Abstract
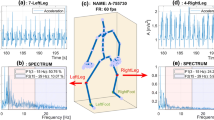
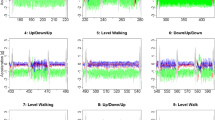
A generic framework for the automated classification of human movements using an accelerometry monitoring system is introduced. The framework was structured around a binary decision tree in which movements were divided into classes and subclasses at different hierarchical levels. General distinctions between movements were applied in the top levels, and successively more detailed subclassifications were made in the lower levels of the tree. The structure was modular and flexible: parts of the tree could be reordered, pruned or extended, without the remainder of the tree being affected. This framework was used to develop a classifier to identify basic movements from the signals obtained from a single, waist-mounted triaxial accelerometer. The movements were first divided into activity and rest. The activities were classified as falls, walking, transition between postural orientations, or other movement. The postural orientations during rest were classified as sitting, standing or lying. In controlled laboratory studies in which 26 normal, healthy subjects carried out a set of basic movements, the sensitivity of every classification exceeded 87%, and the specificity exceeded 94%; the overall accuracy of the system, measured as the number of correct classifications across all levels of the hierarchy, was a sensitivity of 97.7% and a specificity of 98.7% over a data set of 1309 movements.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aminian, K., Robert, P., Jéquier, E., andSchutz, Y. (1995): ‘Incline, speed, and distance assessment during unconstrained walking’,Med. Sci. Sports Exerc.,27, pp. 226–234
Aminian, K., Robert, P., Buchser, E. E., Rutschmann, B., Hayoz, D., andDepairon, M. (1999): ‘Physical activity monitoring based on accelerometry: validation and comparison with video observation’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,37, pp. 304–308
Asada, H. H., Shaltis, P., Reisner, A., Rhee, S., andHutchinson, R. C. (2003): ‘Mobile monitoring with wearable photoplethysmographic biosensors’,IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag.,22, pp. 28–40
Bouten, C. V., Verboeket-van de Venne, W. P., Westerterp, K. R., Verduin, M., andJanssen, J. D. (1996): ‘Daily physical activity assessment: comparison between movement registration and doubly labeled water’,J. Appl. Physiol.,81, pp. 1019–1026
Bouten, C. V., Koekkoek, K. T., Verduin M., Kodde, R., andJanssen, J. D. (1997): ‘A triaxial accelerometer and portable data processing unit for the assessment of daily physical activity’,IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng.,44, pp. 136–147
Celler, B. G., Earnshaw, W., Ilsar, E. D., Betbeder-Matibet, L., Harris, M. F., Clark, R., Hesketh, T., andLovell, N. H. (1995): ‘Remote monitoring of health status of the elderly at home. A multidisciplinary project on aging at the University of New South Wales’,Int. J. BioMed. Comput.,40, pp. 147–155
Celler, B. G., Lovell, N. H., Mathie, M., Basilakis, J., Salleh, R., andMagrabi, F. (2000): ‘Ambulatory monitoring and real time diagnosis of clinical data’. HIC 2000, Integrating Information for Health Care, Adelaide
Currie, G., Rafferty, D., Duncan, G., Bell, F., andEvans, A. L. (1992): ‘Measurement of gait by accelerometer and walkway: a comparison study’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,30, pp. 669–670
Evans, A. L., Duncan, G., andGilchrist, W. (1991): ‘Recording accelerations in body movements’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,29, pp. 102–104
Fahrenberg, J., Foerster, F., Smeja, M., andMüller, W. (1997): ‘Assessment of posture and motion by multichannel piezoresistive accelerometer recordings’,Psychophysiology,34, pp. 607–612
Foerster, F., andFahrenberg, J. (2000): ‘Motion pattern and posture: correctly assessed by calibrated accelerometers’,Behav. Res. Methods, Instrum. Comput.,32, pp. 450–457
Jovanov, E., O'Donnell Lords, A., Raskovic, D., Cox, P. G., Adhami, R., andAdnrasik, F. (2003): ‘Stress monitoring using a distributed wireless intelligent sensor system’,IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag.,22, pp. 49–55
Kamen, G., Patten, C., Du, C., andSison, S. (1998): ‘An accelerometry-based system for the assessment of balance and postural sway’,Gerontology,44, pp. 40–45
Kiani, K., Snijders, C. J., andGelsema, E. S. (1997): ‘Computerized analysis of daily life motor activity for ambulatory monitoring’,Technol. Health Care,5, pp. 307–318
Korhonen, I., Pärkkä, J., andvan Gils, M. (2003): ‘Health monitoring in the home of the future’,IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag.,22, pp. 66–73
Lehrman, M. L., Owens, A. R., Halleck, M. E., andMassman, E. L. (2002): United States Patent Office Document 6,501,386, United States
Makikawa, M., andMurakami, D. (1996): ‘Development of an ambulatory physical activity and behavior map monitoring system’. 18th Ann. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc., Amsterdam, pp. 71–72
Mathie, M. L., Lovell, N. H., Coster, A. C. F., andCeller, B. G. (2002): ‘Determining activity using a triaxial accelerometer’. Proc. 2nd Joint EMBS-BMES Conf. 23rd–26th Oct., Houston, USA
Mathie, M. J., Coster, A. C. F., Lovell, N. H., andCeller, B. G. (2003): ‘Detection of daily physical activities using a triaxial accelerometer’,Med. Biol. Eng. Comput.,41, pp. 296–301
Mathie, M. J., Coster, A. C. F., Lovell, N. H., andCeller, B. G. (2004a). ‘Accelerometry: providing an integrated, practical method for long-term, ambulatory monitoring of human movement’,Physiol. Meas.,25, pp. R1-R20
Mathie, M. J., Coster, A. C. F., Lovell, N. H., Celler, B. G., Lord, S. R., andTiedernamm, A. (2004b). ‘A pilot study of long-term monitoring of human movements in the home using accelerometry’,J. Telemed. Telecare,10, pp. 144–151
Mayagoitia, R. E., Lotters, J. C., Veltink, P. H., andHermens, H. (2002): ‘Standing balance evaluation using a triaxial accelerometer’,Gait Posture,16, pp. 55–59
Ng, A. V., andKent-Braun, J. A. (1997): ‘Quantitation of lower physical activity in persons with multiple sclerosis’,Med. Sci. Sports Exerc.,29, pp. 517–523
Park, S., andJayaraman, S. (2003): ‘Enhancing the quality of life through wearable technology’,IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag.,22, pp. 41–48
Petelenz, T. J., Peterson, S. C., andJacobsen, S. C. (2002): United States Patent Office Document 6,433,690, United States
Steele, B. G., Holt, L., Belza, B., Ferris, S. M., Lakshminaryan, S., andBuchner, D. M. (2000): ‘Quantitating physical activity in COPD using a triaxial accelerometer’,Chest,117, pp. 1359–1367
Tamura, T., Sekine, M., Ogawa, M., Togawa, T., andFukui, Y. (1997): ‘Classification of acceleration waveforms during walking by wavelet transform’,Methods of Inform. Med.,36, pp. 356–369
Uiterwaal, M., Glerum, E. B., Busser, H. J., andvan Lummel, R. C. (1998): ‘Ambulatory monitoring of physical activity in working situations, a validation study’,J. Med. Eng. Technol.,22, pp. 168–172
Veltink, P. H., Bussmann, H. B., De Vries, W., Martens, W. L., andvan Lummel, R. C. (1996): ‘Detection of static and dynamic activities using uniaxial accelerometers’,IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng.,4, pp. 375–385
Winters, J. M., Wang, Y., andWinters, J. M. (2003): ‘Wearable sensors and telerehabilitation’,IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Mag.,22, pp. 56–65
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathie, M.J., Celler, B.G., Lovell, N.H. et al. Classification of basic daily movements using a triaxial accelerometer. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 42, 679–687 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347551
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02347551