Abstract.
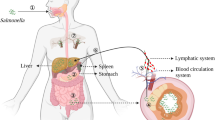
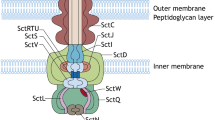
The facultative intracellular pathogen Salmonella enterica resides in a special membrane compartment of the host cell and modifies its host to achieve intracellular survival and proliferation. The type III secretion system encoded by Salmonella pathogenicity island 2 (SPI2) has a central role in the interference of intracellular Salmonella with host cell functions. SPI2 function affects antimicrobial defense mechanisms of the host, intracellular transport processes, integrity and function of the cytoskeleton and host cell death. These modifications are mediated by translocation of a large number of effector proteins by the SPI2 system. In this review, we summarize recent work on the cellular phenotypes related to SPI2 function and contribution of SPI2 effector proteins to these manipulations. These studies reveal a complex set of pathogenic interferences between intracellular Salmonella and its host cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 11 June 2004; received after revision 8 July 2004; accepted 12 July 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuhle, V., Hensel, M. Cellular microbiology of intracellular Salmonella enterica: functions of the type III secretion system encoded by Salmonella pathogenicity island 2. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 61, 2812–2826 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4248-z
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4248-z