Abstract
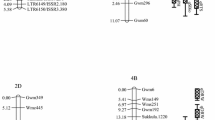
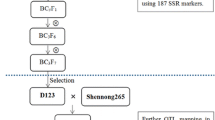
A marker-assisted back-crossing (MABC) breeding programme was conducted to improve the root morphological traits, and thereby drought tolerance, of the Indian upland rice variety, Kalinga III. This variety, the recurrent parent in the MABC, had not previously been used for quantitative trait locus (QTL) mapping. The donor parent was Azucena, an upland japonica variety from Philippines. Five segments on different chromosomes were targeted for introgression; four segments carried QTLs for improved root morphological traits (root length and thickness) and the fifth carried a recessive QTL for aroma. Some selection was made at non-target regions for recurrent parent alleles. We describe the selection made in three backcross (BC) generations and two further crosses between BC3 lines to pyramid (stack) all five target segments. Pyramids with four root QTLs were obtained in eight generations, completed in 6 years using 3,000 marker assays in a total of 323 lines. Twenty-two near-isogenic lines (NILs) were evaluated for root traits in five field experiments in Bangalore, India. The target segment on chromosome 9 (RM242-RM201) significantly increased root length under both irrigated and drought stress treatments, confirming that this root length QTL from Azucena functions in a novel genetic background. No significant effects on root length were found at the other four targets. Azucena alleles at the locus RM248 (below the target root QTL on chromosome 7) delayed flowering. Selection for the recurrent parent allele at this locus produced early-flowering NILs that were suited for upland environments in eastern India.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bouchez A, Hospital F, Causse M, Gallais A, Charcosset A (2002) Marker-assisted introgression of favourable alleles at quantitative trait loci between maize elite line. Genetics 162:1945–1959
Champoux MC, Wang G, Sarkarung S, Mackill DJ, O’Toole JC, Huang N, McCouch SR (1995) Locating genes associated with root morphology and drought avoidance in rice via linkage to molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 90:969–981
Courtois B, Chaitep W, Moolsri S, Sinha PK, Trebuil G, Yadav R (1996) Drought resistance and germplasm improvement. On-going research in the Upland rice research consortium. In: Piggin C, Courtois B, Schmit V (eds) Upland rice research in Partnership IRRI, Los Baños, IRRI Discussion paper Series 16:154–175
Hemamalini GS, Shashidhar HE, Hittalmani S (2000) Molecular marker assisted tagging of morphological and physiological traits under two contrasting moisture regimens at peak vegetative stage in rice (Oryza sativa L). Euphytica 112:69–78
Hospital F, Charcosset A (1997) Marker-assisted introgression of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 147:1469–1485
Kamoshita A, Zhang J, Siopongco J, Sarkarung S, Nguyen HT, Wade L (2002) Effects of phenotyping environment on identification of Quantitative trait loci for rice root morphology under anaerobic conditions. Crop Sci 42:255–265
Lilley JM, Ludlow MM (1996) Expression of osmotic adjustment and dehydration tolerance in 61 diverse rice lines. Field Crops Res 48:185–197
Lilley JM, Ludlow MM, McCouch SR, O’Toole JC (1996) Locating QTL for osmotic adjustment and dehydration tolerance in rice. J Exp Bot 47:1427–1436
Lorieux M, Petrov M, Huang N,Guiderdoni E, Ghesquiere A (1996) Aroma in rice: Genetic analysis of a quantitative trait. Theor Appl Genet 93:1145–1151
Price AH, Tomos AD (1997) Genetic dissection of root growth in rice. II Mapping quantitative trait loci using molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 95:143–152
Price AH, Steele KA, Moore BJ, Barraclough PB, Clark LJ (2000) A combined RFLP and AFLP linkage map of upland rice (Oryza sativa L) used to identify QTLs for root penetration ability. Theor Appl Genet 100:49–56
Price AH, Steele KA, Moore BJ, Jones RGW (2002a) Upland rice grown in soil-filled chambers and exposed to contrasting water-deficit regimes: II Mapping QTL for root morphology and distribution. Field Crops Res 76:25–43
Price AH, Cairns JE, Horton P, Jones HG, Griffiths H (2002b) Linking drought-resistance mechanisms to drought avoidance in upland rice using a QTL approach: progress and new opportunities to integrate stomatal and mesophyll responses. J Exp Bot 53:989–1004
Reyna N, Sneller CH (2001) Evaluation of marker-assisted introgression of yield QTL alleles into adapted soybean. Crop Sci 41:1317–1321
Ribaut J-M, Jiang C, Hoisington D (2002) Simulation experiments on efficiencies of gene introgression by backcrossing. Crop Sci 42:557–565
Schmierer DA, Kandemir N, Kudrna DA, Jones BL, Ullrich SE, Kleinhofs A (2004) Molecular marker-assisted selection for enhanced yield in malting barley. Mol Breed 14:463–473
Servin B, Martin OC, Mezard M, Hospital F (2004) Toward a theory of marker-assisted gene pyramiding. Genetics 168:513–523
Shen L, Courtois B, McNally KL, Robin S, Li Z (2001) Evaluation of near-isogenic lines of rice introgressed with QTLs for root depth through marker-aided selection. Theor Appl Genet 103:427–437
Steele KA, Edwards G, Zhu J, Witcombe JR (2004) Marker-evaluated selection in rice: shifts in allele frequency among bulks selected in contrasting agricultural environments identify genomic regions of importance to rice adaptation and breeding. Theor Appl Genet 109:1247–1260
Venuprasad R, Shashidhar HE, Hittalmani S, Hemamalini GS (2002) Tagging quantitative trait loci associated with grain yield and root morphological traits in rice (Oryza sativa L) under contrasting moisture regimes. Euphytica 128:293–300
Witcombe JR, Petre R, Jones S, Joshi A (1999) Farmer Participatory crop improvement IV The spread and impact of a rice variety identified by participatory varietal selection. Expl Agric 35:471–487
Yadav R, Courtois B, Huang N, McLaren G (1997) Mapping genes controlling root morphology and root distribution on a double-haploid population of rice. Theor Appl Genet 94:619–632
Yan JQ, Zhu J, He CX, Benmoussa M, Wu P (1998) Quantitative trait loci analysis for the developmental behavior of tiller number in rice (Oryza sativa L). Theor Appl Genet 97:267–274
Yoshida S, Hasegawa S (1982) The rice root system: its development and function. In: Drought resistance in crops with emphasis on rice, International Rice Research Institute, Los Banos, Laguna, pp 97–114
Zhang J, Chandra Babu R, Pantuwan G, Kamoshita A, Blum A, Wade L, Sarkarung S, O’Toole JC, Nguyen HT (1999) Molecular dissection of drought tolerance in rice: from physiomorphological traits to field performance. In: Ito O, O’Toole J, Hardy B (eds) Genetic improvement of rice for water-limited environments. Proceedings of the workshop on genetic improvement of rice for water-limited environments, 1–3 December 1998, Los Banos,. Los Banos Philippines:International Rice Research Institute, pp 307–317
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Brigitte Courtois and Modesto Amante for making the first cross and backcross at IRRI, Philippines. We thank Beverley Moore, Gwen Edwards, Elly Rodriguez and Julian Bridges for technical support on molecular and greenhouse experiments in Bangor, and James M. Gibbons for statistical advice. This document is an output from a project (Plant Sciences Research Programme R7434 & R8200) funded by the UK Department for International Development (DFID) and administered by CAZS Natural Resources for the benefit of developing countries. The views expressed are not necessarily those of DFID.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Qifa Zhang
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steele, K.A., Price, A.H., Shashidhar, H.E. et al. Marker-assisted selection to introgress rice QTLs controlling root traits into an Indian upland rice variety. Theor Appl Genet 112, 208–221 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0110-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0110-4