Abstract
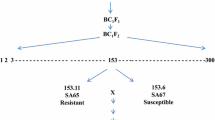
Rye has one of the most efficient groups of genes for aluminum tolerance (Alt) among cultivated species of Triticeae. This tolerance is controlled by, at least, three independent and dominant loci (Alt1, Alt2, and Alt3) located on chromosome arms 6RS, 3RS, and 4RL, respectively. The segregation of Alt genes and several random amplified polymorphic DNA (RAPD), Secale cereale inter-microsatellite (SCIM), and Secale cereale microsatellite (SCM) markers in three F2 between a tolerant cultivar (Ailés) and a non-tolerant inbred line (Riodeva) were studied. The segregation ratio obtained for aluminum tolerance in the three F2 populations analyzed was 3:1 (tolerant:non-tolerant), indicating that tolerance is controlled by one dominant locus. SCIM811 1376 was linked to an Alt gene in the three F2 populations studied, and three different SCIMs and one RAPD (SCIM811 1376 , SCIM812 626 , SCIM812 1138 , and OPQ4 725 ) were linked to the Alt gene in two F2 populations. This result indicated that the same Alt gene was segregating in the three crosses. SCIM819 1434 and OPQ4 578 linked to the tolerance gene in one F2 population were located using wheat–rye ditelosomic addition lines on the 7RS chromosome arm. The Alt locus is mapped between SCIM819 1434 and the OPQ4 578 markers. Two microsatellite loci (SCM-40 and SCM-86), previously located on chromosome 7R, were also linked to the Alt gene. Therefore, the Alt gene segregating in these F2 populations is new and probably could be orthologous to the Alt genes located on wheat chromosome arm 4DL, on barley chromosome arm 4HL, on rye chromosome arm 4RL, and rice chromosome 3. This new Alt gene located on rye chromosome arm 7RS was named Alt4. A map of rye chromosome 7R with the Alt4 gene, 16 SCIM and RAPD, markers and two SCM markers was obtained.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aniol A (1983) Aluminum uptake by roots of two winter wheat varieties of different tolerance to aluminum. Biochem Physiol Pflanzen 178:11–20
Aniol A (1984) Introduction of aluminum tolerance into aluminum sensitive wheat cultivars. Z Pflanzenzuecht 93(4):331–339
Aniol A (1990) Genetic of tolerance to aluminum in wheat (Triticum aestivum L. Thell). Plant Soil 123:223–227
Aniol A (1991) Genetics of acid tolerant plants. In: Wright RJ (ed) Plant soil interactions at low pH. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 1007–1017
Aniol A (2004) Chromosomal location of aluminum tolerance genes in rye. Plant Breed 123:132–136
Aniol A, Gustafson JP (1984) Chromosome location of genes controlling aluminum tolerance in wheat, rye and triticale. Can J Genet Cytol 26:701–705
Aniol A, Madej L (1996) Genetic variation for aluminum tolerance in rye. Vortr Pflanzen 35:201–211
Basu U, McDonald JL, Archambault DJ, Good AG, Briggs KG, Aung T, Taylor GJ (1997) Genetic and physiological analysis of double-haploid, aluminum, resistant lines of wheat provide evidence for the involvement of a 23 kD, root exudates polypeptide in mediating resistance. Plant Soil 196:283–288
Campbell LG, Lafever HN (1981) Heritability of aluminum tolerance in wheat. Cereal Res Commun 9:281–287
Delhaize E, Ryan PR, Randall PJ (1993) Aluminum tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) II. Aluminum-stimulates excretion of malic acid from root apices. Plant Physiol 103:695–702
Devos KM, Atkinson MD, Chinoy CN, Francis HA, Harcourt RL, Koebner RMD, Liu CJ, Masojc P, Xie DX, Gale MD (1993) Chromosomal rearrangements in the rye genome relative to that of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 85:673–680
Fisher JA, Scott BJ (1987) Response to selection for aluminum tolerance. In: Searle PGE, Davey BG (eds) Priorities in soil/plant relations research for plant production. School of Crop Sciences, University of Sydney, Australia, pp 135–137
Foy CD (1983) The physiology of plant adaptation to mineral stress. Iowa State J Res 57:355–392
Foy CD (1988) Plant adaptation to acid, aluminum-toxic soils. Common Soil Sci Plant Anal 19:959–987
Gale MD, Devos KM (1998) Comparative genetics in the grasses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1971–1974
Gallego FJ (1997) Genética de la tolerancia al aluminio en centeno (Secale cereale L.). PhD Thesis, Universidad Complutense Madrid, pp 1–123
Gallego FJ, Benito C (1997) Genetic control of aluminum tolerance in rye (Secale cereale L.). Theor Appl Genet 95:393–399
Gallego FJ, Calles B, Benito C (1998) Molecular markers linked to the aluminum tolerance gene Alt1 in rye (Secale cereale L.). Theor Appl Genet 97:1104–1109
Haug A (1983) Molecular aspects of aluminum toxicity. CRC Crit Rev Plant Sci 1:345–373
Hede AR, Skovmand B, Lopez-Cesati J (2001) Acid soils and aluminum toxicity. In: Reynolds MP, Ortiz-Monasterio JI, MacNab A (eds) Application of physiology in wheat breeding. DF: CYMMYT, Mexico, pp 172–182
Kerridge PC, Kronstad WE (1968) Evidence of genetic resistance to aluminum toxicity in wheat (Triticum aestivum Vill., Host.). Agron J 60:710–711
Kinraide TB (1991) Identity of the rhizotoxic aluminum species. Plant Soil 134:167–178
Kochian LV (1995) Cellular mechanism on aluminum toxicity and resistance in plants. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 46:237–260
Korzun V, Malyshev AV, Voylokov AV, Börner A (2001) A genetic map of rye (Secale cereale L.) combining RFLP, isozyme, protein microsatellite and gene loci. Theor Appl Genet 102:709–717
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Larkin PJ (1987) Calmodulin levels are not responsible for aluminum tolerance in wheat. Aust J Plant Physiol 14:377–385
Little R (1988) Plant soil interactions at low pH. In: Problem solving–the genetic approach. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 19:1239–1257
Ma JF, Taketa S, Yang ZM (2000) Aluminum tolerance genes on the short arm of chromosome 3R are linked to organic acid release in Triticale. Plant Physiol 122:687–694
Ma JF, Ryan PR, Delhaize E (2001a) Aluminum tolerance in plants and the complexing role of organic acids. Trends Plant Sci 6:273–278
Ma X-F, Wanous MK, Houchins K, Rodríguez-Milla MA, Goicoechea PG, Wang Z, Xie M, Gustafson JP (2001b) Molecular linkage mapping in rye (Secale cereale L.). Theor Appl Genet 102:517–523
Magalhaes JV, Garvin DF, Wang Y, Sorrells ME, Klein PE, Schaffert RE, Li L, Kochian LV (2004). Comparative mapping of a major aluminum tolerance gene in sorghum and other species in the Poaceae. Genetics 167:1905–1914
Manyowa NM, Miller TE, Forster BT (1988) Alien species as sources for aluminum tolerance genes for wheat, Triticum aestivum. Proceedings of the seventh international wheat genetics symposium, pp 851–857
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kessell RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease-resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Miftahudin, Scoles GJ, Gustafson JP (2002) AFLP markers tightly linked to the aluminum-tolerance gene Alt3 in rye (Secale cereale L.). Theor Appl Genet 104:626–631
Miftahudin, Scoles GJ, Gustafson JP (2004) Development of PCR-based codominant markers flanking the Alt3 gene in rye. Genome 47:231–248
Miftahudin, Chikmawati T, Ross K, Scoles GJ, Gustafson JP (2005) Targeting the aluminum tolerance gene Alt3 region in rye, using rice/rye micro-colinearity. Theor Appl Genet 110:906–913
Minella E, Sorrells ME (1992) Aluminum tolerance in barley: genetic relationships among genotypes of diverse origin. Crop Sci 32:593–598
Mugwira LM, Elgawhary SM, Patel SU (1978) Aluminum tolerance in triticale, wheat and rye as measured by root growth characteristics and aluminum concentrations. Plant Soil 50:681–690
Naranjo T, Fernández.-Rueda P (1991) Homoeology of rye chromosome arms to wheat. Theor Appl Genet 82:577–586
Naranjo T, Fernandez-Rueda P, Maestra B (1997) Chromosome rearrangements and homoeologous pairing: implications for the introgression of alien genes into wheat. In: Lelley T (ed) Current topics in plant cytogenetics related to plant improvement. WUV-Universitätsverlag, Austria, pp 198–205
Nguyen BD, Brar BS, Bui BC, Nguyen VT, Pham LN, Nguyen HT (2003) Identification and mapping of the QTL for aluminum tolerance introgressed from the new source, Oryza rufipogon griff., into indica rice (Oryza sativa L.). Thero Appl Genet 106:583–593
Raman H, Moroni JS, Sato K, Read BJ, Scott BJ (2002) Identification of AFLP and microsatellite markers linked with an aluminum tolerance gene in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 105:458–464
Rao MI, Zeigler RA, Vera R, Sarkarung S (1993) Selection and breeding for acid soil tolerance in crops. Bioscience 43:454–465
Reid DA, Fleming AL, Foy CD (1971) A method for determining aluminum response of barley in nutrient solution in comparison to response in Al-toxic soil. Agron J 63:600–603
Riede CR, Anderson JA (1996) Linkage of RFLP markers to an aluminum tolerance gene in wheat. Crop Sci 36:905–909
Rodríguez-Milla MA, Gustafson JP (2001) Genetic and physical characterization of chromosome 4DL in wheat. Genome 44:883–892
Rognli OA, Devos KM, Chinoy CN, Harcourt RL, Atkinson MD, Gale MD (1992) RFLP mapping of rye chromosome 7R reveals a highly translocated chromosome relative to wheat. Genome 35:1026–1031
Saal B, Wricke G (1999) Development of simple sequence repeat markers in rye (Secale cereale L.). Genome 42:964–972
Sasaki T, Yamamoto Y, Ezaki B, Katsuhara M, Ahn SJ, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Matsumoto H (2004) A wheat gene encoding an aluminum-activated malate transporter. Plant J 37:645–653
Slootmaker ALJ (1974) Tolerance to high soil acidity in wheat related species, rye and triticale. Euphytica 23:505–513
Somers DJ, Gustafson JP (1995) The expression of aluminum stress induced polypeptides in a population segregating for aluminum tolerance in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Genome 38:1213–1220
Stølen O, Anderson S (1978) Inheritance of tolerance to low soil pH in barley. Hereditas 88:101–105
Tang Y, Sorrells ME, Kochian LV, Garvin DF (2000) Identification of RFLP markers linked to barley aluminum tolerance gene Alp. Crop Sci 40:778–782
Van Wambeke A (1976) Formation, distribution and consequences of acid soils in agricultural development. In: Wright MJ, Ferrari SA (eds) Proceedings of workshop on Plant adaptation to mineral stress in problem soils. Special Publication of the Cornell University Agricultural Experimental Station, Ithaca, pp 15–24
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Zietkiewicz E, Rafalski A, Labuda D (1994) Genome fingerprinting by simple sequence repeat (SSR)-anchored polymerase chain reaction amplification. Genomics 20:176–183
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the research grants BOS 2000-0561 and AGL 200306470 from the Ministry of Education and Science of Spain (DGICYT) and Praxis XXII/15874/98 from the Ministry of Science and Technology (MCT) of Portugal.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Möllers
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Matos, M., Camacho, M.V., Pérez-Flores, V. et al. A new aluminum tolerance gene located on rye chromosome arm 7RS. Theor Appl Genet 111, 360–369 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-2029-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-2029-1