Abstract
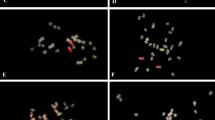
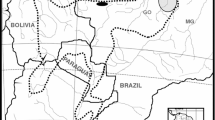
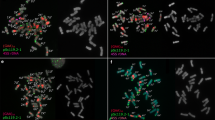
Section Arachis of the homonymous genus includes 29 wild diploid species and two allotetraploids (A. monticola and the domesticated peanut, A. hypogaea L.). Although, three different genomes (A, B and D) have been proposed for diploid species with x = 10, they are still not well characterized. Moreover, neither the relationships among species within each genome group nor between diploids and tetraploids (AABB) are completely resolved. To tackle these issues, particularly within the A genome, in this study the rRNA genes (5S and 18S–26S) and heterochromatic bands were physically mapped using fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) in 13 species of Arachis. These molecular cytogenetic landmarks have allowed individual identification of a set of chromosomes and were used to construct detailed FISH-based karyotypes for each species. The bulk of the chromosome markers mapped revealed that, although the A genome species have a common karyotype structure, the species can be arranged in three groups (La Plata River Basin, Chiquitano, and Pantanal) on the basis of the variability observed in the heterochromatin and 18S–26S rRNA loci. Notably, these groups are consistent with the geographical co-distribution of the species. This coincidence is discussed on the basis of the particular reproductive traits of the species such as autogamy and geocarpy. Combined with geographic distribution of the taxa, the cytogenetic data provide evidence that A. duranensis is the most probable A genome ancestor of tetraploid species. It is expected that the groups of diploid species established, and their relation with the cultigen, may aid to rationally select wild species with agronomic traits desirable for peanut breeding programs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ansari HA, Ellison NW, Williams WM (2008) Molecular and cytogenetic evidence for an allotetraploid origin of Trifolium dubium (Leguminosae). Chromosoma 117:159–167
Appels R, Moran LB, Gustafson JP (1986) The structure of DNA from rye (Secale cereale) NOR R1 locus and its behaviour in wheat backgrounds. Can J Genet Cytol 28:673–685
Burow MD, Simpson CE, Starr JL, Paterson A (2001) Transmission genetics of chromatin from a synthetic amphidiploid to cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.): Broadening the gene pool of a monophyletic polyploid species. Genetics 159:823–837
Cerbah M, Souza-Chies T, Jubier MF, Lejeune B, Siljak-Yakovlev S (1998) Molecular phylogeny of the genus Hypochaeris using internal transcribed spacers of nuclear rDNA: inference for chromosomal evolution. Mol Biol Evol 15(3):345–354
Chung MC, Lee YI, Cheng YY, Chou YJ, Lu CF (2008) Chromosomal polymorphism of ribosomal genes in the genus Oryza. Theor Appl Genet 116:745–753
Custodio AR, Peñaloza APS, Valls JFM (2005) Further cytogenetic information on Arachis stenosperma (Leguminosae). Cytologia 70:331–335
Dwivedi SI, Bertioli DJ, Crouch JH, Valls JFM, Upadhyaya HD, Favero A, Moretzsohn M, Paterson AH (2007) Peanut genetics and genomics: toward marker-assisted genetic enhancement in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L). In: Kole C (ed) Oilseeds series: genome mapping, molecular breeding in plants oilseeds series: genome mapping and molecular breeding in plants, vol 2. Springer, Berlin, pp 115–151
Fávero AP, Simpson CE, Valls JFM, Yuksel B (2006) Study of the evolution of cultivated peanut through crossability studies among Arachis ipaensis, A. duranensis, and A. hypogaea. Crop Sci 46:1546–1552
Fernández A, Krapovickas A (1994) Cromosomas y evolución en Arachis (Leguminosae). Bonplandia 8:187–220
Gimenes MA, Lopes CR, Galgaro ML, Valls JFM, Kochert G (2002) RFLP analysis of genetic variation in species of section Arachis, genus Arachis (Leguminosae). Euphytica 123:421–429
Gregory WC, Gregory MP (1976) Groundnut. Arachis hypogaea (Leguminosae-Papilionatae). In: Simmonds NW (ed) Evolution of crop plants. Longman Group Ltd, London, pp 151–154
Gregory MP, Gregory WC (1979) Exotic germoplasm of Arachis L. interspecific hybrids. J Hered 70:185–193
Guerra M (2000) Patterns of heterochromatin distribution in plant chromosomes. Genet Mol Biol 23:1029–1041
Hizume M, Shibata F, Matsusaki Y, Garajova Z (2002) Chromosome identification and comparative karyotypic analyses of four Pinus species. Theor Appl Genet 105:491–497
Husted L (1933) Cytological studies on the peanut, Arachis I. Chromosome number and morphology. Cytologia 5:109–117
Isleib TG, Holbrook CC, Gorbet DW (2001) Use of Arachis spp. plant introductions in peanut cultivar development. Peanut Sci 28:96–113
Jiang J, Gill BS (1994) New 18S–26S ribosomal gene loci: chromosomal landmarks for the evolution of polyploid wheats. Chromosoma 103:179–185
Kochert G, Halward T, Branch WD, Simpson CE (1991) RFLP variability in peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) cultivars and wild species. Theor Appl Genet 81:565–570
Krapovickas A, Gregory WC (1994) Taxonomía del género Arachis (Leguminosae). Bonplandia 8:1–186
Krapovickas A, Rigoni VA (1951) Estudios citológicos en el genero Arachis. Rev Invest Agric 5:289–294
Lavia GI (1996) Estudios cromosómicos en Arachis (Leguminosae). Bonplandia 9:111–120
Lavia GI (1998) Karyotypes of Arachis palustris and A. praecox (section Arachis), two species with basic chromosome number x = 9. Cytologia 63:177–181
Lavia GI (2000) Chromosome studies of wild Arachis (Leguminosae). Caryologia 53:177–181
Lavia GI, Fernández A, Simpson CE, Seijo G (2001) Meiotic analysis in wild diploid Arachis species. Cytologia 66:293–298
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg AA (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52:201–220
Li X, Guo R, Pedersen C, Hayman D, Langridge P (1997) Physical localization of rRNA genes by two-colour fluorescent in-situ hybridization and sequence analysis of the 5S rRNA gene in Phalaris coerulescens. Hereditas 126:289–294
Lim KY, Matyasek R, Lichtenstein CP, Leitch AR (2000) Molecular cytogenetic analyses and phylogenetic studies in the Nicotiana section Tomentosae. Chromosoma 109:245–258
Liu ZL, Zhang D, Hong DY, Wang XR (2003) Chromosomal localization of 5S and 18S-5.8S-25S ribosomal DNA sites in five Asian pines using fluorescence in situ hybridization. Theor Appl Genet 106:198–204
Martins C, Galetti PM Jr (2001) Two 5S rDNA arrays in Neotropical fish species: is it a general rule for fishes? Genetica 111:439–446
Milla SR, Isleib TG, Stalker HT (2005) Taxonomic relationships among Arachis sect. Arachis species as revealed by AFLP markers. Genome 48:1–11
Moretzsohn MC, Hopkins MS, Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Valls JFM, Ferreira ME (2004) Genetic diversity of peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) and its wild relatives based on the analysis of hypervariable regions of the genome. BMC Plant Biol 4:11
Moscone EA, Matzke MA, Matzke AJM (1996) The use of combined FISH/GISH in conjunction with DAPI counterstaining to identify chromosomes containing transgene inserts in amphidiploid tobacco. Chromosoma 105:231–236
Moscone EA, Klein F, Lambrou M, Fuchs J, Schweizer D (1999) Quantitative karyotyping and dual-color FISH mapping of 5S and 18S–26S rDNA probes in the cultivated Phaseolus species (Leguminosae). Genome 42:1224–1233
Murata M, Heslop-Harrison J-S, Motoyoshi F (1997) Physical mapping of the 5S ribosomal RNA genes in Arabidopsis thaliana by multi-color fluorescence in situ hybridization with cosmid clones. Plant J 12:31–37
Nakamura R, Kitamura S, Inoue M, Ohmido N, Fukui K (2001) Karyotype analysis of Nicotiana kawakamii Y. Ohashi using DAPI banding and rDNA FISH. Theor Appl Genet 102:810–814
Peñaloza A, Valls JFM (2005) Chromosome number and satellited chromosome morphology of eleven species of Arachis (Leguminosae). Bonplandia 14:65–72
Pires JC, Lim KY, Kovarik A, Matyasek R, Boyd A, Leitch AR, Leitch IJ, Bennett MD, Soltis PS, Soltis DE (2004) Molecular cytogenetic analysis of recently evolved Tragopogon (Asteraceae) allopolyploids reveal a karyotype that is additive of the diploid progenitors. Am J Bot 91:1022–1035
Pontes O, Neves N, Silva M, Lewis MS, Madlung A, Comai L, Viegas W, Pikaard CS (2004) Chromosomal locus rearrangements are a rapid response to formation of the allotetraploid Arabidopsis suecica genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:18240–18245
Popolizio E (1982) Geomorphology of the Argentine Northeast. Water Int 7:162–177
Raina SN, Mukai Y (1999) Detection of a variable number of 18S-5.8S-26S and 5S ribosomal DNA loci by fluorescent in situ hybridization in diploid and tetraploid Arachis species. Genome 42:52–59
Raina SN, Mukai Y, Kawaguchi K, Goel S, Jain A (2001a) Physical mapping of 18S-5.8S-26S and 5S ribosomal RNA gene families in three important vetches (Vicia species) and their allied taxa constituting three species complexes. Theor Appl Genet 103:839–845
Raina SN, Rani V, Kojima T, Ogihara Y, Singh KP, Devarumath RM (2001b) RAPD and ISSR fingerprints as useful genetic markers for analysis of genetic diversity, varietal identification, and phylogenetic relationships in peanut (Arachis hypogaea) cultivars and wild species. Genome 44:763–772
Robledo G, Seijo JG (2008) Characterization of Arachis D genome by FISH chromosome markers and total genome DNA hybridization. Genet Mol Biol 31:717–724
Rodríguez V, Seijo JG, Lavia GI, Fernández A, Simpson CE (2004) Meiotic behaviour in wild diploid Arachis (Leguminosae) species. Cytologia 69:209–214
Schubert I, Wobus U (1985) In situ hybridization confirms jumping nucleolus organizing regions in Allium. Chromosoma 92:143–148
Schwarzacher T, Ambros P, Schweizer D (1980) Application of Giemsa banding to orchid karyotype analysis. Plant Syst Evol 134:293–297
Schweizer D, Loidl J (1987) A model for heterochromatin dispersion and the evolution of C-band patterns. Chromosomes Today 9:61–74
Seijo JG, Lavia GI, Fernández A, Krapovickas A, Ducasse D, Moscone EA (2004) Physical mapping of 5S and 18S–25S rRNA genes evidences that Arachis duranensis and A. ipaensis are the wild diploid species involved in the origin of A. hypogaea (Leguminosae). Am J Bot 91:1294–1303
Seijo JG, Lavia GI, Fernández A, Krapovickas A, Ducasse DA, Bertioli DJ, Moscone EA (2007) Genomic relationships between the cultivated peanut (Arachis hypogaea—Leguminosae) and its close relatives revealed by double GISH. Am J Bot 94:1963–1971
Simpson CE (2001) Use of wild Arachis species/introgression of genes into A. hypogaea L. Peanut Sci 28:114–116
Singh AK (1986) Utilization of wild relatives in the genetic improvement of Arachis hypogaea L. Part 8. Synthetic amphidiploids and their importance in interspecific breeding. Theor Appl Genet 72:433–439
Singh AK (1988) Putative genome donors of Arachis hypogaea (Fabaceae), evidence from crosses with synthetic amphidiploid. Plant Syst Evol 160:143–151
Singh AK, Moss JP (1982) Utilization of wild relatives in genetic improvement of Arachis hypogaea L. 2. Chromosome complements of species of section Arachis. Theor Appl Genet 61:305–314
Singh AK, Moss JP (1984) Utilization of wild relatives in genetic improvement of Arachis hypogaea L. 5. Genome analysis in section Arachis and its implications in gene transfer. Theor Appl Genet 68:355–364
Singh AK, Smartt J (1998) The genome donors of the groundnut/peanut (Arachis hypogaea L.) revisited. Genet Resour Crop Evol 45:113–118
Smartt J, Gregory WC (1967) Interspecific cross compatibility relationships between the cultivated peanut Arachis hypogaea L and other species of the genus Arachis. Oléaginuex 22:455–459
Smartt J, Gregory WC, Gregory MP (1978) The genomes of Arachis hypogaea. 1. Cytogenetic studies of putative genome donors. Euphytica 27:665–675
Spichiger R, Calenge C, Bise B (2004) Geographical zonation in the Neotropics of tree species characteristic of the ParaguayParaná Basin. J Biogeogr 31:1489–1501
Stalker HT (1991) A new species section Arachis of peanuts with D genome. Am J Bot 78:630–637
Stalker HT, Wynne JC (1979) Cytology of interspecific hybrids in section Arachis of peanuts. Peanut Sci 6:110–114
Suja JA, Gébrane-Younès J, Géraud G, Hernandez-Verdun D (1997) Relative distribution of rDNA and proteins of the RNA polymerase I transcription machinery at chromosomal NORs. Chromosoma 105:459–469
Tallury SP, Hilu KW, Milla SR, Friend SA, Alsaghir M, Stalker HT, Quandt D (2005) Genomic affinities in Arachis section Arachis (Fabaceae): molecular and cytogenetic evidence. Theor Appl Genet 111:1229–1237
Valls JFM, Simpson CE (2005) New species of Arachis from Brazil, Paraguay, and Bolivia. Bonplandia 14:35–64
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Consejo Nacional de Investigaciones Científicas y Técnicas (CONICET)PIP5807, and Agencia Nacional de Promoción Científica y Técnica, PICT 2005 Nº34458, Argentina.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Heslop-Harrison.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robledo, G., Lavia, G.I. & Seijo, G. Species relations among wild Arachis species with the A genome as revealed by FISH mapping of rDNA loci and heterochromatin detection. Theor Appl Genet 118, 1295–1307 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-0981-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-0981-x