Abstract.
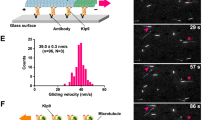
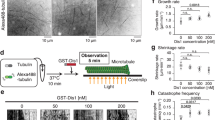
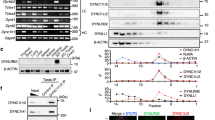
S. cerevisiae anaphase spindle elongation is accomplished by the overlapping function of dynein and the kinesin-5 motor proteins, Cin8 and Kip1. Cin8 and dynein are synthetically lethal, yet the arrest phenotypes of cells eliminated for their function had not been identified. We found that at a non-permissive temperature, dyn1Δ cells that carry a temperature-sensitive cin8 – 3 mutation arrest at mid-anaphase with a unique phenotype, which we named TAN (two microtubule asters in one nucleus). These cells enter anaphase, but fail to proceed through the slow phase of anaphase B. At a permissive temperature, dyn1Δ, cin8 – 3 or dyn1Δcin8 – 3 cells exhibit perturbed spindle midzone morphologies, with dyn1Δcin8 – 3 anaphase spindles also being profoundly bent and nonrigid. Sorbitol, which has been suggested to stabilize microtubules, corrects these defects and suppresses the TAN phenotype. We conclude that dynein and Cin8 cooperate in anaphase midzone organization and influence microtubule dynamics, thus enabling progression through the slow phase of anaphase B.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 10 August 2008; received after revision 22 October 2008; accepted 27 October 2008
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerson-Gurwitz, A., Movshovich, N., Avunie, R. et al. Mid-anaphase arrest in S. cerevisiae cells eliminated for the function of Cin8 and dynein. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 301–313 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8479-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-008-8479-2