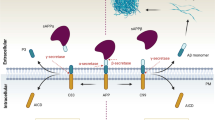
Abstract
The family of mammalian type-I transmembrane receptors containing a Vps10p domain contains five members, Sortilin, SorCS1, SorCS2, SorCS3, and SorLA. The common characteristic of these receptors is an N-terminal Vps10p domain, which either represents the only module of the luminal/extracellular moiety or is combined with additional domains. Family members play roles in protein transport and signal transduction. The individual receptors bind and internalize a variety of ligands, such as neuropeptides and trophic factors, and Sortilin and SorLA mediate trans-Golgi network-to-endosome sorting. Their prominent neuronal expression, several of the identified ligands, and recent results support the notion that members of this receptor family have important functions in neurogenesis, plasticity-related processes, and functional maintenance of the nervous system. For instance, it has been demonstrated that Sortilin partakes in the transduction of proapoptotic effects, and there is converging biochemical and genetic evidence that implies that SorLA is an Alzheimer’s disease risk factor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marcusson EG, Horazdovsky BF, Cereghino JL, Gharakhanian E, Emr SD (1994) The sorting receptor for yeast vacuolar carboxypeptidase Y is encoded by the VPS10 gene. Cell 77:579–586
Hermey G, Riedel IB, Hampe W, Schaller HC, Hermans-Borgmeyer I (1999) Identification and characterization of SorCS, a third member of a novel receptor family. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 266:347–351
Jacobsen L, Madsen P, Moestrup SK, Lund AH, Tommerup N, Nykjaer A, Sottrup-Jensen L, Gliemann J, Petersen CM (1996) Molecular characterization of a novel human hybrid-type receptor that binds the alpha2-macroglobulin receptor-associated protein. J Biol Chem 271:31379–31383
Kikuno R, Nagase T, Ishikawa K, Hirosawa M, Miyajima N, Tanaka A, Kotani H, Nomura N, Ohara O (1999) Prediction of the coding sequences of unidentified human genes. XIV. The complete sequences of 100 new cDNA clones from brain which code for large proteins in vitro. DNA Res 6:197–205
Petersen CM, Nielsen MS, Nykjaer A, Jacobsen L, Tommerup N, Rasmussen HH, Roigaard H, Gliemann J, Madsen P, Moestrup SK (1997) Molecular identification of a novel candidate sorting receptor purified from human brain by receptor-associated protein affinity chromatography. J Biol Chem 272:3599–3605
Rezgaoui M, Hermey G, Riedel IB, Hampe W, Schaller HC, Hermans-Borgmeyer I (2001) Identification of SorCS2, a novel member of the VPS10 domain containing receptor family, prominently expressed in the developing mouse brain. Mech Dev 100:335–338
Mazella J, Zsurger N, Navarro V, Chabry J, Kaghad M, Caput D, Ferrara P, Vita N, Gully D, Maffrand JP, Vincent JP (1998) The 100-kDa neurotensin receptor is gp95/sortilin, a non-G-protein-coupled receptor. J Biol Chem 273:26273–26276
Yamazaki H, Bujo H, Kusunoki J, Seimiya K, Kanaki T, Morisaki N, Schneider WJ, Saito Y (1996) Elements of neural adhesion molecules and a yeast vacuolar protein sorting receptor are present in a novel mammalian low density lipoprotein receptor family member. J Biol Chem 271:24761–24768
Marchler-Bauer A, Anderson JB, Derbyshire MK, Weese-Scott C, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Hao L, He S, Hurwitz DI, Jackson JD, Ke Z, Krylov D, Lanczycki CJ, Liebert CA, Liu C, Lu F, Lu S, Marchler GH, Mullokandov M, Song JS, Thanki N, Yamashita RA, Yin JJ, Zhang D, Bryant SH (2007) CDD: a conserved domain database for interactive domain family analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 35:D237–D240
Hampe W, Urny J, Franke I, Hoffmeister-Ullerich SA, Herrmann D, Petersen CM, Lohmann J, Schaller HC (1999) A head-activator binding protein is present in hydra in a soluble and a membrane-anchored form. Development 126:4077–4086
Hampe W, Rezgaoui M, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Schaller HC (2001) The genes for the human VPS10 domain-containing receptors are large and contain many small exons. Hum Genet 108:529–536
Hermey G, Plath N, Hubner CA, Kuhl D, Schaller HC, Hermans-Borgmeyer I (2004) The three sorCS genes are differentially expressed and regulated by synaptic activity. J Neurochem 88:1470–1476
Hermey G, Schaller HC (2000) Alternative splicing of murine SorCS leads to two forms of the receptor that differ completely in their cytoplasmic tails. Biochim Biophys Acta 1491:350–354
Hermey G, Keat SJ, Madsen P, Jacobsen C, Petersen CM, Gliemann J (2003) Characterization of sorCS1, an alternatively spliced receptor with completely different cytoplasmic domains that mediate different trafficking in cells. J Biol Chem 278:7390–7396
Nielsen MS, Keat SJ, Hamati JW, Madsen P, Gutzmann JJ, Engelsberg A, Pedersen KM, Gustafsen C, Nykjaer A, Gliemann J, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Kuhl D, Petersen CM, Hermey G (2008) Different motifs regulate trafficking of SorCS1 isoforms. Traffic 9:980–994
Edwalds-Gilbert G, Veraldi KL, Milcarek C (1997) Alternative poly(A) site selection in complex transcription units: means to an end? Nucleic Acids Res 25:2547–2561
Sarret P, Krzywkowski P, Segal L, Nielsen MS, Petersen CM, Mazella J, Stroh T, Beaudet A (2003) Distribution of NTS3 receptor/sortilin mRNA and protein in the rat central nervous system. J Comp Neurol 461:483–505
Riedel IB, Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Hubner CA (2002) SorLA, a member of the LDL receptor family, is expressed in the collecting duct of the murine kidney. Histochem Cell Biol 118:183–191
Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Hampe W, Schinke B, Methner A, Nykjaer A, Susens U, Fenger U, Herbarth B, Schaller HC (1998) Unique expression pattern of a novel mosaic receptor in the developing cerebral cortex. Mech Dev 70:65–76
Hermans-Borgmeyer I, Hermey G, Nykjaer A, Schaller C (1999) Expression of the 100-kDa neurotensin receptor sortilin during mouse embryonal development. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 65:216–219
Hermey G, Schaller HC, Hermans-Borgmeyer I (2001) Transient expression of SorCS in developing telencephalic and mesencephalic structures of the mouse. Neuroreport 12:29–32
Seidah NG, Chretien M (1997) Eukaryotic protein processing: endoproteolysis of precursor proteins. Curr Opin Biotechnol 8:602–607
Jacobsen L, Madsen P, Jacobsen C, Nielsen MS, Gliemann J, Petersen CM (2001) Activation and functional characterization of the mosaic receptor SorLA/LR11. J Biol Chem 276:22788–22796
Munck PC, Nielsen MS, Jacobsen C, Tauris J, Jacobsen L, Gliemann J, Moestrup SK, Madsen P (1999) Propeptide cleavage conditions sortilin/neurotensin receptor-3 for ligand binding. EMBO J 18:595–604
Westergaard UB, Kirkegaard K, Sorensen ES, Jacobsen C, Nielsen MS, Petersen CM, Madsen P (2005) SorCS3 does not require propeptide cleavage to bind nerve growth factor. FEBS Lett 579:1172–1176
Westergaard UB, Sorensen ES, Hermey G, Nielsen MS, Nykjaer A, Kirkegaard K, Jacobsen C, Gliemann J, Madsen P, Petersen CM (2004) Functional organization of the sortilin Vps10p domain. J Biol Chem 279:50221–50229
Paiardini A, Caputo V (2008) Insights into the interaction of sortilin with proneurotrophins: a computational approach. Neuropeptides 42:205–214
Quistgaard EM, Madsen P, Groftehauge MK, Nissen P, Petersen CM, Thirup SS (2009) Ligands bind to Sortilin in the tunnel of a ten-bladed beta-propeller domain. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:96–98
Conticello SG, Kowalsman ND, Jacobsen C, Yudkovsky G, Sato K, Elazar Z, Petersen CM, Aronheim A, Fainzilber M (2003) The prodomain of a secreted hydrophobic mini-protein facilitates its export from the endoplasmic reticulum by hitchhiking on sorting receptors. J Biol Chem 278:26311–26314
Jorgensen MU, Emr SD, Winther JR (1999) Ligand recognition and domain structure of Vps10p, a vacuolar protein sorting receptor in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem 260:461–469
Gliemann J, Hermey G, Nykjaer A, Petersen CM, Jacobsen C, Andreasen PA (2004) The mosaic receptor sorLA/LR11 binds components of the plasminogen-activating system and platelet-derived growth factor-BB similarly to LRP1 (low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein), but mediates slow internalization of bound ligand. Biochem J 381:203–212
Fiete D, Mi Y, Oats EL, Beranek MC, Baenziger JU (2007) N-linked oligosaccharides on the low density lipoprotein receptor homolog SorLA/LR11 are modified with terminal GalNAc-4-SO4 in kidney and brain. J Biol Chem 282:1873–1881
Braulke T, Bonifacino JS (2008) Sorting of lysosomal proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793:697–709
Cooper AA, Stevens TH (1996) Vps10p cycles between the late-Golgi and prevacuolar compartments in its function as the sorting receptor for multiple yeast vacuolar hydrolases. J Cell Biol 133:529–541
Deloche O, Yeung BG, Payne GS, Schekman R (2001) Vps10p transport from the trans-Golgi network to the endosome is mediated by clathrin-coated vesicles. Mol Biol Cell 12:475–485
Hermey G, Riedel IB, Rezgaoui M, Westergaard UB, Schaller C, Hermans-Borgmeyer I (2001) SorCS1, a member of the novel sorting receptor family, is localized in somata and dendrites of neurons throughout the murine brain. Neurosci Lett 313:83–87
Nielsen MS, Madsen P, Christensen EI, Nykjaer A, Gliemann J, Kasper D, Pohlmann R, Petersen CM (2001) The sortilin cytoplasmic tail conveys Golgi-endosome transport and binds the VHS domain of the GGA2 sorting protein. EMBO J 20:2180–2190
Nielsen MS, Gustafsen C, Madsen P, Nyengaard JR, Hermey G, Bakke O, Mari M, Schu P, Pohlmann R, Dennes A, Petersen CM (2007) Sorting by the cytoplasmic domain of the amyloid precursor protein binding receptor SorLA. Mol Cell Biol 27:6842–6851
Navarro V, Martin S, Sarret P, Nielsen MS, Petersen CM, Vincent J, Mazella J (2001) Pharmacological properties of the mouse neurotensin receptor 3. Maintenance of cell surface receptor during internalization of neurotensin. FEBS Lett 495:100–105
Nielsen MS, Jacobsen C, Olivecrona G, Gliemann J, Petersen CM (1999) Sortilin/neurotensin receptor-3 binds and mediates degradation of lipoprotein lipase. J Biol Chem 274:8832–8836
Seaman MN (2007) Identification of a novel conserved sorting motif required for retromer-mediated endosome-to-TGN retrieval. J Cell Sci 120:2378–2389
Canuel M, Lefrancois S, Zeng J, Morales CR (2008) AP-1 and retromer play opposite roles in the trafficking of sortilin between the Golgi apparatus and the lysosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 366:724–730
Mari M, Bujny MV, Zeuschner D, Geerts WJ, Griffith J, Petersen CM, Cullen PJ, Klumperman J, Geuze HJ (2008) SNX1 defines an early endosomal recycling exit for sortilin and mannose 6-phosphate receptors. Traffic 9:380–393
McCormick PJ, Dumaresq-Doiron K, Pluviose AS, Pichette V, Tosato G, Lefrancois S (2008) Palmitoylation controls recycling in lysosomal sorting and trafficking. Traffic 9:1984–1997
Lefrancois S, Zeng J, Hassan AJ, Canuel M, Morales CR (2003) The lysosomal trafficking of sphingolipid activator proteins (SAPs) is mediated by sortilin. EMBO J 22:6430–6437
Ni X, Morales CR (2006) The lysosomal trafficking of acid sphingomyelinase is mediated by sortilin and mannose 6-phosphate receptor. Traffic 7:889–902
Lin BZ, Pilch PF, Kandror KV (1997) Sortilin is a major protein component of Glut4-containing vesicles. J Biol Chem 272:24145–24147
Morris NJ, Ross SA, Lane WS, Moestrup SK, Petersen CM, Keller SR, Lienhard GE (1998) Sortilin is the major 110-kDa protein in GLUT4 vesicles from adipocytes. J Biol Chem 273:3582–3587
Ariga M, Nedachi T, Katagiri H, Kanzaki M (2008) Functional role of sortilin in myogenesis and development of insulin-responsive glucose transport system in C2C12 myocytes. J Biol Chem 283:10208–10220
Shi J, Kandror KV (2005) Sortilin is essential and sufficient for the formation of Glut4 storage vesicles in 3T3–L1 adipocytes. Dev Cell 9:99–108
Nykjaer A, Lee R, Teng KK, Jansen P, Madsen P, Nielsen MS, Jacobsen C, Kliemannel M, Schwarz E, Willnow TE, Hempstead BL, Petersen CM (2004) Sortilin is essential for proNGF-induced neuronal cell death. Nature 427:843–848
Teng HK, Teng KK, Lee R, Wright S, Tevar S, Almeida RD, Kermani P, Torkin R, Chen ZY, Lee FS, Kraemer RT, Nykjaer A, Hempstead BL (2005) ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin. J Neurosci 25:5455–5463
Nilsson SK, Christensen S, Raarup MK, Ryan RO, Nielsen MS, Olivecrona G (2008) Endocytosis of apolipoprotein a–v by members of the low density lipoprotein receptor and the vps10p domain receptor families. J Biol Chem 283:25920–25927
Mazella J, Vincent JP (2006) Functional roles of the NTS2 and NTS3 receptors. Peptides 27:2469–2475
Botta R, Lisi S, Pinchera A, Giorgi F, Marcocci C, Taddei AR, Fausto AM, Bernardini N, Ippolito C, Mattii L, Persani L, de Filippis T, Calebiro D, Madsen P, Petersen CM, Marino M (2009) Sortilin is a putative postendocytic receptor of thyroglobulin. Endocrinology 150:509–518
Marino M, McCluskey RT (2000) Role of thyroglobulin endocytic pathways in the control of thyroid hormone release. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279:C1295–C1306
Lisi S, Pinchera A, McCluskey RT, Willnow TE, Refetoff S, Marcocci C, Vitti P, Menconi F, Grasso L, Luchetti F, Collins AB, Marino M (2003) Preferential megalin-mediated transcytosis of low-hormonogenic thyroglobulin: a control mechanism for thyroid hormone release. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:14858–14863
Fahnestock M, Michalski B, Xu B, Coughlin MD (2001) The precursor pro-nerve growth factor is the predominant form of nerve growth factor in brain and is increased in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Cell Neurosci 18:210–220
Harrington AW, Leiner B, Blechschmitt C, Arevalo JC, Lee R, Morl K, Meyer M, Hempstead BL, Yoon SO, Giehl KM (2004) Secreted proNGF is a pathophysiological death-inducing ligand after adult CNS injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6226–6230
Jansen P, Giehl K, Nyengaard JR, Teng K, Lioubinski O, Sjoegaard SS, Breiderhoff T, Gotthardt M, Lin F, Eilers A, Petersen CM, Lewin GR, Hempstead BL, Willnow TE, Nykjaer A (2007) Roles for the pro-neurotrophin receptor sortilin in neuronal development, aging and brain injury. Nat Neurosci 10:1449–1457
Kumar A, Sinha RA, Tiwari M, Pal L, Shrivastava A, Singh R, Kumar K, Kumar GS, Godbole MM (2006) Increased pro-nerve growth factor and p75 neurotrophin receptor levels in developing hypothyroid rat cerebral cortex are associated with enhanced apoptosis. Endocrinology 147:4893–4903
Peng S, Wuu J, Mufson EJ, Fahnestock M (2004) Increased proNGF levels in subjects with mild cognitive impairment and mild Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:641–649
Volosin M, Song W, Almeida RD, Kaplan DR, Hempstead BL, Friedman WJ (2006) Interaction of survival and death signaling in basal forebrain neurons: roles of neurotrophins and proneurotrophins. J Neurosci 26:7756–7766
Fan YJ, Wu LL, Li HY, Wang YJ, Zhou XF (2008) Differential effects of pro-BDNF on sensory neurons after sciatic nerve transection in neonatal rats. Eur J Neurosci 27:2380–2390
Taira K, Bujo H, Hirayama S, Yamazaki H, Kanaki T, Takahashi K, Ishii I, Miida T, Schneider WJ, Saito Y (2001) LR11, a mosaic LDL receptor family member, mediates the uptake of ApoE-rich lipoproteins in vitro. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 21:1501–1506
Jacobsen L, Madsen P, Nielsen MS, Geraerts WP, Gliemann J, Smit AB, Petersen CM (2002) The sorLA cytoplasmic domain interacts with GGA1 and -2 and defines minimum requirements for GGA binding. FEBS Lett 511:155–158
Scott GK, Fei H, Thomas L, Medigeshi GR, Thomas G (2006) A PACS-1, GGA3 and CK2 complex regulates CI-MPR trafficking. EMBO J 25:4423–4435
Schmidt V, Sporbert A, Rohe M, Reimer T, Rehm A, Andersen OM, Willnow TE (2007) SorLA/LR11 regulates processing of amyloid precursor protein via interaction with adaptors GGA and PACS-1. J Biol Chem 282:32956–32964
Rogaeva E, Meng Y, Lee JH, Gu Y, Kawarai T, Zou F, Katayama T, Baldwin CT, Cheng R, Hasegawa H, Chen F, Shibata N, Lunetta KL, Pardossi-Piquard R, Bohm C, Wakutani Y, Cupples LA, Cuenco KT, Green RC, Pinessi L, Rainero I, Sorbi S, Bruni A, Duara R, Friedland RP, Inzelberg R, Hampe W, Bujo H, Song YQ, Andersen OM, Willnow TE, Graff-Radford N, Petersen RC, Dickson D, Der SD, Fraser PE, Schmitt-Ulms G, Younkin S, Mayeux R, Farrer LA, St George-Hyslop P (2007) The neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat Genet 39:168–177
Andersen OM, Reiche J, Schmidt V, Gotthardt M, Spoelgen R, Behlke J, von Arnim CA, Breiderhoff T, Jansen P, Wu X, Bales KR, Cappai R, Masters CL, Gliemann J, Mufson EJ, Hyman BT, Paul SM, Nykjaer A, Willnow TE (2005) Neuronal sorting protein-related receptor sorLA/LR11 regulates processing of the amyloid precursor protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13461–13466
Offe K, Dodson SE, Shoemaker JT, Fritz JJ, Gearing M, Levey AI, Lah JJ (2006) The lipoprotein receptor LR11 regulates amyloid beta production and amyloid precursor protein traffic in endosomal compartments. J Neurosci 26:1596–1603
Willnow TE, Petersen CM, Nykjaer A (2008) VPS10P-domain receptors - regulators of neuronal viability and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:899–909
Beel AJ, Sanders CR (2008) Substrate specificity of gamma-secretase and other intramembrane proteases. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:1311–1334
Andersen OM, Schmidt V, Spoelgen R, Gliemann J, Behlke J, Galatis D, McKinstry WJ, Parker MW, Masters CL, Hyman BT, Cappai R, Willnow TE (2006) Molecular dissection of the interaction between amyloid precursor protein and its neuronal trafficking receptor SorLA/LR11. Biochemistry 45:2618–2628
Spoelgen R, von Arnim CA, Thomas AV, Peltan ID, Koker M, Deng A, Irizarry MC, Andersen OM, Willnow TE, Hyman BT (2006) Interaction of the cytosolic domains of sorLA/LR11 with the amyloid precursor protein (APP) and beta-secretase beta-site APP-cleaving enzyme. J Neurosci 26:418–428
Dodson SE, Gearing M, Lippa CF, Montine TJ, Levey AI, Lah JJ (2006) LR11/SorLA expression is reduced in sporadic Alzheimer disease but not in familial Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 65:866–872
Scherzer CR, Offe K, Gearing M, Rees HD, Fang G, Heilman CJ, Schaller C, Bujo H, Levey AI, Lah JJ (2004) Loss of apolipoprotein E receptor LR11 in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 61:1200–1205
Lee JH, Cheng R, Schupf N, Manly J, Lantigua R, Stern Y, Rogaeva E, Wakutani Y, Farrer L, St George-Hyslop P, Mayeux R (2007) The association between genetic variants in SORL1 and Alzheimer disease in an urban, multiethnic, community-based cohort. Arch Neurol 64:501–506
Andersen OM, Willnow TE (2006) Lipoprotein receptors in Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci 29:687–694
Zhu Y, Bujo H, Yamazaki H, Ohwaki K, Jiang M, Hirayama S, Kanaki T, Shibasaki M, Takahashi K, Schneider WJ, Saito Y (2004) LR11, an LDL receptor gene family member, is a novel regulator of smooth muscle cell migration. Circ Res 94:752–758
Nilsson SK, Lookene A, Beckstead JA, Gliemann J, Ryan RO, Olivecrona G (2007) Apolipoprotein A–V interaction with members of the low density lipoprotein receptor gene family. Biochemistry 46:3896–3904
Bohm C, Seibel NM, Henkel B, Steiner H, Haass C, Hampe W (2006) SorLA signaling by regulated intramembrane proteolysis. J Biol Chem 281:14547–14553
Hermey G, Sjogaard SS, Petersen CM, Nykjaer A, Gliemann J (2006) Tumour necrosis factor alpha-converting enzyme mediates ectodomain shedding of Vps10p-domain receptor family members. Biochem J 395:285–293
Kanaki T, Bujo H, Hirayama S, Ishii I, Morisaki N, Schneider WJ, Saito Y (1999) Expression of LR11, a mosaic LDL receptor family member, is markedly increased in atherosclerotic lesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 19:2687–2695
Zhu Y, Bujo H, Yamazaki H, Hirayama S, Kanaki T, Takahashi K, Shibasaki M, Schneider WJ, Saito Y (2002) Enhanced expression of the LDL receptor family member LR11 increases migration of smooth muscle cells in vitro. Circulation 105:1830–1836
Navarro V, Vincent JP, Mazella J (2002) Shedding of the luminal domain of the neurotensin receptor-3/sortilin in the HT29 cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 298:760–764
Nyborg AC, Ladd TB, Zwizinski CW, Lah JJ, Golde TE (2006) Sortilin, SorCS1b, and SorLA Vps10p sorting receptors, are novel gamma-secretase substrates. Mol Neurodegener 1:3
Clee SM, Yandell BS, Schueler KM, Rabaglia ME, Richards OC, Raines SM, Kabara EA, Klass DM, Mui ET, Stapleton DS, Gray-Keller MP, Young MB, Stoehr JP, Lan H, Boronenkov I, Raess PW, Flowers MT, Attie AD (2006) Positional cloning of Sorcs1, a type 2 diabetes quantitative trait locus. Nat Genet 38:688–693
Goodarzi MO, Lehman DM, Taylor KD, Guo X, Cui J, Quinones MJ, Clee SM, Yandell BS, Blangero J, Hsueh WA, Attie AD, Stern MP, Rotter JI (2007) SORCS1: a novel human type 2 diabetes susceptibility gene suggested by the mouse. Diabetes 56:1922–1929
Granhall C, Park HB, Fakhrai-Rad H, Luthman H (2006) High-resolution quantitative trait locus analysis reveals multiple diabetes susceptibility loci mapped to intervals <800 kb in the species-conserved Niddm1i of the GK rat. Genetics 174:1565–1572
Grupe A, Li Y, Rowland C, Nowotny P, Hinrichs AL, Smemo S, Kauwe JS, Maxwell TJ, Doil L, Cherny S, Tacey K, van Luchene R, Myers A, Wavrant-De VF, Kaleem M, Hollingworth P, Jehu L, Foy C, Archer N, Hamilton G, Holmans P, Morris CM, Catanese J, Sninsky J, White TJ, Powell J, Hardy J, O’Donovan M, Lovestone S, Jones L, Morris JC, Thal L, Owen M, Williams J, Goate A (2006) A scan of chromosome 10 identifies a novel locus showing strong association with late-onset Alzheimer disease. Am J Hum Genet 78:78–88
Li H, Wetten S, Li L, St Jean PL, Upmanyu R, Surh L, Hosford D, Barnes MR, Briley JD, Borrie M, Coletta N, Delisle R, Dhalla D, Ehm MG, Feldman HH, Fornazzari L, Gauthier S, Goodgame N, Guzman D, Hammond S, Hollingworth P, Hsiung GY, Johnson J, Kelly DD, Keren R, Kertesz A, King KS, Lovestone S, Loy-English I, Matthews PM, Owen MJ, Plumpton M, Pryse-Phillips W, Prinjha RK, Richardson JC, Saunders A, Slater AJ, St George-Hyslop PH, Stinnett SW, Swartz JE, Taylor RL, Wherrett J, Williams J, Yarnall DP, Gibson RA, Irizarry MC, Middleton LT, Roses AD (2008) Candidate single-nucleotide polymorphisms from a genomewide association study of Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 65:45–53
Schjeide BM, McQueen MB, Mullin K, Divito J, Hogan MF, Parkinson M, Hooli B, Lange C, Blacker D, Tanzi RE, Bertram L (2009) Assessment of Alzheimer’s disease case–control associations using family-based methods. Neurogenetics 10:19–25
Liang X, Slifer M, Martin ER, Schnetz-Boutaud N, Bartlett J, Anderson B, Zuchner S, Gwirtsman H, Gilbert JR, Pericak-Vance MA, Haines JL (2009) Genomic convergence to identify candidate genes for Alzheimer disease on chromosome 10. Hum Mutat 30:463–471
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Acknowledgements
I am grateful to Sady Keat for discussions and Claudia Mahlke, Jakob Gutzmann, and Nils Blüthgen for their helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hermey, G. The Vps10p-domain receptor family. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 2677–2689 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0043-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0043-1