Abstract
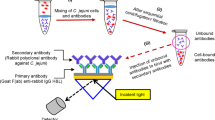
An indirect enzyme immunoassay for rapid detection ofCampylobacter jejuni subsp.jejuni O:23 has been developed. Optimum concentrations of immobilized cells, polyclonal chicken IgY, and rabbit anti-IgY antibody-horseradish peroxidase conjugate were 3.1 CFU/nL, 10 µg/mL, and 8 µg/mL, respectively. Under such conditions, the detection limit reached 50 CFU/µL, limit of quantification being 480 CFU/µL. By testing 5 chromogens.viz. 1,2-benzenediamine, 2,2′-azinobis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid), 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine, bi(4,4′-anisidine) and 3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazone, in horseradish peroxidase substrate, 1,2-benzenediamine or 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine as H-donors in the enzyme substrate provided the highest ELISA sensitivity. The applied polyclonal antibody was specific for homogeneous antigen. The cross-reactions were observed only with one strain ofC. sputorum subsp.sputorum (21.5 %) and with G+ bacteriumMicrococcus luteus (6.1 %). Preliminary tests have been performed with a limited number of artificially contaminated food samples. No matrix effects on the ELISA sensitivity were observed. The results (by means of ELISA) were comparable with those given by both a standard cultivation method performed according toČSN ISO 10272 and commercially available Singlepath® Campylobacter GLISA-Rapid Test.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABS:
-
2,2′-azinobis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid)
- BAN:
-
bi(4,4′-anisidine) (3,3′-dimethoxybenzidine)
- BDA:
-
1,2-benzenediamine
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- DAB:
-
3-dimethylaminobenzoic acid
- HRP:
-
horseradish peroxidase
- MBH:
-
3-methyl-2-benzothiazolinone hydrazone
- PBS:
-
phosphate buffered saline
- TMB:
-
3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine
References
Blaser M.J., Cravens J., Powers B.W., Wang W.-L.L.:Campylobacter enteritidis associated with canine infection.Lancetii, 979–981 (1978).
Blaser M.J., Waldman R.J., Barrett T., Erlandson A.L.: Outbreaks ofCampylobacter enteritis in two extended families — evidence for person-to-person transmission.J.Pediatr.98, 254–257 (1981).
Birkenhead D., Hawkey P.M., Heritage J., Gascoyne-Binzi D.M., Kite P.: PCR for detection and typing ofCampylobacters.Lett.Appl.Microbiol.17, 235–237 (1993).
Bolton F.J., Hutchinson D.N., Coates D.: Blood-free selective medium for isolation ofCampylobacter jejuni from feces.J.Clin.Microbiol.19, 169–171 (1984).
Bryan F.L., Doyle M.P.: Health risks and consequences ofSalmonella andCampylobacter jejuni in raw poultry.J.Food Protect.58, 326–344 (1995).
ČSN ISO 10272: Microbiology of Food and Animal Stuffs — Horizontal Method for Detection of ThermotolerantCampylobacter (1997).
Dedič K., Bockemuhl J., Kühn H., Volkmer K.-J., Weinke U.T.: Campylobacteriosen, pp. 49–65 inBakterielle Zoonosen Bei Tier und Mensch. Ferdinand-Enke-Verlag, Stuttgart 1993.
Docherty L., Adams M.R., Patel P., McFadden J.: The magnetic immuno-polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection ofCampylobacter in milk and poultry.Lett.Appl.Microbiol.22, 288–292 (1996).
Hochel I., Jeníková G., Dursi C.F., Pazlarová J., Girotti S., Demnerová K.: Application of mouse antibodies to somatic antigen for detection ofSalmonella enteritidis by competitive ELISA.Food Agric.Immunol.13, 115–126 (2001).
Hodinka R.L., Gilligan P.H.: Evaluation of the Campyslide agglutination test for confirmatory identification of selectedCampylobacter species.J.Clin.Microbiol.26, 47–49 (1988).
Humprey T.J.: Techniques for the optimum recovery of cold injuredCampylobacter jejuni from milk or water.J.Appl.Bacteriol.61, 125–132 (1986).
Humprey T.J., Henley A., Lanning U.D.G.: The colonization of broiler chickens withCampylobacter jejuni; some epidemiological investigations.Epidemiol.Infect.110, 601–607 (1993).
Jackson T.M., Marshall N.J., Etkins R.P.: Optimization of immunoradiometric (labelled antibody) assays, pp. 557–575 in W.M. Hunter, J.E.T. Corrie (Eds):Immunoassays for Clinical Chemistry. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh 1983.
Jackson C.J., Fox A.J., Jones D.M.: A novel polymerase chain reaction assay for the detection and specification of thermophilicCampylobacter spp.J.Appl.Bacteriol.81, 467–473 (1996).
Jacob L., Schmitt E., Bruemmer W.: Purification of antibodies by new chromatography techniques.Am.Biotechnol.Lab.12, 44–45 (1994).
Karmali M.A., Simor A.E., Roscoe M., Fleming P.C., Smith S.S., Lane J.: Evaluation of blood-free, charcoal-based, selective medium for the isolation ofCampylobacter organisms from feces.J.Clin.Microbiol.23, 456–459 (1986).
Karpinsky K.F.: Optimality assessment in the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).Biometrics46, 381–390 (1990).
Lior H., Woodward D.L., Edgar J.A., Laroche L.J., Gill P.: Serotyping ofCampylobacter jejuni by slide agglutination based on heat-labile antigenic factors.J.Clin.Microbiol.15, 761–768 (1982).
Lu P., Brooks B.W., Robertson R.H., Nielsen K.H., García M.M.: Characterization of monoclonal antibodies for the rapid detection of food borne campylobacters.Internat.J.Food Microbiol.37, 87–91 (1997).
Mentzing L.O.: Waterborne outbreaks ofCampylobacter enteritis in central Sweden.Lancetii, 352–354 (1981).
Mills S.D., Congi R.V., Hennessy J.N., Penner J.L.: Evaluation of a simplified procedure for serotypingCampylobacter jejuni andCampylobacter coli which is based on the O antigen.J.Clin.Microbiol.29, 2093–2098 (1991).
Ng L.K., Kingombe I.B., Yan W., Taylor D.E., Hiratsuka K., García M.M.: Specific detection and confirmation ofCampylobacter jejuni by DNA hybridization and PCR.Appl.Environ.Microbiol.63, 4558–4563 (1997).
Nielsen E.M., Engberg J., Madsen M.: Distribution of serotypes ofCampylobacter jejuni andC. coli from Danish patients, poultry, cattle and swine.FEMS Immunol.Med.Microbiol.19, 47–56 (1997).
Park C.E., Stankiewitz Z.K., Lovett J., Hunt J.: Incidence ofCampylobacter jejuni in fresh eviscerated whole market chickens.Can.J.Microbiol.27, 841–842 (1981).
Penner J.L., Hennessy J.N.: Passive hemagglutination technique for serotypingCampylobacter fetus subsp.jejuni on the basis of soluble heat-stable antigens.J.Clin.Microbiol.12, 732–737 (1980).
Penner J.L., Hennessy J.N., Congi R.V.: Serotyping ofCampylobacter jejuni andCampylobacter coli on the basis of thermostable antigens.Eur.J.Clin.Microbiol.2, 378–383 (1983).
Porstmann T., Porstmann B.: Chromogenic substrates for enzyme immunoassay, pp. 57–84 inNonisotopic Immunoassay (T.T. Ngo, Ed.). Plenum Press, New York 1988.
Porstmann T., Porstmann B., Wietschke R., von Baehr R., Egger E.: Stabilization of the substrate reaction of horseradish peroxidase witho-phenylenediamine in the immunoassay.J.Clin.Chem.Clin.Biochem.23, 41–44 (1985).
Prusak-Sochaczewski E., Luong J.H.T.: An improved ELISA method for detection ofSalmonella typhimurium.J.Appl.Bacteriol.66, 127–135 (1989).
Rice B.E., Rollins D.M., Mallinson E.T., Carr L., Joseph S.W.:Campylobacter jejuni in broiler chickens: colonization and humoral immunity following oral vaccination and experimental infection.Vaccine15, 1922–1932 (1997).
Robinson D.A., Jones D.M.: Milk-borneCampylobacter infection.Brit.Med.J.282, 1374–1376 (1981).
Skirrow M.B.:Campylobacter enteritis: a “new” disease.Brit.Med.J.2, 9–11 (1977).
Skirrow M.B., Turnbull G.L., Walker R.E., Young S.E.J.:Campylobacter jejuni enteritis transmitted from cat to man.Lanceti, 1188 (1980).
Steinhauserová I., Fojtíková K., Klimeš J.: The incidence and PCR detection ofCampylobacter upsaliensis in dogs and cats.Lett.Appl.Microbiol.31, 209–212 (2000).
Studahl A., Andersson Y.: Risk factors for indigenousCampylobacter infections: a Swedish case-control study.Epidemiol.Infectol.125, 269–275 (2000).
Svedhem A., Norkrans G.:Campylobacter jejuni enteritis transmitted from cat to man.Lanceti, 713–714 (1980).
Tijjsen P., Su D.-M., Kurstak E.: Rapid and sensitive heterologous enzyme immunoassays for densonucleosis virus (Parvoviridae).Arch.Virol.74, 277–291 (1982).
Wedderkopp A., Gradel K.O., Jørgensen J.C., Madsen M.: Pre-harvest surveillance ofCampylobacter andSalmonella in Danish broiler flocks: 2-year study.Internat.J.Food Microbiol.68, 53–59 (2001).
Wegmüller B., Lüthy J., Candrian U.: Direct polymerase chain reaction detection ofCampylobacter jejuni andCampylobacter coli in raw milk and dairy products.Appl.Environ.Microbiol.59, 2961–2965 (1993).
Willis W.L., Murray C.:Campylobacter jejuni seasonal recovery observations of retail market broilers.Poultry Sci.76, 314–317 (1997).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The project no. 525/02/0287 (Development of Screening ELISA and PCR Methods for Detection of Campylobacteria in Foods) was supported byGrant Agency of the Czech Republic.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hochel, I., Viochna, D., Škvor, J. et al. Development of an indirect competitive ELISA for detection ofCampylobacter jejuni subsp.jejuni O:23 in foods. Folia Microbiol 49, 579–586 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931537
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02931537