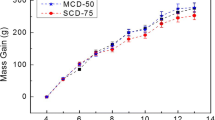
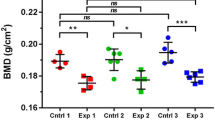
Abstract
Excessive administration of ammonium chloride to normal adult male rats receiving a diet adequate in vitamin D caused the development of osteoporosis. The osteoporosis was due to loss of bone substance and bone mineral associated with increased bone resorption.
Résumé
L'administration chronique de chlorure d ammonium à des rats adultes normaux, soumis à un régime contenant un taux approprié de vitamine D, provoque une ostéoporose. Celle-ci est provoquée par une perte de substance d'os et de minéral osseux, associée à l'augmentation de la résorption osseuse.
Zusammenfassung
Chronische Verabreichung von Ammoniumchlorid an normale ausgewachsene männliche Ratten, die eine entsprechende Vitamin-D-haltige Diät erhalten, verursacht die Entwicklung einer Osteoporose.
Die Osteoporose entsteht auf Grund eines Verlustes von Knochensubstanz und Knochenmineral, in Begleitung einer erhöhten Knochenresorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright, F., Reifenstein, F. G., Jr.: The parathyroid glands and metabolic bone disease, p. 241–247. Baltimore: Williams & Wilkins Co. 1948.
Barzel, U., Jowsey, J.: The effect of chronic acid and alkali intake on bone turnover in adult rats. Clin. Sci.36, 517–524 (1969).
Bauer, W., Aub, J. C., Albright, F.: Studies of calcium and phosphorus metabolism. v. A study of the bone trabeculae as a readily available reserve supply of calcium. J. exp. Med.49, 145–161 (1929).
Goto, K.: Mineral metabolism in experimental acidosis. J. biol. Chem.36, 355 (1918).
Gron, P., McCann, H. G., Bernstein, D.: Effect of fluoride on human osteoporotic bone mineral. J. Bone Jt Surg. A48, 892–898 (1966).
Harper, R. A., Posner, A. S.: Measurement of non crystalline calcium phosphate in bone mineral. Proc. Soc.122, 137–142 (1966).
Harrison, M., Fraser, R.: Bone structure and metabolism in calcium-deficient rats. J. Endocr.21, 197–204 (1960).
Jaffe, H. L., Bodansky, A., Chandler, J. P.: Ammonium chloride decalcification, as modified by calcium intake: The relation between generalized osteoporosis and ostitis fibrosa. J. exp. Med.56, 823–834 (1932).
Jowsey, J., Gershon-Cohen, J.: Effect of dietary calcium levels on production and reversal of experimental osteoporosis in cats. Proc. Soc.116, 437–441 (1964).
—, Raisz, L. G.: Experimental osteoporosis and parathyroid activity. Endocrinology82, 384–396 (1968).
Nichols, G., Jr., Nichols, N.: Effect of parathyroidectomy on content and availability of skeletal sodium in the rat. Amer. J. Physiol.198, 749–753 (1960).
Willis, J. B.: Determination of calcium and magnesium in urine by atomic absorption spectrometer. Analyt. Chem.33, 556–559 (1961).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by a research grant from The Arthritis Foundation, New York Chapter, Inc. The author wishes to acknowledge generous support by Dr. J. Tobis, Chief, Division of Rehalbilitation Medicine at Montefiore Hospital and Medical Center.
Histological examination was performed in cooperation with Doctor H. Dorfman, Director of Laboratories, Hospital for Joint Diseases and Medical Center.
Technical help was furnished by Mr. M. Fein.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barzel, U.S. The effect of excessive acid feeding on bone. Calc. Tis Res. 4, 94–100 (1969). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02279111
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02279111