Abstract
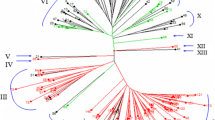
The genetic similarity between 150 accessions, representing 14 diploidand polyploid species of the Triticeae tribe, was investigated following the UPGMA clustering method. Seventy-three common wheat EST-derived SSR markers (EST-SSRs) that were demonstrated to be transferable across several wheat-related species were used. When diploid species only are concerned, all the accessions bearing the same genome were clustered together without ambiguity while the separation between the different sub-species of tetraploid as well as hexaploid wheats was less clear. Dendrograms reconstructed based on data of 16 EST-SSRs mapped on the A genome confirmed that Triticum aestivum and Triticum durum had closer relationships with Triticum urartu than with Triticum monococcum and Triticum boeoticum, supporting the evidence that T. urartu is the A-genome ancestor of polyploid wheats. Similarly, another tree reconstructed based on data of ten EST-SSRs mapped on the B genome showed that Aegilops speltoides had the closest relationship with T. aestivum and T. durum, suggesting that it was the main contributor of the B genome of polyploid wheats. All these results were expected and demonstrate thus that EST-SSR markers are powerful enough for phylogenetic analysis among the Triticeae tribe.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appels R, Reddy P, McIntyre CL, Moran LB, Frankel OH, Clarke BC (1989) The molecular-cytogenetic analysis of grasses and its application to studying relationships among species of the Triticeae. Genome 31:122–133
Bandopadhyay R, Sharma S, Rustgi S, Singh R, Kumar A, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2004) DNA polymorphism among 18 species of Triticum–Aegilops complex using wheat EST-SSRs. Plant Sci 166:349–356
Ben Amer IM, Börner A, Röder MS (2001) Detection of genetic diversity in Libyan wheat genotypes using wheat microsatellite markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 48:579–585
Brown GR, Kadel EE III, Bassoni DL, Kiehne KL, Temesgen B, van Buijtenen JP, Sewell MM, Marshall KA, Neale DB (2001) Anchor reference loci in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.) for integrating pine genomics. Genetics 159:799–809
Chen K, Gray JC, Wildman SG (1975) Fraction I protein and the origin of polyploid wheats. Science 190:1304–1305
Donini P, Law JR, Koebner RMD, Reeves JC, Cooke RJ (2000) Temporal trends in the diversity of UK wheat. Theor Appl Genet 100:912–917
Dvorak J, di Terlizzi P, Zhang HB, Resta P (1993) The evolution of polyploid wheats: identification of the A genome donor species. Genome 36:21–31
von Eig A (1929) Monographisch-Kretische Ubersicht der Gattung Aegilops. Repertorium specierum novarum regni vegetabilis 55:24–28
Eujayl I, Sorrells ME, Baum M, Wolters P, Powell W (2001) Assessment of genotypic variation among cultivated durum wheat based on EST-SSRs and genomic SSRs. Euphytica 119:39–43
Eujayl I, Sorrells ME, Baum M, Wolters P, Powell W (2002) Isolation of EST-derived microsatellite markers for genotyping the A and B genomes of wheat. Theor Appl Genet 104:399–407
Feldman M (1978) New evidence on the origin of the B genome of wheat. In: Ramanujam S (ed) Proceedings of the 5th international wheat genetics symposium, New Delhi, India, pp. 120–132
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence-limits on phylogenies—an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (Phylogeny Inference Package) version 3.5c. Distributed by the author. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle
Gupta PK, Varshney RK (1999) Molecular markers for genetic fidelity during micropropagation and germplasm conservation. Curr Sci 77:1308–1310
Hassan MD, Gustafson JP (1996) Molecular evidence for Triticum speltoides as a B-genome progenitor of wheat (Triticum aestivum). Genome 39:543–548
Huang SX, Sirikhachornkit A, Su XJ, Faris J, Gill B, Haselkorn R, Gornicki P (2002) Genes encoding plastid acetyl-CoA carboxylase and 3-phosphoglycerate kinase of the Triticum/Aegilops complex and the evolutionary history of polyploid wheat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99(12):8133–8138
Jaaska V (1980) Electrophoretic survey of seedling esterases in wheats in relation to their phylogeny. Theor Appl Genet 56:273–283
Jaccard P (1908) Nouvelles recherches sur la distribution florale. Bull Soc Vaud Sci Nat 4:223–270
Leisova L, Ovesna J (2001) The use of microsatellite analysis for the identification of wheat varieties. Czech J Genet Plant Breed 37:29–33
Lelley T, Stachel M, Grausgruber H, Vollmann J (2000) Analysis of relationships between Aegilops tauschii and the D genome of wheat utilizing microsatellites. Genome 43:661–668
Lilienfeld FA, Kihara H (1934) Genomanalyse bei Triticum und Aegilops von H. Kihara. V. Triticum timopheevi Zhuk. Cytologia 6:87–122
Maestra B, Naranjo T (1998) Homoeologous relationships of Aegilops speltoides chromosomes to bread wheat. Theor Appl Genet 97:181–186
Manifesto MM, Schlatter AR, Hopp HE, Suarez EY, Dubcovsky J (2001) Quantitative evaluation of genetic diversity in wheat germplasm using molecular markers. Crop Sci 41:682–690
McFadden ES, Sears ER (1946) The origin of Triticum spelta and its free-threshing hexaploid relatives. J Hered 37:81–89
McIntyre CL (1988) Variation at isozyme loci in Triticeae. Plant Syst Evol 160:123–142
Miller TE (1990) Systematics and evolution. In: Lupton FGH (ed) Wheat breeding. Chapman and Hall Ltd, London, pp 1–30
Monte JV, McIntyre CL, Gustafson JP (1993) Analysis of phylogenetic relationship in the Triticeae tribe using RFLP. Theor Appl Genet 83:649–655
Natarajan AT, Sharma NP (1974) Chromosome banding patterns and the origin of the B genome in wheat. Genet Res 24:103–108
Nicot N, Chiquet V, Gandon B, Amilhat L, Legeai F, Leroy F, Bernard M, Sourdille P (2004) Study of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers from wheat expressed sequence tags (ESTs). Theor Appl Genet 109:800–805
Ogihara Y, Tsunewaki K (1988) Diversity and evolution of chloroplast DNA in Triticum and Aegilops as revealed by restriction fragment analysis. Theor Appl Genet 76:321–332
Plaschke J, Ganal M, Röder M (1995) Detection of genetic diversity in closely related bread wheat using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 91:1001–1007
Prasad M, Varshney RK, Roy JK, Balyan HS, Gupta PK (2000) The use of microsatellites for detecting DNA polymorphism, genotype identification and genetic diversity in wheat. Theor Appl Genet 100:584–592
Rees H, Walters MR (1965) Nuclear DNA and the evolution of the wheat. Heredity 20:73–82
Reif JC, Melchinger AE, Frisch M (2005) Genetical and mathematical properties of similarity and dissimilarity coefficients applied in plant breeding and seed bank management. Crop Sci 2005 45:1–7
Riley R, Unrau J, Chapman V (1958) Evidence on the origin of the B genome of wheat. J Hered 49:91–98
Röder MS, Wendehake K, Korzun V, Bredemeijer G, Laborie D, Bertrand L, Isaac P, Rendell S, Jackson J, Cooke R, Vosman B, Ganal M (2002) Construction and analysis of a microsatellite-based database of European wheat varieties. Theor Appl Genet 106:67–73
Roussel V, Leisova L, Exbrayat F, Stehno Z, Balfourier F (2005) SSR allelic diversity changes in 480 European bread wheat varieties released from 1840 to 2000. Theor Appl Genet 111:162–170
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic tree. Mol Biol Evol 4(4):406–425
Salamini F, Özkan H, Brandolini A, Schäfer-Pregl R, Martin W (2002) Genetics and geography of wild cereal domestication in the Near East. Nat Rev Genet 3:429–441
Sarkar P, Stebbins GL (1956) Morphological evidence concerning the origin of the B genome of wheat. Am J Bot 43:297–304
Sasanuma T, Miyashita NT, Tsunewaki K (1996) Wheat phylogeny determined by RFLP analysis of nuclear DNA. 3. Intra- and interspecific variations of five Aegilops Sitopsis species. Theor Appl Genet 92:928–934
Sasanuma T, Chabane K, Endo TR, Valkoun J (2004) Characterization of genetic variation in and phylogenetic relationships among diploid Aegilops species by AFLP: incongruity of chloroplast and nuclear data. Theor Appl Genet 108:612–618
Sax K (1922) Sterility in wheat hybrids. II. Chromosome behavior in partially sterile hybrids. Genetics 7:513–552
Slatkin M (1995) A measure of population subdivision based on microsatellite allele frequencies. Genetics 139:457–462
Sourdille P, Tavaud M, Charmet G, Bernard M (2001) Transferability of wheat microsatellites to diploid Triticeae species carrying the A, B and D genomes. Theor Appl Genet 103:346–352
Tixier MH, Sourdille P, Charmet G, Gay G, Jaby C, Cadalen T, Bernard S, Nicolas P, Bernard M (1998) Detection of QTLs for crossability in wheat using a doubled-haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 97:1076–1082
Xu Y, Ma RC, Xie H, Liu JT, Cao MQ (2004) Development of SSR markers for the phylogenetic analysis of almond trees from China and the Mediterranean region. Genome 47(6):1091–1104
Zhang W, Qu LJ, Gu H, Gao W, Liu M, Chen J, Chen Z (2002) Studies on the origin and evolution of tetraploid wheats based on the internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Theor Appl Genet 104:1099–1106
Zhang LY, Bernard M, Leroy P, Feuillet C, Sourdille P (2005) High transferability of bread wheat EST-derived SSRs to other cereals. Theor Appl Genet 111:677–687
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully thank G. Gay and A. Loussert for growing the plants and J. David for providing with T. turgidum sub-species. G. Boutet and C. Pont are also greatly acknowledged for their help in managing the robotics of the genotyping platform. This work was funded by the China Scholarship Council (CSC). All these experiments comply with the current laws of France.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by M. Sorrells
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, L.Y., Ravel, C., Bernard, M. et al. Transferable bread wheat EST-SSRs can be useful for phylogenetic studies among the Triticeae species. Theor Appl Genet 113, 407–418 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0304-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0304-4