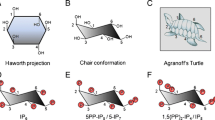
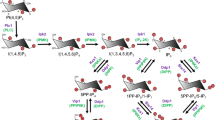
Abstract
The stereochemistry of the inositol backbone provides a platform on which to generate a vast array of distinct molecular motifs that are used to convey information both in signal transduction and many other critical areas of cell biology. Diphosphoinositol phosphates, or inositol pyrophosphates, are the most recently characterized members of the inositide family. They represent a new frontier with both novel targets within the cell and novel modes of action. This includes the proposed pyrophosphorylation of a unique subset of proteins. We review recent insights into the structures of these molecules and the properties of the enzymes which regulate their concentration. These enzymes also act independently of their catalytic activity via protein–protein interactions. This unique combination of enzymes and products has an important role in diverse cellular processes including vesicle trafficking, endo- and exocytosis, apoptosis, telomere length regulation, chromatin hyperrecombination, the response to osmotic stress, and elements of nucleolar function.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berridge MJ (2007) Inositol trisphosphate and calcium oscillations. Biochem Soc Symp 7:1–7
Michell RH (2008) Inositol derivatives: evolution and functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:151–161
Irvine RF (2005) Inositide evolution—towards turtle domination? J Physiol 566:295–300
Seeds AM, Frederick JP, Tsui MM, York JD (2007) Roles for inositol polyphosphate kinases in the regulation of nuclear processes and developmental biology. Adv Enzym Regul 47:10–25
Shears SB (2004) How versatile are inositol phosphate kinases? Biochem J 377:265–280
Alcázar-Román AR, Wente SR (2008) Inositol polyphosphates: a new frontier for regulating gene expression. Chromosoma 117:1–13
Duronio V (2008) The life of a cell: apoptosis regulation by the PI3K/PKB pathway. Biochem J 415:333–344
Yuan TL, Cantley LC (2008) PI3K pathway alterations in cancer: variations on a theme. Oncogene 27:5497–5510
Vicinanza M, D’Angelo G, Di Campli A, De Matteis MA (2008) Phosphoinositides as regulators of membrane trafficking in health and disease. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:2833–2841
Europe-Finner GN, Ludérus ME, Small NV, Van Driel R, Reymond CD, Firtel RA, Newell PC (1988) Mutant ras gene induces elevated levels of inositol tris- and hexakisphosphates in Dictyostelium. J Cell Sci 89:13–20
Europe-Finner GN, Gammon B, Newell PC (1991) Accumulation of [3H]-inositol into inositol polyphosphates during development of Dictyostelium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 181:191–196
Oliver KG, Putney JW Jr, Obie JF, Shears SB (1992) The interconversion of inositol 1, 3, 4, 5, 6-pentakisphosphate and inositol tetrakisphosphates in AR4–2J cells. J Biol Chem 267:21528–21534
Wong NS, Barker CJ, Morris AJ, Craxton A, Kirk CJ, Michell RH (1992) The inositol phosphates in WRK1 rat mammary tumour cells. Biochem J 286:459–468
Mayr GW, Radenberg T, Thiel U, Vogel G, Stephens LR (1992) Phosphoinositol diphosphates: non-enzymic formation in vitro and occurrence in vivo in the cellular slime mold Dictyostelium. Carbohydr Res 234:247–262
Stephens L, Radenberg T, Thiel U, Vogel G, Khoo KH, Dell A, Jackson TR, Hawkins PT, Mayr GW (1993) The detection, purification, structural characterization, and metabolism of diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate(s) and bisdiphosphoinositol tetrakisphosphate(s). J Biol Chem 268:4009–4015
Menniti FS, Miller RN, Putney JW, Shears SB (1993) Turnover of inositol polyphosphate pyrophosphates in pancreatoma cells. J Biol Chem 268:3850–3856
Voglmaier SM, Bembenek ME, Kaplin AI, Dormán G, Olszewski JD, Prestwich GD, Snyder SH (1996) Purified inositol hexakisphosphate kinase is an atp synthase: diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate as a high-energy phosphate donor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:4305–4310
Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemistry (1988) Numbering of atoms in myo-inositol recommendations. 1988: nomenclature committee of the international union of biochemistry. Biochem J 258:1–2
Agranoff BW (1978) Cyclitol confusion. Trends Biochem Sci 3:N283–N285
Albert C, Safrany ST, Bembenek ME, Reddy KM, Reddy K, Falck J, Bröcker M, Shears SB, Mayr GW (1997) Biological variability in the structures of diphosphoinositol polyphosphates in Dictyostelium discoideum and mammalian cells. Biochem J 327:553–560
Mulugu S, Bai W, Fridy PC, Bastidas RJ, Otto JC, Dollins DE, Haystead TA, Ribeiro AA, York JD (2007) A conserved family of enzymes that phosphorylate inositol hexakisphosphate. Science 316:106–109
Lin H, Fridy PC, Ribeiro AA, Choi JH, Barma DK, Vogel G, Falck JR, Shears SB, York JD, Mayr GW (2008) Structural analysis and detection of biological inositol pyrophosphates reveals that the vip/ppip5k family are 1/3-kinases. J Biol Chem 284:1863–1872
Draskovic P, Saiardi A, Bhandari R, Burton A, Ilc G, Kovacevic M, Snyder SH, Podobnik M (2008) Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase products contain diphosphate and triphosphate groups. Chem Biol 15:274–286
Dubois E, Scherens B, Vierendeels F, Ho MMW, Messenguy F, Shears SB (2002) In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, the inositol polyphosphate kinase activity of kcs1p is required for resistance to salt stress, cell wall integrity, and vacuolar morphogenesis. J Biol Chem 277:23755–23763
Seeds AM, Bastidas RJ, York JD (2005) Molecular definition of a novel inositol polyphosphate metabolic pathway initiated by inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate 3-kinase activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 280:27654–27661
Laussmann T, Reddy KM, Reddy KK, Falck JR, Vogel G (1997) Diphospho-myo-inositol phosphates from Dictyostelium identified as d-6-diphospho-myo-inositol pentakis-phosphate and d-5, 6-bisdiphospho-myo-inositol tetrakisphosphate. Biochem J 322:31–33
Laussmann T, Hansen A, Reddy KM, Reddy KK, Falck JR, Vogel G (1998) Diphospho-myo-inositol phosphates in Dictyostelium and Polysphondylium: identification of a new bisdiphospho-myo-inositol tetrakisphosphate. FEBS Lett 426:145–150
Martin JB, Laussmann T, Bakker-Grunwald T, Vogel G, Klein G (2000) Neo-inositol polyphosphates in the amoeba Entamoeba histolytica. J Biol Chem 275:10134–10140
Norbis F, Boll M, Stange G, Markovich D, Verrey F, Biber J, Murer H (1997) Identification of a cDNA/protein leading to an increased Pi-uptake in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Membr Biol 156:19–24
Saiardi A, Erdjument-Bromage H, Snowman AM, Tempst P, Snyder SH (1999) Synthesis of diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate by a newly identified family of higher inositol polyphosphate kinases. Curr Biol 9:1323–1326
Schell MJ, Letcher AJ, Brearley CA, Biber J, Murer H, Irvine RF (1999) PiUS (Pi uptake stimulator) is an inositol hexakisphosphate kinase. FEBS Lett 461:169–172
Saiardi A, Nagata E, Luo HR, Snowman AM, Snyder SH (2001) Identification and characterization of a novel inositol hexakisphosphate kinase. J Biol Chem 276:39179–39185
Bennett M, Onnebo SM, Azevedo C, Saiardi A (2006) Inositol pyrophosphates: metabolism and signaling. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:552–564
Shears SB (2007) Understanding the biological significance of diphosphoinositol polyphosphates (‘inositol pyrophosphates’). Biochem Soc Symp 7:211–221
Saiardi A, Nagata E, Luo HR, Sawa A, Luo X, Snowman AM, Snyder SH (2001) Mammalian inositol polyphosphate multikinase synthesizes inositol 1, 4, 5-trisphosphate and an inositol pyrophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2306–2311
Zhang T, Caffrey JJ, Shears SB (2001) The transcriptional regulator, Arg82, is a hybrid kinase with both monophosphoinositol- and diphosphoinositol-polyphosphate synthase activity. FEBS Lett 494:208–212
Saiardi A, Resnick AC, Snowman AM, Wendland B, Snyder SH (2005) Inositol pyrophosphates regulate cell death and telomere length through phosphoinositide 3-kinase-related protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1911–1914
York SJ, Armbruster BN, Greenwell P, Petes TD, York JD (2005) Inositol diphosphate signaling regulates telomere length. J Biol Chem 280:4264–4269
Illies C, Gromada J, Fiume R, Leibiger B, Yu J, Juhl K, Yang S-N, Barma DK, Falck JR, Saiardi A, Barker CJ, Berggren P-O (2007) Requirement of inositol pyrophosphates for full exocytotic capacity in pancreatic beta cells. Science 318:1299–1302
Watahiki A, Waki K, Hayatsu N, Shiraki T, Kondo S, Nakamura M, Sasaki D, Arakawa T, Kawai J, Harbers M, Hayashizaki Y, Carninci P (2004) Libraries enriched for alternatively spliced exons reveal splicing patterns in melanocytes and melanomas. Nat Methods 1:233–239
Maruyama Y, Wakamatsu A, Kawamura Y, Kimura K, Yamamoto J, Nishikawa T, Kisu Y, Sugano S, Goshima N, Isogai T, Nomura N (2009) Human gene and protein database (HGPD): a novel database presenting a large quantity of experiment-based results in human proteomics. Nucl Acids Res. 37(Database issue):D762–D766
Scamuffa N, Calvo F, Chrétien M, Seidah NG, Khatib AM (2006) Proprotein convertases: lessons from knockouts. FASEB J 20:1954–1963
Tomita T (2001) Immunocytochemical localization of prohormone convertase 1/3 and 2 in pancreatic islet cells and islet cell tumors. Pancreas 23:172–176
Dephoure N, Zhou C, Villen J, Beausoleil SA, Bakalarski CE, Elledge SJ, Gygi SP (2008) A quantitative atlas of mitotic phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:10762–10767
Lu PJ, Zhou XZ, Liou YC, Noel JP, Lu KP (2002) Critical role of WW domain phosphorylation in regulating phosphoserine binding activity and Pin1 function. J Biol Chem 277:2381–2384
Barker CJ, Wright J, Hughes PJ, Kirk CJ, Michell RH (2004) Complex changes in cellular inositol phosphate complement accompany transit through the cell cycle. Biochem J 380:465–473
Bhandari R, Saiardi A, Ahmadibeni Y, Snowman AM, Resnick AC, Kristiansen TZ, Molina H, Pandey A, Werner JK, Juluri KR, Xu Y, Prestwich GD, Parang K, Snyder SH (2007) Protein pyrophosphorylation by inositol pyrophosphates is a posttranslational event. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15305–15310
Saiardi A, Caffrey JJ, Snyder SH, Shears SB (2000) The inositol hexakisphosphate kinase family: catalytic flexibility and function in yeast vacuole biogenesis. J Biol Chem 275:24686–24692
Larsson O, Barker CJ, Sjöholm A, Carlqvist H, Michell RH, Bertorello A, Nilsson T, Honkanen RE, Mayr GW, Zwiller J, Berggren PO (1997) Inhibition of phosphatases and increased Ca2+ channel activity by inositol hexakisphosphate. Science 278:471–474
Michell RH, King CE, Piper CJ, Stephens LR, Bunce CM, Guy GR, Brown G (1988) Inositol lipids and phosphates in erythrocytes and HL60 cells. Soc Gen Physiol Ser 43:345–355
Luo HR, Saiardi A, Nagata E, Ye K, Yu H, Jung TS, Luo X, Jain S, Sawa A, Snyder SH (2001) Grab: a physiologic guanine nucleotide exchange factor for rab3a, which interacts with inositol hexakisphosphate kinase. Neuron 31:439–451
Tickenbrock L, Cramer J, Vetter IR, Muller O (2002) The coiled coil region (amino acids 129–250) of the tumor suppressor protein adenomatous polyposis coli (APC): its structure and its interaction with chromosome maintenance region 1 (Crm-1). J Biol Chem 277:32332–32338
Vanacova S, Stefl R (2007) The exosome and RNA quality control in the nucleus. EMBO Rep 8:651–657
Rual JF, Venkatesan K, Hao T, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Dricot A, Li N, Berriz GF, Gibbons FD, Dreze M, Ayivi-Guedehoussou N, Klitgord N, Simon C, Boxem M, Milstein S, Rosenberg J, Goldberg DS, Zhang LV, Wong SL, Franklin G, Li S, Albala JS, Lim J, Fraughton C, Llamosas E, Cevik S, Bex C, Lamesch P, Sikorski RS, Vandenhaute J, Zoghbi HY, Smolyar A, Bosak S, Sequerra R, Doucette-Stamm L, Cusick ME, Hill DE, Roth FP, Vidal M (2005) Towards a proteome-scale map of the human protein–protein interaction network. Nature 437:1173–1178
Saiardi A, Bhandari R, Resnick AC, Snowman AM, Snyder SH (2004) Phosphorylation of proteins by inositol pyrophosphates. Science 306:2101–2105
Lexicon knockout mouse NIH-0750, mouse genome database (MGD), mouse genome informatics Web Site, http://www.informatics.jax.org/external/ko/lexicon/1223.html (18 July 2006)
Bhandari R, Juluri KR, Resnick AC, Snyder SH (2008) Gene deletion of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1 reveals inositol pyrophosphate regulation of insulin secretion, growth, and spermiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:2349–2353
Azevedo C, Burton A, Bennett M, Onnebo SMN, Saiardi A (2010) Synthesis of InsP7 by the inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1 (IP6K1) In: Barker CJ (ed) Methods in molecular biology. Preliminary entry 2203, 2010, ISBN 978-1-60327-174-5, Hardcover, Due: July 2010 (in press)
Morrison BH, Tang Z, Jacobs BS, Bauer JA, Lindner DJ (2005) Apo2L/TRAIL induction and nuclear translocation of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 during IFN-beta-induced apoptosis in ovarian carcinoma. Biochem J 385:595–603
Nagata E, Luo HR, Saiardi A, Bae BI, Suzuki N, Snyder SH (2005) Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase-2, a physiologic mediator of cell death. J Biol Chem 280:1634–1640
Morrison BH, Bauer JA, Lupica JA, Tang Z, Schmidt H, DiDonato JA, Lindner DJ (2007) Effect of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 on transforming growth factor beta-activated kinase 1 and NF-kappaB activation. J Biol Chem 282:15349–15356
Chakraborty A, Koldobskiy MA, Sixt KM, Juluri KR, Mustafa AK, Snowman AM, van Rossum DB, Patterson RL, Snyder SH (2008) Hsp90 regulates cell survival via inositol hexakisphosphate kinase-2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:1134–1139
Morrison BH, Haney R, Lamarre E, Drazba J, Prestwich GD, Lindner DJ (2009) Gene deletion of inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 predisposes to aerodigestive tract carcinoma. Oncogene 28:2383–2392
Xuhua, X (2007) Bioinformatics and the cell : modern computational approaches in genomics, proteomics and transcriptomics. Springer, New York
Luo HR, Huang YE, Chen JC, Saiardi A, Iijima M, Ye K, Huang Y, Nagata E, Devreotes P, Snyder SH (2003) Inositol pyrophosphates mediate chemotaxis in Dictyostelium via pleckstrin homology domain-PtdIns(3, 4, 5)P3 interactions. Cell 114:559–572
Huang KN, Symington LS (1995) Suppressors of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae pkc1 mutation identify alleles of the phosphatase gene PTC1 and of a novel gene encoding a putative basic leucine zipper protein. Genetics 141:1275–1285
Uetz P, Glot L, Cagney G, Mansfield TA, Judson RS, Knight JR, Lockshon D, Narayan V, Srinivasan M, Pochart P, Qureshi-Emill A, Li Y, Godwin B, Conover D, Kalbfleisch T, Vijayadamodar G, Yang M, Johnston M, Fields S, Rothberg JM (2000) A comprehensive analysis of protein–protein interactions in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 403:623–627
Aitken A (2006) 14-3-3 proteins: a historic overview. Semin Cancer Biol 16:162–172
York SJ, Armbruster BN, Greenwell P, Petes TD, York JD (2005) Inositol diphosphate signaling regulates telomere length. J Biol Chem 280:4264–4269
Shears SB, Ali N, Craxton A, Bembenek ME (1995) Synthesis and metabolism of bis-diphosphoinositol tetrakisphosphate in vitro and in vivo. J Biol Chem 270:10489–10497
Huang CF, Voglmaier SM, Bembenek ME, Saiardi A, Snyder SH (1998) Identification and purification of diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate kinase, which synthesizes the inositol pyrophosphate bis(diphospho)inositol tetrakisphosphate. Biochemistry 37:14998–15004
Fridy PC, Otto JC, Dollins DE, York JD (2007) Cloning and characterization of two human VIP1-like inositol hexakisphosphate and diphosphoinositol pentakisphosphate kinases. J Biol Chem 282:30754–30762
Choi JH, Williams J, Cho J, Falck JR, Shears SB (2007) Purification, sequencing, and molecular identification of a mammalian PP-InsP5 kinase that is activated when cells are exposed to hyperosmotic stress. J Biol Chem 282:30763–30775
Grishin NV (1999) Phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase: a link between protein kinase and glutathione synthase folds. J Mol Biol 291:239–247
Craxton A, Caffrey JJ, Burkhart W, Safrany ST, Shears SB (1997) Molecular cloning and expression of a rat hepatic multiple inositol polyphosphate phosphatase. Biochem J 328:75–81
Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, Macek B, Kumar C, Mortensen P, Mann M (2006) Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell 127:635–648
Cantin GT, Yi W, Lu B, Park SK, Xu T, Lee JD, Yates JRIII (2008) Combining protein-based IMAC, peptide-based IMAC, and MudPIT for efficient phosphoproteomic analysis. J Proteome Res 7:1346–1351
Safrany ST, Caffrey JJ, Yang X, Bembenek ME, Moyer MB, Burkhart WA, Shears SB (1998) A novel context for the ‘mutt’ module, a guardian of cell integrity, in a diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolase. EMBO J 17:6599–6607
McLennan AG (2000) Dinucleoside polyphosphates-friend or foe? Pharmacol Ther 87:73–89
Bessman MJ, Frick DN, O’Handley SF (1996) The mutt proteins or “nudix” hydrolases, a family of versatile, widely distributed, “housecleaning” enzymes. J Biol Chem 271:25059–25062
Yang X, Safrany ST, Shears SB (1999) Site-directed mutagenesis of diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolase, a dual specificity nudt enzyme that attacks diadenosine polyphosphates and diphosphoinositol polyphosphates. J Biol Chem 274:35434–35440
Caffrey JJ, Shears SB (2001) Genetic rationale for microheterogeneity of human diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolase type 2. Gene 269:53–60
Leslie NR, McLennan AG, Safrany ST (2002) Cloning and characterisation of haps1 and haps2, human diadenosine polyphosphate-metabolising nudix hydrolases. BMC Biochem 3:20
Hidaka K, Caffrey JJ, Hua L, Zhang T, Falck JR, Nickel GC, Carrel L, Barnes LD, Shears SB (2002) An adjacent pair of human nudt genes on chromosome x are preferentially expressed in testis and encode two new isoforms of diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolase. J Biol Chem 277:32730–32738
Hua LV, Hidaka K, Pesesse X, Barnes LD, Shears SB (2003) Paralogous murine nudt10 and nudt11 genes have differential expression patterns but encode identical proteins that are physiologically competent diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolases. Biochem J 373:81–89
Chu C, Alapat D, Wen X, Timo K, Burstein D, Lisanti M, Shears S, Kohtz DS (2004) Ectopic expression of murine diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolase 1 attenuates signaling through the erk1/2 pathway. Cell Signal 16:1045–1059
Caffrey JJ, Safrany ST, Yang X, Shears SB (2000) Discovery of molecular and catalytic diversity among human diphosphoinositol-polyphosphate phosphohydrolases an expanding nudt family. J Biol Chem 275:12730–12736
Hua LV, Green M, Warsh JJ, Li PP (2001) Molecular cloning of a novel isoform of diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolase: a potential target of lithium therapy. Neuropsychopharmacology 24:640–651
Cartwright JL, McLennan AG (1999) The Saccharomyces cerevisiae yor163w gene encodes a diadenosine 5′, 5″‘-p1, p6-hexaphosphate (ap6a) hydrolase member of the mutt motif (nudix hydrolase) family. J Biol Chem 274:8604–8610
Ingram SW, Stratemann SA, Barnes LD (1999) Schizosaccharomyces pombe aps1, a diadenosine 5′, 5′ “-p1, p6-hexaphosphate hydrolase that is a member of the nudix (mutt) family of hydrolases: cloning of the gene and characterization of the purified enzyme. Biochemistry 38:3649–3655
Safrany ST, Ingram SW, Cartwright JL, Falck JR, McLennan AG, Barnes LD, Shears SB (1999) The diadenosine hexaphosphate hydrolases from schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae are homologues of the human diphosphoinositol polyphosphate phosphohydrolase: overlapping substrate specificities in a mutt-type protein. J Biol Chem 274:21735–21740
Fisher DI, Safrany ST, Strike P, McLennan AG, Cartwright JL (2002) Nudix hydrolases that degrade dinucleoside and diphosphoinositol polyphosphates also have 5-phosphoribosyl 1-pyrophosphate (prpp) pyrophosphatase activity that generates the glycolytic activator ribose 1, 5-bisphosphate. J Biol Chem 277:47313–47317
Fersht A (1998) Structure and mechanism in protein science. Freeman, New York
Ash DE, Schramm VL (1982) Determination of free and bound manganese(ii) in hepatocytes from fed and fasted rats. J Biol Chem 257:9261–9264
Ali N, Craxton A, Shears SB (1993) Hepatic ins(1, 3, 4, 5)p4 3-phosphatase is compartmentalized inside endoplasmic reticulum. J Biol Chem 268:6161–6167
Glennon MC, Shears SB (1993) Turnover of inositol pentakisphosphates, inositol hexakisphosphate and diphosphoinositol polyphosphates in primary cultured hepatocytes. Biochem J 293(Pt 2):583–590
Harwood AJ (2005) Lithium and bipolar mood disorder: the inositol-depletion hypothesis revisited. Mol Psychiatry 10:117–126
Cartwright JL, Safrany ST, Dixon LK, Darzynkiewicz E, Stepinski J, Burke R, McLennan AG (2002) The g5r (d250) gene of african swine fever virus encodes a nudix hydrolase that preferentially degrades diphosphoinositol polyphosphates. J Virol 76:1415–1421
Ingram SW, Safrany ST, Barnes LD (2003) Disruption and overexpression of the schizosaccharomyces pombe aps1 gene, and effects on growth rate, morphology and intracellular diadenosine 5′, 5″‘-p1, p5-pentaphosphate and diphosphoinositol polyphosphate concentrations. Biochem J 369:519–528
Pinna LA (1990) Casein kinase 2: an ‘eminence grise’ in cellular regulation? Biochim Biophys Acta 1054:267–284
Caizergues-Ferrer M, Belenguer P, Lapeyre B, Amalric F, Wallace MO, Olson MO (1987) Phosphorylation of nucleolin by a nucleolar type nii protein kinase. Biochemistry 26:7876–7883
Meier UT (1996) Comparison of the rat nucleolar protein nopp140 with its yeast homolog srp40: differential phosphorylation in vertebrates and yeast. J Biol Chem 271:19376–19384
Meier UT, Blobel G (1992) Nopp140 shuttles on tracks between nucleolus and cytoplasm. Cell 70:127–138
Jones NC, Farlie PG, Minichiello J, Newgreen DF (1999) Detection of an appropriate kinase activity in branchial arches i and ii that coincides with peak expression of the treacher collins syndrome gene product, treacle. Hum Mol Genet 8:2239–2245
Kim Y-K, Lee KJ, Jeon H, Yu YG (2006) Protein kinase ck2 is inhibited by human nucleolar phosphoprotein p140 in an inositol hexakisphosphate-dependent manner. J Biol Chem 281:36752–36757
Lee W-K, Lee S-Y, Kim W-I, Rho Y-H, Bae Y-S, Lee C, Kim IY, Yu YG (2008) Characterization of the insp6-dependent interaction between ck2 and nopp140. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 376:439–444
Valdez BC, Henning D, So RB, Dixon J, Dixon MJ (2004) The treacher collins syndrome (tcof1) gene product is involved in ribosomal dna gene transcription by interacting with upstream binding factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:10709–10714
Ginisty H, Serin G, Ghisolfi-Nieto L, Roger B, Libante V, Amalric F, Bouvet P (2000) Interaction of nucleolin with an evolutionarily conserved pre-ribosomal rna sequence is required for the assembly of the primary processing complex. J Biol Chem 275:18845–18850
Lee WC, Zabetakis D, Mélèse T (1992) Nsr1 is required for pre-rrna processing and for the proper maintenance of steady-state levels of ribosomal subunits. Mol Cell Biol 12:3865–3871
Horigome C, Ikeda R, Okada T, Takenami K, Mizuta K (2009) Genetic interaction between ribosome biogenesis and inositol polyphosphate metabolism in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 73:443–446
Yang L, Reece JM, Cho J, Bortner CD, Shears SB (2008) The nucleolus exhibits an osmotically regulated gatekeeping activity that controls the spatial dynamics and functions of nucleolin. J Biol Chem 283:11823–11831
Beck KA, Keen JH (1991) Interaction of phosphoinositide cycle intermediates with the plasma membrane-associated clathrin assembly protein ap-2. J Biol Chem 266:4442–4447
Voglmaier SM, Keen JH, Murphy JE, Ferris CD, Prestwich GD, Snyder SH, Theibert AB (1992) Inositol hexakisphosphate receptor identified as the clathrin assembly protein ap-2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 187:158–163
Fleischer B, Xie J, Mayrleitner M, Shears SB, Palmer DJ, Fleischer S (1994) Golgi coatomer binds, and forms k(+)-selective channels gated by, inositol polyphosphates. J Biol Chem 269:17826–17832
Ali N, Duden R, Bembenek ME, Shears SB (1995) The interaction of coatomer with inositol polyphosphates is conserved in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem J 310(Pt 1):279–284
Norris FA, Ungewickell E, Majerus PW (1995) Inositol hexakisphosphate binds to clathrin assembly protein 3 (ap-3/ap180) and inhibits clathrin cage assembly in vitro. J Biol Chem 270:214–217
Ye W, Ali N, Bembenek ME, Shears SB, Lafer EM (1995) Inhibition of clathrin assembly by high affinity binding of specific inositol polyphosphates to the synapse-specific clathrin assembly protein ap-3. J Biol Chem 270:1564–1568
Saiardi A, Sciambi C, McCaffery JM, Wendland B, Snyder SH (2002) Inositol pyrophosphates regulate endocytic trafficking. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:14206–14211
Gaidarov I, Chen Q, Falck JR, Reddy KK, Keen JH (1996) A functional phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate/phosphoinositide binding domain in the clathrin adaptor ap-2 alpha subunit: implications for the endocytic pathway. J Biol Chem 271:20922–20929
Hao W, Tan Z, Prasad K, Reddy KK, Chen J, Prestwich GD, Falck JR, Shears SB, Lafer EM (1997) Regulation of ap-3 function by inositides: identification of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate as a potent ligand. J Biol Chem 272:6393–6398
Chaudhary A, Gu QM, Thum O, Profit AA, Qi Y, Jeyakumar L, Fleischer S, Prestwich GD (1998) Specific interaction of golgi coatomer protein alpha-cop with phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem 273:8344–8350
Padmanabhan U, Dollins DE, Fridy PC, York JD, Downes CP (2009) Characterization of a selective inhibitor of inositol hexakisphosphate kinases: use in defining biological roles and metabolic relationships of inositol pyrophosphates. J Biol Chem 284:10571–10582
Pesesse X, Choi K, Zhang T, Shears SB (2004) Signaling by higher inositol polyphosphates: synthesis of bisdiphosphoinositol tetrakisphosphate (“InsP8”) is selectively activated by hyperosmotic stress. J Biol Chem 279:43378–43381
Choi K, Mollapour E, Shears SB (2005) Signal transduction during environmental stress: InsP8 operates within highly restricted contexts. Cell Signal 17:1533–1541
Baxi MD, Vishwanatha JK (1995) Diadenosine polyphosphates: their biological and pharmacological significance. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 33:121–128
Di Ciano C, Nie Z, Szászi K, Lewis A, Uruno T, Zhan X, Rotstein OD, Mak A, Kapus A (2002) Osmotic stress-induced remodeling of the cortical cytoskeleton. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 283:C850–C865
Chiasson JL, Aris-Jilwan N, Bélanger R, Bertrand S, Beauregard H, Ekoé JM, Fournier H, Havrankova J (2003) Diagnosis and treatment of diabetic ketoacidosis and the hyperglycemic hyperosmolar state. Can Med Assoc J 168:859–866
Sonna LA, Fujita J, Gaffin SL, Lilly CM (2002) Invited review: effects of heat and cold stress on mammalian gene expression. J Appl Physiol 92:1725–1742
Morrison BH, Bauer JA, Kalvakolanu DV, Lindner DJ (2001) Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 mediates growth suppressive and apoptotic effects of interferon-beta in ovarian carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem 276:24965–24970
Morrison BH, Bauer JA, Hu J, Grane RW, Ozdemir AM, Chawla-Sarkar M, Gong B, Almasan A, Kalvakolanu DV, Lindner DJ (2002) Inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 2 sensitizes ovarian carcinoma cells to multiple cancer therapeutics. Oncogene 21:1882–1889
Arch RH, Gedrich RW, Thompson CB (1998) Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors (TRAFs)—a family of adapter proteins that regulates life and death. Genes Dev 12:2821–2830
Barginear MF, Van Poznak C, Rosen N, Modi S, Hudis CA, Budman DR (2008) The heat shock protein 90 chaperone complex: an evolving therapeutic target. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 8:522–532
Sharp S, Workman P (2006) Inhibitors of the HSP90 molecular chaperone: current status. Adv Cancer Res 95:323–348
Whitesell L, Lindquist SL (2005) HSP90 and the chaperoning of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 5:761–772
Basso AD, Solit DB, Chiosis G, Giri B, Tsichlis P, Rosen N (2002) Akt forms an intracellular complex with heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) and Cdc37 and is destabilized by inhibitors of Hsp90 function. J Biol Chem 277:39858–39866
Sahu SK, Gummadi SN, Manoj N, Aradhyam GK (2007) Phospholipid scramblases: an overview. Arch Biochem Biophys 462:103–114
Aoki M, Sobek V, Maslyar DJ, Hecht A, Vogt PK (2002) Oncogenic transformation by beta-catenin: deletion analysis and characterization of selected target genes. Oncogene 21:6983–6991
Harley CB, Futcher AB, Greider CW (1990) Telomeres shorten during ageing of human fibroblasts. Nature 345:458–460
Shears SB (2005) Telomere maintenance by intracellular signals: new kid on the block? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1811–1812
Luo HR, Saiardi A, Yu H, Nagata E, Ye K, Snyder SH (2002) Inositol pyrophosphates are required for DNA hyperrecombination in protein kinase c1 mutant yeast. Biochemistry 41:2509–2515
Katai K, Miyamoto K, Kishida S, Segawa H, Nii T, Tanaka H, Tani Y, Arai H, Tatsumi S, Morita K, Taketani Y, Takeda E (1999) Regulation of intestinal Na+-dependent phosphate co-transporters by a low-phosphate diet and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3. Biochem J 343:705–712
Lee YS, Mulugu S, York JD, O’Shea EK (2007) Regulation of a cyclin-CDK-CDK inhibitor complex by inositol pyrophosphates. Science 316:109–112
Lee YS, Huang K, Quiocho FA, O’Shea EK (2008) Molecular basis of cyclin-CDK-CKI regulation by reversible binding of an inositol pyrophosphate. Nat Chem Biol 4:25–32
Onnebo SM, Saiardi A (2007) Inositol pyrophosphates get the vip1 treatment. Cell 129:647–649
Pyerin W, Barz T, Ackermann K (2005) Protein kinase CK2 in gene control at cell cycle entry. Mol Cell Biochem 274:189–200
Dhariwala FA, Rajadhyaksha MS (2008) An unusual member of the Cdk family: Cdk5. Cell Mol Neurobiol 28:351–369
Lilja L, Yang SN, Webb DL, Juntti-Berggren L, Berggren PO, Bark C (2001) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 promotes insulin exocytosis. J Biol Chem 276:34199–341205
Maffucci T, Falasca M (2001) Specificity in pleckstrin homology (PH) domain membrane targeting: a role for a phosphoinositide-protein co-operative mechanism. FEBS Lett 506:173–179
Chan TO, Rittenhouse SE, Tsichlis PN (1999) AKT/PKB and other D3 phosphoinositide-regulated kinases: kinase activation by phosphoinositide-dependent phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem 68:965–1014
Piccolo E, Vignati S, Maffucci T, Innominato PF, Riley AM, Potter BV, Pandolfi PP, Broggini M, Iacobelli S, Innocenti P, Falasca M (2004) Inositol pentakisphosphate promotes apoptosis through the PI 3-K/Akt pathway. Oncogene 23:1754–1765
Jackson SG, Zhang Y, Haslam RJ, Junop MS (2007) Structural analysis of the carboxy terminal PH domain of pleckstrin bound to D-myo-inositol 1, 2, 3, 5, 6-pentakisphosphate. BMC Struct Biol 7:80
Downes CP, Gray A, Fairservice A, Safrany ST, Batty IH, Fleming I (2005) The regulation of membrane to cytosol partitioning of signalling proteins by phosphoinositides and their soluble headgroups. Biochem Soc Trans 33:1303–1307
Komander D, Fairservice A, Deak M, Kular GS, Prescott AR, Downes CP, Safrany ST, Alessi DR, van Aalten DM (2004) Structural insights into the regulation of PDK1 by phosphoinositides and inositol phosphates. EMBO J 23:3918–3928
Takeuchi H, Kanematsu T, Misumi Y, Sakane F, Konishi H, Kikkawa U, Watanabe Y, Katan M, Hirata M (1997) Distinct specificity in the binding of inositol phosphates by pleckstrin homology domains of pleckstrin, RAC-protein kinase, diacylglycerol kinase and a new 130 kDa protein. Biochim Biophys Acta 1359:275–285
Frech M, Andjelkovic M, Ingley E, Reddy KK, Falck JR, Hemmings BA (1997) High affinity binding of inositol phosphates and phosphoinositides to the pleckstrin homology domain of RAC/protein kinase B and their influence on kinase activity. J Biol Chem 272:8474–8481
Milburn CC, Deak M, Kelly SM, Price NC, Alessi DR, Van Aalten DM (2003) Binding of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate to the pleckstrin homology domain of protein kinase B induces a conformational change. Biochem J 375:531–538
Acknowledgments
We thank S.H. Snyder and A. Chakraborty for providing unpublished work and B.M. Hallberg, for structural insights. The 3-D figure was constructed in trueSpace 7.6, Caligari Inc. This work was supported by grants from Karolinska Institutet, Novo Nordisk Foundation, the Swedish Research Council, the Swedish Diabetes Association, EFSD, The Family Erling-Persson Foundation, Berth von Kantzow’s Foundation and EuroDia (LSHM-CT-2006-518153).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barker, C.J., Illies, C., Gaboardi, G.C. et al. Inositol pyrophosphates: structure, enzymology and function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 66, 3851–3871 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0115-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-009-0115-2