. Uses of direct and indirect immunofluorescence tests for identification ofXanthomonas campestris. Phytopathology68:249–252.
Schaad, N. W. 1980. Serological identification of plant pathogenic bacteria. Annual Review of Phytopathology17:123–147.
Thomson, S. V., Davis, M. J., Kloepper, J. W., Purcell, A. H. 1978. Alfalfa dwarf: Relationship to the bacterium causing Pierce's disease of grapevines and almond leaf scorch disease. Abstract of the Proceedings of the Third International Congress of Plant Pathology, Munich, West Germany,1978:65.
Wells, J. M., Raju, B. C., Nyland, G., Lowe, S. K. 1981. Medium for isolation and growth of bacteria associated with plum leaf scald and phony peach diseases. Applied and Environmental Microbiology42:357–363.
Wells, J. M., Weaver, D. J., Raju, B. C. 1980. Distribution of rickettsialike bacteria in peach, and their occurrence in plum, cherry, and some perennial weeds. Phytopathology70:817–820.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davis, M.J., French, W.J. & Schaad, N.W. Axenic culture of the bacteria associated with phony disease of peach and plum leaf scald. Current Microbiology 6, 309–314 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01566883
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01566883