Abstract
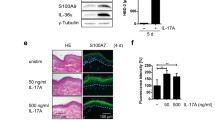
Psoriasis is a common chronic skin disease with a largely unknown pathogenesis. We demonstrate here that transgenic over-expression of interleukin (IL)-22 in mice resulted in neonatal mortality and psoriasis-like skin alterations including acanthosis and hypogranularity. This cutaneous phenotype may be caused by the direct influence of IL-22 on keratinocytes, since this cytokine did not affect skin fibroblasts, endothelial cells, melanocytes, or adipocytes. The comparison of cytokines with hypothesized roles in psoriasis pathogenesis determined that neither interferon (IFN)-γ nor IL-17, but only IL-22 and, with lower potency, IL-20 caused psoriasis-like morphological changes in a three-dimensional human epidermis model. These changes were associated with inhibited keratinocyte terminal differentiation and with STAT3 upregulation. The IL-22 effect on differentiation-regulating genes was STAT3-dependent. In contrast to IL-22 and IL-20, IFN-γ and IL-17 strongly induced T-cell and neutrophilic granulocyte-attracting chemokines, respectively. Tumor necrosis factor-α potently induced diverse chemokines and additionally enhanced the expression of IL-22 receptor pathway elements and amplified some IL-22 effects. This study suggests that different cytokines are players in the psoriasis pathogenesis although only the IL-10 family members IL-22 and IL-20 directly cause the characteristic epidermal alterations.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Griffiths CE, Barker JN (2007) Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 370:263–271
Schon MP, Boehncke WH (2005) Psoriasis. N Engl J Med 352:1899–1912
Kupper TS, Fuhlbrigge RC (2004) Immune surveillance in the skin: mechanisms and clinical consequences. Nat Rev Immunol 4:211–222
Lew W, Bowcock AM, Krueger JG (2004) Psoriasis vulgaris: cutaneous lymphoid tissue supports T-cell activation and “Type 1” inflammatory gene expression. Trends Immunol 25:295–305
Wolk K, Sabat R (2006) Interleukin-22: a novel T- and NK-cell derived cytokine that regulates the biology of tissue cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 17:367–380
Chung Y, Yang X, Chang SH, Ma L, Tian Q, Dong C (2006) Expression and regulation of IL-22 in the IL-17-producing CD4+ T lymphocytes. Cell Res 16:902–907
Liang SC, Tan XY, Luxenberg DP, Karim R, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K, Collins M, Fouser LA (2006) Interleukin (IL)-22 and IL-17 are coexpressed by Th17 cells and cooperatively enhance expression of antimicrobial peptides. J Exp Med 203:2271–2279
Wolk K, Kunz S, Asadullah K, Sabat R (2002) Cutting edge: immune cells as sources and targets of the IL-10 family members? J Immunol 168:5397–5402
Zheng Y, Danilenko DM, Valdez P, Kasman I, Eastham-Anderson J, Wu J, Ouyang W (2007) Interleukin-22, a T(H)17 cytokine, mediates IL-23-induced dermal inflammation and acanthosis. Nature 445:648–651
Satoh-Takayama N, Vosshenrich CA, Lesjean-Pottier S, Sawa S, Lochner M, Rattis F, Mention JJ, Thiam K, Cerf-Bensussan N, Mandelboim O, Eberl G, Di Santo JP (2008) Microbial flora drives interleukin 22 production in intestinal NKp46+ cells that provide innate mucosal immune defense. Immunity 29:958–970
Wolk K, Kunz S, Witte E, Friedrich M, Asadullah K, Sabat R (2004) IL-22 increases the innate immunity of tissues. Immunity 21:241–254
Wolk K, Witte E, Reineke U, Witte K, Friedrich M, Sterry W, Asadullah K, Volk HD, Sabat R (2005) Is there an interaction between interleukin-10 and interleukin-22. Genes Immun 6:8–18
Wolk K, Witte E, Wallace E, Docke WD, Kunz S, Asadullah K, Volk HD, Sterry W, Sabat R (2006) IL-22 regulates the expression of genes responsible for antimicrobial defense, cellular differentiation, and mobility in keratinocytes: a potential role in psoriasis. Eur J Immunol 36:1309–1323
Boniface K, Bernard FX, Garcia M, Gurney AL, Lecron JC, Morel F (2005) IL-22 inhibits epidermal differentiation and induces proinflammatory gene expression and migration of human keratinocytes. J Immunol 174:3695–3702
Sa SM, Valdez PA, Wu J, Jung K, Zhong F, Hall L, Kasman I, Winer J, Modrusan Z, Danilenko DM, Ouyang W (2007) The effects of IL-20 subfamily cytokines on reconstituted human epidermis suggest potential roles in cutaneous innate defense and pathogenic adaptive immunity in psoriasis. J Immunol 178:2229–2240
Sabat R, Philipp S, Hoflich C, Kreutzer S, Wallace E, Asadullah K, Volk HD, Sterry W, Wolk K (2007) Immunopathogenesis of psoriasis. Exp Dermatol 16:779–798
Blumberg H, Conklin D, Xu WF, Grossmann A, Brender T, Carollo S, Eagan M, Foster D, Haldeman BA, Hammond A, Haugen H, Jelinek L, Kelly JD, Madden K, Maurer MF, Parrish-Novak J, Prunkard D, Sexson S, Sprecher C, Waggie K, West J, Whitmore TE, Yao L, Kuechle MK, Dale BA, Chandrasekher YA (2001) Interleukin 20: discovery, receptor identification, and role in epidermal function. Cell 104:9–19
Wolk K, Kunz S, Crompton NE, Volk HD, Sabat R (2003) Multiple mechanisms of reduced major histocompatibility complex class II expression in endotoxin tolerance. J Biol Chem 278:18030–18036
Dumoutier L, Van Roost E, Colau D, Renauld JC (2000) Human interleukin-10-related T cell-derived inducible factor: molecular cloning and functional characterization as an hepatocyte-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:10144–10149
Kotenko SV, Izotova LS, Mirochnitchenko OV, Esterova E, Dickensheets H, Donnelly RP, Pestka S (2001) Identification of the functional interleukin-22 (IL-22) receptor complex: the IL-10R2 chain (IL-10Rbeta) is a common chain of both the IL-10 and IL-22 (IL-10-related T cell-derived inducible factor, IL-TIF) receptor complexes. J Biol Chem 276:2725–2732
Xie MH, Aggarwal S, Ho WH, Foster J, Zhang Z, Stinson J, Wood WI, Goddard AD, Gurney AL (2000) Interleukin (IL)-22, a novel human cytokine that signals through the interferon receptor-related proteins CRF2-4 and IL-22R. J Biol Chem 275:31335–31339
Asarch A, Barak O, Loo DS, Gottlieb AB (2008) Th17 cells: a new paradigm for cutaneous inflammation. J Dermatolog Treat 19(5):259–266
Haider AS, Lowes MA, Suarez-Farinas M, Zaba LC, Cardinale I, Khatcherian A, Novitskaya I, Wittkowski KM, Krueger JG (2008) Identification of cellular pathways of “type 1,” Th17 T cells, and TNF- and inducible nitric oxide synthase-producing dendritic cells in autoimmune inflammation through pharmacogenomic study of cyclosporine A in psoriasis. J Immunol 180:1913–1920
Sano S, Chan KS, Carbajal S, Clifford J, Peavey M, Kiguchi K, Itami S, Nickoloff BJ, DiGiovanni J (2005) Stat3 links activated keratinocytes and immunocytes required for development of psoriasis in a novel transgenic mouse model. Nat Med 11:43–49
Sano S, Itami S, Takeda K, Tarutani M, Yamaguchi Y, Miura H, Yoshikawa K, Akira S, Takeda J (1999) Keratinocyte-specific ablation of Stat3 exhibits impaired skin remodeling, but does not affect skin morphogenesis. EMBO J 18:4657–4668
Kleyn CE, Griffiths CE (2006) Infliximab for the treatment of psoriasis. Expert Opin Biol Ther 6:797–805
Philipp S, Wolk K, Kreutzer S, Wallace E, Ludwig N, Roewert J, Hoflich C, Volk HD, Sterry W, Sabat R (2006) The evaluation of psoriasis therapy with biologics leads to a revision of the current view of the pathogenesis of this disorder. Expert Opin Ther Targets 10:817–831
Dumoutier L, Leemans C, Lejeune D, Kotenko SV, Renauld JC (2001) Cutting edge: STAT activation by IL-19, IL-20 and mda-7 through IL-20 receptor complexes of two types. J Immunol 167:3545–3549
Otkjaer K, Kragballe K, Funding AT, Clausen JT, Noerby PL, Steiniche T, Iversen L (2005) The dynamics of gene expression of interleukin-19 and interleukin-20 and their receptors in psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 153:911–918
Romer J, Hasselager E, Norby PL, Steiniche T, Thorn Clausen J, Kragballe K (2003) Epidermal overexpression of interleukin-19 and -20 mRNA in psoriatic skin disappears after short-term treatment with cyclosporine a or calcipotriol. J Invest Dermatol 121:1306–1311
Kunz S, Wolk K, Witte E, Witte K, Doecke WD, Volk HD, Sterry W, Asadullah K, Sabat R (2006) Interleukin (IL)-19, IL-20 and IL-24 are produced by and act on keratinocytes and are distinct from classical ILs. Exp Dermatol 15:991–1004
Ma HL, Liang S, Li J, Napierata L, Brown T, Benoit S, Senices M, Gill D, Dunussi-Joannopoulos K, Collins M, Nickerson-Nutter C, Fouser LA, Young DA (2008) IL-22 is required for Th17 cell-mediated pathology in a mouse model of psoriasis-like skin inflammation. J Clin Invest 118:597–607
Fossiez F, Djossou O, Chomarat P, Flores-Romo L, Ait-Yahia S, Maat C, Pin JJ, Garrone P, Garcia E, Saeland S, Blanchard D, Gaillard C, Das Mahapatra B, Rouvier E, Golstein P, Banchereau J, Lebecque S (1996) T cell interleukin-17 induces stromal cells to produce proinflammatory and hematopoietic cytokines. J Exp Med 183:2593–2603
Hirota K, Hashimoto M, Yoshitomi H, Tanaka S, Nomura T, Yamaguchi T, Iwakura Y, Sakaguchi N, Sakaguchi S (2007) T cell self-reactivity forms a cytokine milieu for spontaneous development of IL-17+ Th cells that cause autoimmune arthritis. J Exp Med 204:41–47
Komiyama Y, Nakae S, Matsuki T, Nambu A, Ishigame H, Kakuta S, Sudo K, Iwakura Y (2006) IL-17 plays an important role in the development of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 177:566–573
Lohr J, Knoechel B, Wang JJ, Villarino AV, Abbas AK (2006) Role of IL-17 and regulatory T lymphocytes in a systemic autoimmune disease. J Exp Med 203:2785–2791
Sato K, Suematsu A, Okamoto K, Yamaguchi A, Morishita Y, Kadono Y, Tanaka S, Kodama T, Akira S, Iwakura Y, Cua DJ, Takayanagi H (2006) Th17 functions as an osteoclastogenic helper T cell subset that links T cell activation and bone destruction. J Exp Med 203:2673–2682
Zhang Z, Zheng M, Bindas J, Schwarzenberger P, Kolls JK (2006) Critical role of IL-17 receptor signaling in acute TNBS-induced colitis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 12:382–388
Acosta-Rodriguez EV, Rivino L, Geginat J, Jarrossay D, Gattorno M, Lanzavecchia A, Sallusto F, Napolitani G (2007) Surface phenotype and antigenic specificity of human interleukin 17-producing T helper memory cells. Nat Immunol 8:639–646
Le Borgne M, Etchart N, Goubier A, Lira SA, Sirard JC, van Rooijen N, Caux C, Ait-Yahia S, Vicari A, Kaiserlian D, Dubois B (2006) Dendritic cells rapidly recruited into epithelial tissues via CCR6/CCL20 are responsible for CD8+ T cell crosspriming in vivo. Immunity 24:191–201
Candi E, Schmidt R, Melino G (2005) The cornified envelope: a model of cell death in the skin. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:328–340
Nograles KE, Zaba LC, Guttman-Yassky E, Fuentes-Duculan J, Suarez-Farinas M, Cardinale I, Khatcherian A, Gonzalez J, Pierson KC, White TR, Pensabene C, Coats I, Novitskaya I, Lowes MA, Krueger JG (2008) Th17 cytokines interleukin (IL)-17 and IL-22 modulate distinct inflammatory and keratinocyte-response pathways. Br J Dermatol 159:1092–1102
Tjabringa G, Bergers M, van Rens D, de Boer R, Lamme E, Schalkwijk J (2008) Development and validation of human psoriatic skin equivalents. Am J Pathol 173:815–823
Wolk K, Witte K, Witte E, Proesch S, Schulze-Tanzil G, Nasilowska K, Thilo J, Asadullah K, Sterry W, Volk HD, Sabat R (2008) Maturing dendritic cells are an important source of IL-29 and IL-20 that may cooperatively increase the innate immunity of keratinocytes. J Leukoc Biol 83:1181–1193
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge B. Ketel, A. Buss, and Wendy Curtis for excellent technical assistance and E. Wallace for accurately proofreading the manuscript. Prof. J. Lademann is acknowledged for placing the Olympus microscope at our disposal. We also thank the German Ministry of Education and Research for the generous support.
Disclosure
H. S. Haugen, W. Xu, K. Waggie, and M. Anderson are stockholders of ZymoGenetics. Inc. K. Wolk was consultant for Merck Serono S. A. until July 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Kerstin Wolk and Harald S. Haugen equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wolk, K., Haugen, H.S., Xu, W. et al. IL-22 and IL-20 are key mediators of the epidermal alterations in psoriasis while IL-17 and IFN-γ are not. J Mol Med 87, 523–536 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0457-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0457-0