Abstract
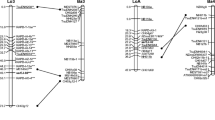
Several genetic linkage maps have been published in recent years on different Prunus species suggesting a high level of resemblance among the genomes of these species. One of these maps (Joobeur et al., Theor Appl Genet 97:1034–1041 [(1998); Aranzana et al., Theor Appl Genet 106:819–825 (2002b)] constructed from interspecific almond Texas × peach Earlygold F2 progeny (T×E) was considered to be saturated. We selected 142 F1 apricot hybrids obtained from a cross between P. armeniaca cvs. Polonais and Stark Early Orange for mapping. Eighty-eight RFLP probes and 20 peach SSR primer pairs used for the ‘reference map’ were selected to cover the eight linkage groups. One P. davidiana and an additional 14 apricot simple sequence repeats (SSRs) were mapped for the F1 progeny. Eighty-three amplified fragment length polymorphisms were added in order to increase the density of the maps. Separate maps were made for each parent according to the ‘double pseudo-testcross’ model of analysis. A total of 141 markers were placed on the map of Stark Early Orange, defining a total length of 699 cM, and 110 markers were placed on the map of Polonais, defining a total length of 538 cM. Twenty-one SSRs and 18 restriction placed in the T×E map were heterozygous in both parents (anchor loci), thereby enabling the alignment of the eight homologous linkage groups of each map. Except for 15 markers, most markers present in each linkage group in apricot were aligned with those in T×E map, indicating a high degree of colinearity between the apricot genome and the peach and almond genomes. These results suggest a strong homology of the genomes between these species and probably between Prunophora and Amygdalus sub-genera.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aranzana MJ, Garcia-Mas J, Carbo J, Arús P (2002a) Development and variability analysis of microsatellite markers in peach. Plant Breed 121:87–92
Aranzana MJ, Pineda A, Cosson P, Dirlewanger E, Ascasibar J, Cipriani G, Ryder CD, Testolin R, Abbott A, King GJ, Iezzoni AF, Arús P (2002b) A set of simple-sequence repeat (SSR) markers covering the Prunus genome. Theor Appl Genet 106:819–825
Arumuganathan K, Earle E (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Arús P, Messeguer R, Viruel M, Tobutt K, Dirlewanger E, Santi F, Quarta R, Ritter E (1994) The European Prunus mapping project. Euphytica 77:97–100
Ballester J, Boskovic R, Battle I, Arus P, Vargas F, de Vicente MC (1998) Location of the self-incompatibility gene on the almond linkage map. Plant Breed 117:69–72
Bernatzky R, Tanksley SD (1986a) Methods for detection of single or low copy sequences in tomato on southern blots. Plant Mol Biol Rep 4:37–4
Bernatzky R, Tanksley SD (1986b) Genetics of actin-related sequences in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 72:314–321
Bliss FA, Arulsekar S, Foolad MR, Becerra V, Gillen AM, Warburton ML, Dandekar AM, Kocsisne GM, Mydin KK (2002) An expanded genetic linkage map of Prunus based on an interspecific cross between almond and peach. Genome 45:520–529
Byrne DH, Littleton TG (1989) Characterization of isozyme variability in apricots. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 114:674–678
Castiglioni P, Ajmone-Marsan P, van Wijk R, Motto M (1999) AFLP markers in a molecular linkage map of maize: codominant scoring and linkage group distribution. Theor Appl Genet 99:425–431
Chapparo JX, Werner DJ, O’Malley DO, Sederoff RR (1994) Targeted mapping and linkage analysis of morphological isozyme and RAPD markers in peach. Theor Appl Genet 87:805–815
Cipriani G, Lot G, Huang WG, Marrazzo MT, Peterlunger E, Testolin R (1999) AC/GT and AG/CT microsatellite repeats in peach [Prunus persica (L) Batsch]: isolation, characterisation and cross-species amplification in Prunus. Theor Appl Genet 99:65–72
Decroocq V, Favé MG, Hagen L, Bordenave L, Decroocq S (2003) Development and transferability of apricot and grape EST microsatellite markers across taxa. Theor Appl Genet 106:912–922
Dettori MT, Quarta R, Verde I (2001) A peach linkage map integrating RFLPs, SSRs, RAPDs and morphological markers. Genome 44:783–790
Dirlewanger E, Pronier V, Parvery C, Rothan C, Guye A, Monnet R (1998) Genetic linkage map of peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] using morphological and molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:888–895
Dirlewanger E, Cosson P, Tavaud M, Aranzana MJ, Poizat C, Zanetto A, Arus P, Laigret F (2002a) Development of microsatellite markers in peach [Prunus persica (L.) Batsch] and their use in genetic diversity analysis in peach and sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.). Theor Appl Genet 105:127-138
Dirlewanger E, Garbowski C, Claverie J, Renaud C, Zanetto A (2002b) Microsatellite markers for the construction of a linkage map in sweet cherry (Prunus avium L.) and map comparison between sweet cherry and other Prunus species. In: Plant Anim Microbe Genomes, 10th Meet
FAO (2002) FAOSTAT database 2000. Web site at http://apps.fao.org
Foolad MR, Arulsekar S, Becerra V, Bliss FA (1995) A genetic map of Prunus based on an interspecific cross between peach and almond. Theor Appl Genet 91:262–269
Grattapaglia D, Sederoff R (1994) Genetic linkage maps of Eucalyptus grandis and E. urophylla using a pseudo-testcross mapping strategy and RAPD markers. Genetics 137:1121–1137
Hagen LS, Khadari B, Lambert P, Audergon JM (2002) Genetic diversity in apricot revealed by AFLP markers: species and cultivar comparisons. Theor Appl Genet 105:298–305
Hurtado MA, Romero C, Vilanova S, Abbott AG, Llacer G, Badenes ML (2002) Genetic linkage map of two apricot cultivars (Prunus armeniaca L.) and mapping of PPV (sharka) resistance. Theor Appl Genet 105:182–191
Joobeur T, Viruel MA, de Vicente MC, Jauregui B, Ballester J, Dettori MT, Verde I, Truco MJ, Messeguer R, Battle I, Quarta R, Dirlewanger E, Arús P (1998) Construction of a saturated linkage map for Prunus using an almond × peach F2 progeny. Theor Appl Genet 97:1034–1041
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distance from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lincoln SE, Daly MJ, Lander ES (1992) Constructing genetic maps with mapmaker/exp 3.0, 3rd edn. Whitehead Institute Technical Report, Cambridge, Mass.
Lorieux M, Perrier X, Goffinet B, Lanaud C, Gonzalez de Leon D (1995) Maximum-likelihood models for mapping genetic markers showing segregation distorsion. 2. F2 populations. Theor Appl Genet 90:81–89
Lu ZX, Sosinski A, Reighard GL, Baird WV, Abbott AG (1998) Construction of a genetic linkage map and identification of AFLP markers for resistance to root-not nematodes in peach rootstock. Genome 41:199–207
Maliepaard C, Jansen J, Van Ooijen JW (1997) Linkage analysis in a full-sib family of an outbreeding plant species overview and consequences for applications. Gene Res 70:237–250
Rajapakse S, Belthoff L, He G, Estager AE, Scorza R, Verde I, Ballard RE, Baird WV, Callahan A, Monnet R, Abbott AG (1995) Genetic linkage mapping in peach using morphological, RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 90:503–510
Rehder A (1949) Bibliography of cultivated trees and shrubs hardy in the cooler temperate regions of the Northern hemisphere. The Arnold Arboretum of Harvard University, Jamaica Plain, Mass.
Sosinski B, Gannavarapu M, Hager LD, Beck LE, King GJ, Ryder CD, Rajapakse S, Baird WV, Ballard RE, Abbott AG (2000) Characterization of microsatellite markers in peach (Prunus persica L. Batsch). Theor Appl Genet 101:421–428
Testolin R, Marrazzo T, Cipriani G, Quarta R, Verde I, Dettori MT, Pancaldi M, Sansavini S, (2000) Microsatellite DNA in peach (Prunus Persica L. Batsch) and its use in fingerprinting and testing the genetic origin of cultivars. Genome 43:512–520
Vicente MC de, Truco MJ, Egea J, Burgos L, Arús P (1998) RFLP variability in apricot [Prunus armeniaca (L.)]. Plant Breed 117:153–158
Vilanova S, Romero C, Abbott AG, Llacer G, Badenes ML (2003) An apricot (Prunus armeniaca L.) F2 progeny linkage map based on SSR and AFLP markers mapping plum pox virus resistance and self-incompatibility traits. Theor Appl Genet 107:239–247
Viruel MA., Messeguer R, de Vicente MC, Garcia-Mas J, Puigdomenech P, Vargas F, Arús P (1995) A linkage map with RFLP and isoenzyme markers for almond. Theor Appl Genet 91:964–971
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans, van der Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper m, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang D, Karle R, Brettin TS, Iezzoni AF (1998) Genetic linkage map in sour cherry using RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 97:1217–1224
Waugh R, Bonar N, Baird E, Thomas B, Granet A, Hayes P, Powelle W (1997) Homology of AFLP products in three mapping populations of barley. Mol Gen Genet 255:311–321
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Jocelyne Kervella and Mireille Faurobert (GAFL-INRA Avignon) for their critical reading of this manuscript and all of the groups involved in the European Prunus mapping project (AIR3-CT93-1585) for kindly providing the DNA probes and SSR primers that we used for mapping—Stephane and Véronique Decroocq (UREFV-INRA-Bordeaux) for providing the apricot cDNA-SSR clones; Isabelle Marty and Gaia Sarkissian (SQPOV-INRA-Avignon) for the apricot probes; Jamila Chaib, Guillaume Gerez and Lamia Krichen for their participation. They also wish to thank Guy Clauzel, INRA-Domaine de Gotheron for maintaining the hybrid population. This work and that of L.S. Hagen were funded by the European project ABRIGEN-FAIR6 CT98–4345 “Optimization of apricot improvement by a joint conventional and molecular approach applied to the main agronomic traits”.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Möllers
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lambert, P., Hagen, L.S., Arus, P. et al. Genetic linkage maps of two apricot cultivars (Prunus armeniaca L.) compared with the almond Texas × peach Earlygold reference map for Prunus . Theor Appl Genet 108, 1120–1130 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1526-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1526-3