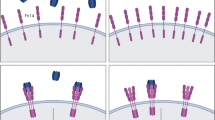
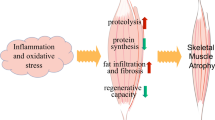
Abstract
Skeletal muscle atrophy/wasting is a serious complication of a wide range of diseases and conditions such as aging, disuse, AIDS, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, space travel, muscular dystrophy, chronic heart failure, sepsis, and cancer. Emerging evidence suggests that nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) is one of the most important signaling pathways linked to the loss of skeletal muscle mass in various physiological and pathophysiological conditions. Activation of NF-κB in skeletal muscle leads to degradation of specific muscle proteins, induces inflammation and fibrosis, and blocks the regeneration of myofibers after injury/atrophy. Recent studies employing genetic mouse models have provided strong evidence that NF-κB can serve as an important molecular target for the prevention of skeletal muscle loss. In this article, we have outlined the current understanding regarding the role of NF-κB in skeletal muscle with particular reference to different models of muscle wasting and the development of novel therapy.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AP-1:
-
activator protein-1
- CHF:
-
chronic heart failure
- COPD:
-
chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder
- DMD:
-
Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- IFN:
-
interferon
- IGF:
-
insulin growth factor
- IkB:
-
I kappa B
- IKK:
-
IkB kinase
- IL:
-
interleukin
- LGMD2A:
-
limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A
- LLC:
-
Lewis lung carcinoma
- MMP:
-
matrix metalloproteinase
- MuRF1:
-
muscle RING finger protein 1
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor-kappa B
- NIK:
-
NF-κB-inducing kinase
- iNOS:
-
inducible nitric oxide synthase
- PDTC:
-
pyrrolidine dithiocarbamate
- PIF:
-
proteolysis-inducing factor
- TNF:
-
tumor necrosis factor
- TWEAK:
-
TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis
References
Jackman RW, Kandarian SC (2004) The molecular basis of skeletal muscle atrophy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 287:C834–C843
Kandarian SC, Jackman RW (2006) Intracellular signaling during skeletal muscle atrophy. Muscle Nerve 33:155–165
Boonyarom O, Inui K (2006) Atrophy and hypertrophy of skeletal muscles: structural and functional aspects. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 188:77–89
Tisdale MJ (2004) Cancer cachexia. Langenbecks Arch Surg 389:299–305
Ventadour S, Attaix D (2006) Mechanisms of skeletal muscle atrophy. Curr Opin Rheumatol 18:631–635
Eley HL, Tisdale MJ (2007) Skeletal muscle atrophy, a link between depression of protein synthesis and increase in degradation. J Biol Chem 282:7087–7097
Kandarian SC, Stevenson EJ (2002) Molecular events in skeletal muscle during disuse atrophy. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 30:111–116
McKinnell IW, Rudnicki MA (2004) Molecular mechanisms of muscle atrophy. Cell 119:907–910
Guttridge DC (2004) Signaling pathways weigh in on decisions to make or break skeletal muscle. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 7:443–450
Cai D, Frantz JD, Tawa NE Jr, Melendez PA, Oh BC, Lidov HG, Hasselgren PO, Frontera WR, Lee J, Glass DJ, Shoelson SE (2004) IKKbeta/NF-kappaB activation causes severe muscle wasting in mice. Cell 119:285–298
Hunter RB, Kandarian SC (2004) Disruption of either the Nfkb1 or the Bcl3 gene inhibits skeletal muscle atrophy. J Clin Invest 114:1504–1511
Mourkioti F, Kratsios P, Luedde T, Song YH, Delafontaine P, Adami R, Parente V, Bottinelli R, Pasparakis M, Rosenthal N (2006) Targeted ablation of IKK2 improves skeletal muscle strength, maintains mass, and promotes regeneration. J Clin Invest 116:2945–2954
Acharyya S, Villalta SA, Bakkar N, Bupha-Intr T, Janssen PM, Carathers M, Li ZW, Beg AA, Ghosh S, Sahenk Z, Weinstein M, Gardner KL, Rafael-Fortney JA, Karin M, Tidball JG, Baldwin AS, Guttridge DC (2007) Interplay of IKK/NF-kappaB signaling in macrophages and myofibers promotes muscle degeneration in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. J Clin Invest 117:889–901
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2004) Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 18:2195–2224
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2008) Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 132:344–362
Kumar A, Takada Y, Boriek AM, Aggarwal BB (2004) Nuclear factor-kappaB: its role in health and disease. J Mol Med 82:434–448
Aggarwal BB (2003) Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3:745–756
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-kappaB regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2:725–734
Hunter RB, Stevenson E, Koncarevic A, Mitchell-Felton H, Essig DA, Kandarian SC (2002) Activation of an alternative NF-kappaB pathway in skeletal muscle during disuse atrophy. FASEB J 16:529–538
Cao PR, Kim HJ, Lecker SH (2005) Ubiquitin-protein ligases in muscle wasting. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:2088–2097
Gomes MD, Lecker SH, Jagoe RT, Navon A, Goldberg AL (2001) Atrogin-1, a muscle-specific F-box protein highly expressed during muscle atrophy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:14440–14445
Bodine SC, Latres E, Baumhueter S, Lai VK, Nunez L, Clarke BA, Poueymirou WT, Panaro FJ, Na E, Dharmarajan K, Pan ZQ, Valenzuela DM, DeChiara TM, Stitt TN, Yancopoulos GD, Glass DJ (2001) Identification of ubiquitin ligases required for skeletal muscle atrophy. Science 294:1704–1708
Whitehouse AS, Tisdale MJ (2003) Increased expression of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway in murine myotubes by proteolysis-inducing factor (PIF) is associated with activation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. Br J Cancer 89:1116–1122
Spate U, Schulze PC (2004) Proinflammatory cytokines and skeletal muscle. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 7:265–269
Debigare R, Cote CH, Maltais F (2001) Peripheral muscle wasting in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clinical relevance and mechanisms. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 164:1712–1717
Roubenoff R (2003) Catabolism of aging: is it an inflammatory process? Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 6:295–299
Phillips T, Leeuwenburgh C (2005) Muscle fiber specific apoptosis and TNF-alpha signaling in sarcopenia are attenuated by life-long calorie restriction. FASEB J 19:668–670
Fernandez-Celemin L, Pasko N, Blomart V, Thissen JP (2002) Inhibition of muscle insulin-like growth factor I expression by tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283:E1279–E1290
Foulstone EJ, Meadows KA, Holly JM, Stewart CE (2001) Insulin-like growth factors (IGF-I and IGF-II) inhibit C2 skeletal myoblast differentiation and enhance TNF alpha-induced apoptosis. J Cell Physiol 189:207–215
Demoule A, Divangahi M, Danialou G, Gvozdic D, Larkin G, Bao W, Petrof BJ (2005) Expression and regulation of CC class chemokines in the dystrophic (mdx) diaphragm. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 33:178–185
Srivastava AK, Qin X, Wedhas N, Arnush M, Linkhart TA, Chadwick RB, Kumar A (2007) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha augments matrix metalloproteinase-9 production in skeletal muscle cells through the activation of transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 (TAK1)-dependent signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 282:35113–35124
Charge SB, Rudnicki MA (2004) Cellular and molecular regulation of muscle regeneration. Physiol Rev 84:209–238
Langen RC, Schols AM, Kelders MC, van der Velden JL, Wouters EF, Janssen-Heininger YM (2006) Muscle wasting and impaired muscle regeneration in a murine model of chronic pulmonary inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 35:689–696
Langen RC, Schols AM, Kelders MC, Wouters EF, Janssen-Heininger YM (2001) Inflammatory cytokines inhibit myogenic differentiation through activation of nuclear factor-kappaB. FASEB J 15:1169–1180
Guttridge DC, Albanese C, Reuther JY, Pestell RG, Baldwin AS Jr (1999) NF-kappaB controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol Cell Biol 19:5785–5799
Mitin N, Kudla AJ, Konieczny SF, Taparowsky EJ (2001) Differential effects of Ras signaling through NFkappaB on skeletal myogenesis. Oncogene 20:1276–1286
Lehtinen SK, Rahkila P, Helenius M, Korhonen P, Salminen A (1996) Down-regulation of transcription factors AP-1, Sp-1, and NF-kappa B precedes myocyte differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 229:36–43
Wang H, Hertlein E, Bakkar N, Sun H, Acharyya S, Wang J, Carathers M, Davuluri R, Guttridge DC (2007) NF-kappaB regulation of YY1 inhibits skeletal myogenesis through transcriptional silencing of myofibrillar genes. Mol Cell Biol 27:4374–4387
Thaloor D, Miller KJ, Gephart J, Mitchell PO, Pavlath GK (1999) Systemic administration of the NF-kappaB inhibitor curcumin stimulates muscle regeneration after traumatic injury. Am J Physiol 277:C320–C329
Shishodia S, Sethi G, Aggarwal BB (2005) Curcumin: getting back to the roots. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1056:206–217
Dogra C, Changotra H, Wedhas N, Qin X, Wergedal JE, Kumar A (2007) TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) is a potent skeletal muscle-wasting cytokine. FASEB J 21:1857–1869
Dogra C, Changotra H, Mohan S, Kumar A (2006) Tumor necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis inhibits skeletal myogenesis through sustained activation of nuclear factor-kappaB and degradation of MyoD protein. J Biol Chem 281:10327–10336
Berkes CA, Tapscott SJ (2005) MyoD and the transcriptional control of myogenesis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 16:585–595
Guttridge DC, Mayo MW, Madrid LV, Wang CY, Baldwin AS Jr (2000) NF-kappaB-induced loss of MyoD messenger RNA: possible role in muscle decay and cachexia. Science 289:2363–2366
Sitcheran R, Cogswell PC, Baldwin AS Jr (2003) NF-kappaB mediates inhibition of mesenchymal cell differentiation through a posttranscriptional gene silencing mechanism. Genes Dev 17:2368–2373
Di Marco S, Mazroui R, Dallaire P, Chittur S, Tenenbaum SA, Radzioch D, Marette A, Gallouzi IE (2005) NF-kappa B-mediated MyoD decay during muscle wasting requires nitric oxide synthase mRNA stabilization, HuR protein, and nitric oxide release. Mol Cell Biol 25:6533–6545
Kaliman P, Canicio J, Testar X, Palacin M, Zorzano A (1999) Insulin-like growth factor-II, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, nuclear factor-kappaB and inducible nitric-oxide synthase define a common myogenic signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 274:17437–17444
Canicio J, Ruiz-Lozano P, Carrasco M, Palacin M, Chien K, Zorzano A, Kaliman P (2001) Nuclear factor kappa B-inducing kinase and Ikappa B kinase-alpha signal skeletal muscle cell differentiation. J Biol Chem 276:20228–20233
Bakkar N, Wang J, Ladner KJ, Wang H, Dahlman JM, Carathers M, Acharyya S, Rudnicki MA, Hollenbach AD, Guttridge DC (2008) IKK/NF-kappaB regulates skeletal myogenesis via a signaling switch to inhibit differentiation and promote mitochondrial biogenesis. J Cell Biol 180:787–802
Dalkilic I, Kunkel LM (2003) Muscular dystrophies: genes to pathogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev 13:231–238
Hoffman EP, Brown RH, Kunkel LM (1987) Dystrophin: the protein product of the Duchenne muscular dystrophy locus. Cell 51:919–928
Spencer MJ, Montecino-Rodriguez E, Dorshkind K, Tidball JG (2001) Helper (CD4(+)) and cytotoxic (CD8(+)) T cells promote the pathology of dystrophin-deficient muscle. Clin Immunol 98:235–243
Chen YW, Zhao P, Borup R, Hoffman EP (2000) Expression profiling in the muscular dystrophies: identification of novel aspects of molecular pathophysiology. J Cell Biol 151:1321–1336
Tidball JG, Wehling-Henricks M (2004) Evolving therapeutic strategies for Duchenne muscular dystrophy: targeting downstream events. Pediatr Res 56:831–841
Kumar A, Boriek AM (2003) Mechanical stress activates the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in skeletal muscle fibers: a possible role in Duchenne muscular dystrophy. FASEB J 17:386–396
Monici MC, Aguennouz M, Mazzeo A, Messina C, Vita G (2003) Activation of nuclear factor-kappaB in inflammatory myopathies and Duchenne muscular dystrophy. Neurology 60:993–997
Carlson CG, Samadi A, Siegel A (2005) Chronic treatment with agents that stabilize cytosolic IkappaB-alpha enhances survival and improves resting membrane potential in MDX muscle fibers subjected to chronic passive stretch. Neurobiol Dis 20:719–730
Messina S, Bitto A, Aguennouz M, Minutoli L, Monici MC, Altavilla D, Squadrito F, Vita G (2006) Nuclear factor kappa-B blockade reduces skeletal muscle degeneration and enhances muscle function in Mdx mice. Exp Neurol 198:234–241
Messina S, Altavilla D, Aguennouz M, Seminara P, Minutoli L, Monici MC, Bitto A, Mazzeo A, Marini H, Squadrito F, Vita G (2006) Lipid peroxidation inhibition blunts nuclear factor-kappaB activation, reduces skeletal muscle degeneration, and enhances muscle function in mdx mice. Am J Pathol 168:918–926
Auphan N, DiDonato JA, Rosette C, Helmberg A, Karin M (1995) Immunosuppression by glucocorticoids: inhibition of NF-kappa B activity through induction of I kappa B synthesis. Science 270:286–290
Richard I, Roudaut C, Marchand S, Baghdiguian S, Herasse M, Stockholm D, Ono Y, Suel L, Bourg N, Sorimachi H, Lefranc G, Fardeau M, Sebille A, Beckmann JS (2000) Loss of calpain 3 proteolytic activity leads to muscular dystrophy and to apoptosis-associated IkappaBalpha/nuclear factor kappaB pathway perturbation in mice. J Cell Biol 151:1583–1590
Baghdiguian S, Martin M, Richard I, Pons F, Astier C, Bourg N, Hay RT, Chemaly R, Halaby G, Loiselet J, Anderson LV, Lopez de Munain A, Fardeau M, Mangeat P, Beckmann JS, Lefranc G (1999) Calpain 3 deficiency is associated with myonuclear apoptosis and profound perturbation of the IkappaB alpha/NF-kappaB pathway in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A. Nat Med 5:503–511
Benayoun B, Baghdiguian S, Lajmanovich A, Bartoli M, Daniele N, Gicquel E, Bourg N, Raynaud F, Pasquier MA, Suel L, Lochmuller H, Lefranc G, Richard I (2007) NF-{kappa}B-dependent expression of the antiapoptotic factor c-FLIP is regulated by calpain 3, the protein involved in limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A. FASEB J 22:1521–1529
Deans C, Wigmore SJ (2005) Systemic inflammation, cachexia and prognosis in patients with cancer. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 8:265–269
Wyke SM, Russell ST, Tisdale MJ (2004) Induction of proteasome expression in skeletal muscle is attenuated by inhibitors of NF-kappaB activation. Br J Cancer 91:1742–1750
Moore-Carrasco R, Busquets S, Almendro V, Palanki M, Lopez-Soriano FJ, Argiles JM (2007) The AP-1/NF-kappaB double inhibitor SP100030 can revert muscle wasting during experimental cancer cachexia. Int J Oncol 30:1239–1245
Wang Z, Corey E, Hass GM, Higano CS, True LD, Wallace D Jr, Tisdale MJ, Vessella RL (2003) Expression of the human cachexia-associated protein (HCAP) in prostate cancer and in a prostate cancer animal model of cachexia. Int J Cancer 105:123–129
Jiang Z, Clemens PR (2006) Cellular caspase-8-like inhibitory protein (cFLIP) prevents inhibition of muscle cell differentiation induced by cancer cells. FASEB J 20:2570–2572
Kuroda K, Horiguchi Y, Nakashima J, Kikuchi E, Kanao K, Miyajima A, Ohigashi T, Umezawa K, Murai M (2005) Prevention of cancer cachexia by a novel nuclear factor {kappa}B inhibitor in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 11:5590–5594
Juttler E, Potrovita I, Tarabin V, Prinz S, Dong-Si T, Fink G, Schwaninger M (2004) The cannabinoid dexanabinol is an inhibitor of the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B). Neuropharmacology 47:580–592
Mishra A, Chaudhary A, Sethi S (2004) Oxidized omega-3 fatty acids inhibit NF-kappaB activation via a PPARalpha-dependent pathway. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:1621–1627
Li WG, Gavrila D, Liu X, Wang L, Gunnlaugsson S, Stoll LL, McCormick ML, Sigmund CD, Tang C, Weintraub NL (2004) Ghrelin inhibits proinflammatory responses and nuclear factor-kappaB activation in human endothelial cells. Circulation 109:2221–2226
Futakuchi M, Ogawa K, Tamano S, Takahashi S, Shirai T (2004) Suppression of metastasis by nuclear factor kappaB inhibitors in an in vivo lung metastasis model of chemically induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Sci 95:18–24
Majumdar S, Lamothe B, Aggarwal BB (2002) Thalidomide suppresses NF-kappa B activation induced by TNF and H2O2, but not that activated by ceramide, lipopolysaccharides, or phorbol ester. J Immunol 168:2644–2651
Gilad E, Wong HR, Zingarelli B, Virag L, O’Connor M, Salzman AL, Szabo C (1998) Melatonin inhibits expression of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase in murine macrophages: role of inhibition of NFkappaB activation. FASEB J 12:685–693
Penner CG, Gang G, Wray C, Fischer JE, Hasselgren PO (2001) The transcription factors NF-kappab and AP-1 are differentially regulated in skeletal muscle during sepsis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 281:1331–1336
Frost RA, Lang CH (2005) Skeletal muscle cytokines: regulation by pathogen-associated molecules and catabolic hormones. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 8:255–263
Callahan LA, Nethery D, Stofan D, DiMarco A, Supinski G (2001) Free radical-induced contractile protein dysfunction in endotoxin-induced sepsis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 24:210–217
Boyd JH, Divangahi M, Yahiaoui L, Gvozdic D, Qureshi S, Petrof BJ (2006) Toll-like receptors differentially regulate CC and CXC chemokines in skeletal muscle via NF-kappaB and calcineurin. Infect Immun 74:6829–6838
Demoule A, Divangahi M, Yahiaoui L, Danialou G, Gvozdic D, Labbe K, Bao W, Petrof BJ (2006) Endotoxin triggers nuclear factor-kappaB-dependent up-regulation of multiple proinflammatory genes in the diaphragm. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 174:646–653
Casadevall C, Coronell C, Ramirez-Sarmiento AL, Martinez-Llorens J, Barreiro E, Orozco-Levi M, Gea J (2007) Upregulation of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the intercostal muscles of COPD patients. Eur Respir J 30:701–707
Gosker HR, Wouters EF, van der Vusse GJ, Schols AM (2000) Skeletal muscle dysfunction in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and chronic heart failure: underlying mechanisms and therapy perspectives. Am J Clin Nutr 71:1033–1047
Staib JL, Swoap SJ, Powers SK (2002) Diaphragm contractile dysfunction in MyoD gene-inactivated mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283:R583–R590
Agusti A, Morla M, Sauleda J, Saus C, Busquets X (2004) NF-kappaB activation and iNOS upregulation in skeletal muscle of patients with COPD and low body weight. Thorax 59:483–487
Broekhuizen R, Wouters EF, Creutzberg EC, Weling-Scheepers CA, Schols AM (2005) Polyunsaturated fatty acids improve exercise capacity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Thorax 60:376–382
Bolger AP, Anker SD (2000) Tumour necrosis factor in chronic heart failure: a peripheral view on pathogenesis, clinical manifestations and therapeutic implications. Drugs 60:1245–1257
Adams V, Nehrhoff B, Spate U, Linke A, Schulze PC, Baur A, Gielen S, Hambrecht R, Schuler G (2002) Induction of iNOS expression in skeletal muscle by IL-1beta and NFkappaB activation: an in vitro and in vivo study. Cardiovasc Res 54:95–104
Adams V, Spate U, Krankel N, Schulze PC, Linke A, Schuler G, Hambrecht R (2003) Nuclear factor-kappa B activation in skeletal muscle of patients with chronic heart failure: correlation with the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Eur J Cardiovasc Prev Rehabil 10:273–277
Jankowska EA, von Haehling S, Czarny A, Zaczynska E, Kus A, Anker SD, Banasiak W, Ponikowski P (2005) Activation of the NF-kappaB system in peripheral blood leukocytes from patients with chronic heart failure. Eur J Heart Fail 7:984–990
Siednienko J, Jankowska EA, Banasiak W, Gorczyca WA, Ponikowski P (2007) Nuclear factor-kappaB activity in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in cachectic and non-cachectic patients with chronic heart failure. Int J Cardiol 122:111–116
Mitch WE, Bailey JL, Wang X, Jurkovitz C, Newby D, Price SR (1999) Evaluation of signals activating ubiquitin–proteasome proteolysis in a model of muscle wasting. Am J Physiol 276:C1132–C1138
Guillet C, Boirie Y (2005) Insulin resistance: a contributing factor to age-related muscle mass loss? Diabetes Metab 31(Spec No 2):5S20–25S26
Willey KA, Singh MA (2003) Battling insulin resistance in elderly obese people with type 2 diabetes: bring on the heavy weights. Diabetes Care 26:1580–1588
Li YP, Chen Y, Li AS, Reid MB (2003) Hydrogen peroxide stimulates ubiquitin-conjugating activity and expression of genes for specific E2 and E3 proteins in skeletal muscle myotubes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 285:C806–C812
Mastrocola R, Reffo P, Penna F, Tomasinelli CE, Boccuzzi G, Baccino FM, Aragno M, Costelli P (2008) Muscle wasting in diabetic and in tumor-bearing rats: role of oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 44:584–593
Judge AR, Koncarevic A, Hunter RB, Liou HC, Jackman RW, Kandarian SC (2007) Role for IkappaBalpha, but not c-Rel, in skeletal muscle atrophy. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C372–C382
Degens H, Alway SE (2006) Control of muscle size during disuse, disease, and aging. Int J Sports Med 27:94–99
Bruunsgaard H, Pedersen BK (2003) Age-related inflammatory cytokines and disease. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am 23:15–39
Bar-Shai M, Carmeli E, Coleman R, Rozen N, Perek S, Fuchs D, Reznick AZ (2005) The effect of hindlimb immobilization on acid phosphatase, metalloproteinases and nuclear factor-kappaB in muscles of young and old rats. Mech Ageing Dev 126:289–297
Cuthbertson D, Smith K, Babraj J, Leese G, Waddell T, Atherton P, Wackerhage H, Taylor PM, Rennie MJ (2005) Anabolic signaling deficits underlie amino acid resistance of wasting, aging muscle. FASEB J 19:422–424
Acknowledgments
We would like to apologize to the many researchers whose contributions were not cited due to our oversight or space limitation. This work was supported by RO1 grant AG029623 from National Institute of Health (to AK).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, H., Malhotra, S. & Kumar, A. Nuclear factor-kappa B signaling in skeletal muscle atrophy. J Mol Med 86, 1113–1126 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-008-0373-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-008-0373-8