Abstract
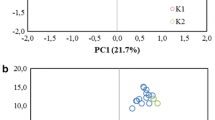
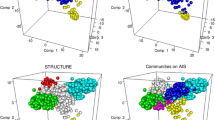
Population structure and genome-wide linkage disequilibrium (LD) were investigated in 192 Hordeum vulgare accessions providing a comprehensive coverage of past and present barley breeding in the Mediterranean basin, using 50 nuclear microsatellite and 1,130 DArT® markers. Both clustering and principal coordinate analyses clearly sub-divided the sample into five distinct groups centred on key ancestors and regions of origin of the germplasm. For given genetic distances, large variation in LD values was observed, ranging from closely linked markers completely at equilibrium to marker pairs at 50 cM separation still showing significant LD. Mean LD values across the whole population sample decayed below r 2 of 0.15 after 3.2 cM. By assaying 1,130 genome-wide DArT® markers, we demonstrated that, after accounting for population substructure, current genome coverage of 1 marker per 1.5 cM except for chromosome 4H with 1 marker per 3.62 cM is sufficient for whole genome association scans. We show, by identifying associations with powdery mildew that map in genomic regions known to have resistance loci, that associations can be detected in strongly stratified samples provided population structure is effectively controlled in the analysis. The population we describe is, therefore, shown to be a valuable resource, which can be used in basic and applied research in barley.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badr A, Muller K, Schafer-Pregl R, El Rabey H, Effgen S et al (2000) On the origin and domestication history of Barley (Hordeum vulgare). Mol Biol Evol 17:499–510
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc 57:289–300
Bowcock AM, Ruiz-Linares A, Tomfohrde J, Minch E, Kidd JR et al (1994) High resolution of human evolutionary trees with polymorphic microsatellites. Nature 368:455–457
Breseghello F, Sorrells ME (2006) Association mapping of kernel size and milling quality in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) cultivars. Genetics 172:1165–1177
Buckler ES, Gaut BS, McMullen MD (2006) Molecular and functional diversity of maize. Curr Opin Plant Biol 9:172–176
Caldwell KS, Russell J, Langridge P, Powell W (2006) Extreme population-dependent linkage disequilibrium detected in an inbreeding plant species, Hordeum vulgare. Genetics 172:557–567
Casas AM, Yahiaoui S, Ciudad F, Igartua E (2005) Distribution of MWG699 polymorphism in Spanish European barleys. Genome 48:41–45
Chelkowski J, Tyrka M, Sobkiewicz A (2003) Resistance genes in barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and their identification with molecular markers. J Appl Genet 44:291–309
Comadran J, Russell J, Eeuwijk FA, Ceccarelli S, Grando S et al (2008) Mapping adaptation of barley to droughted environments. Euphytica 161:35–45
Falush D, Stephens M, Pritchard JK (2003) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data: linked loci and correlated allele frequencies. Genetics 164:1567–1587
Felsenstein J (1997) An alternating least squares approach to inferring phylogenies from pairwise distances. Syst Biol 46:101–111
Fischbeck G (2002) Contribution of barley to agriculture: a brief overview. In: Slafer GA, Molina-Cano JS, Savin R, Araus JL, Romagosa I (eds) Barley science: recent advances from molecular biology to agronomy of yield and quality. Food Products Press, New York, pp 1–29
Flint-Garcia SA, Thornsberry JM, Buckler ES (2003) Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:357–374
Grando S, von Bothmer R, Ceccarelli S (2001) Genetic diversity of barley: use of locally adapted germplasm to enhance yield and yield stability of barley in dry areas. In: Cooper HD, Spillane C, Hodgkin T (eds) Broadening the genetic base of crop production, pp 351–372
Gupta PK, Rustgi S, Kulwal PL (2005) Linkage disequilibrium and association studies in higher plants: present status and future prospects. Plant Mol Biol 57:461–485
Heun M (1992) Mapping quantitative powdery mildew resistance of barley using a restriction fragment length polymorphism map. Genome 35:1019–1025
Kilian B, Ozkan H, Kohl J, von Haeseler A, Barale F et al (2006) Haplotype structure at seven barley genes: relevance to gene pool bottlenecks, phylogeny of ear type and site of barley domestication. Mol Genet Genom 276:230–241
Kim HS, Ward RW (2000) Patterns of RFLP-based genetic diversity in germplasm pools of common wheat with different geographical or breeding program origins. Euphytica 115:108–197
Kraakman AT, Niks RE, Van PM, den Berg P, Stam FA, Eeuwijk Van (2004) Linkage disequilibrium mapping of yield and yield stability in modern spring barley cultivars. Genetics 168:435–446
Kunzel G, Korzun L, Meister A (2000) Cytologically integrated physical restriction fragment length polymorphism maps for the barley genome based on translocation breakpoints. Genetics 154:397–412
Lin JZ, Morrell PL, Clegg MT (2002) The influence of linkage and inbreeding on patterns of nucleotide sequence diversity at duplicate alcohol dehydrogenase loci in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum). Genetics 162:2007–2015
Mackay I, Powell W (2007) Methods for linkage disequilibrium mapping in crops. Trends Plant Sci 12:57–63
Malysheva-Otto LV, Ganal MW, Roder MS (2006) Analysis of molecular diversity, population structure and linkage disequilibrium in a worldwide survey of cultivated barley germplasm (Hordeum vulgare L.). BMC Genet 24:6–7
Morrell PL, Lundy KE, Clegg MT (2003) Distinct geographic patterns of genetic diversity are maintained in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum) despite migration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10812–10817
Morrell PL, Toleno DM, Lundy KE, Clegg MT (2005) Low levels of linkage disequilibrium in wild barley (Hordeum vulgare ssp. spontaneum) despite high rates of self-fertilization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2442–2447
Park SDE (2001) Trypano tolerance in West African cattle and the population genetic effects of selection. University of Dublin, Dublin
Payne RW, Harding SA, Murray DA, Soutar DM, Baird DB et al (2006) GenStat release 9 reference manual. Part 2. Directives. VSN International, Hemel Hempstead
Piepho HP, Mohring J, Melchinger AE, Buchse A (2008) BLUP for phenotypic selection in plant breeding and variety testing. Euphytica 161:209–228
Pritchard JK, Donnelly P (2001) Case–control studies of association in structured or admixed populations. Theor Popul Biol 60:227–237
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000a) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Rosenberg NA, Donnelly P (2000b) Association mapping in structured populations. Am J Hum Genet 67:170–181
Remington DL, Thornsberry JM, Matsuoka Y, Wilson LM, Whitt SR et al (2001) Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic associations in the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11479–11484
Rostoks N, Mudie S, Cardle L, Russell J, Ramsay L et al (2005) Genome-wide SNP discovery and linkage analysis in barley based on genes responsive to abiotic stress. Mol Genet Genom 274:515–527
Rostoks N, Ramsay L, MacKenzie K, Cardle L, Bhat PR et al (2006) Recent history of artificial outcrossing facilitates whole-genome association mapping in elite inbred crop varieties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18656–18661
Russell J, Fuller J, Young G, Thomas B, Taramino G et al (1997) Discriminating between barley genotypes using microsatellite markers. Genome 40:442–450
Russell J, Ellis RP, Thomas B, Waugh R, Provan J et al (2000) A retrospective analysis of spring barley germplasm development from ‘foundation genotypes’ to currently successful cultivars. Mol Breed 6:553–568
Shtaya MJY, Marcel TC, Sillero JC, Niks RE, Rubiales D (2006) Identification of QTLs for powdery mildew and scald resistance in barley. Euphytica 151:421–429
Smith JSC, Kresovich S, Hopkins MS, Mitchell SE, Dean RE et al (2000) Genetic diversity among elite sorghum inbred lines assessed with simple sequence repeats. Crop Sci 40:226–232
Steffenson BJ, Olivera P, Roy JK, Jin Y, Smith KP et al (2007) A walk on the wild side: mining wild wheat and barley collections for rust resistance genes. Aust J Agr Res 58:532–544
Stracke S, Presterl T, Stein N, Perovic D, Ordon F et al (2006) Effects of introgression and recombination on haplotype structure and linkage disequilibrium surrounding a locus encoding Bymovirus resistance in barley. Genetics 175:805–817
Thomas WTB, Powell W, Waugh R, Chalmers KJ, Barua UM et al (1995) Detection of quantitative trait loci for agronomic, yield, grain and disease characters in spring barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). Theor Appl Genet 91:1037–1047
Waugh R, Jannink JL, Muller K, Ramsay L (2009) The emergence of whole genome association scans in barley. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:1–5
Weir BS (1979) Inferences about linkage disequilibrium. Biometrics 35:235–254
Wenzl P, Carling J, Kudrna D, Jaccoud D, Huttner E et al (2004) Diversity Arrays Technology (DArT) for whole-genome profiling of barley. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9915–9920
Wenzl P, Li H, Carling J, Zhou M, Raman H et al (2006) A high-density consensus map of barley linking DArT markers to SSR, RFLP and STS loci and agricultural traits. BMC Genom 7:206
Yahiaoui S, Igartua E, Moralejo M, Ramsay L, Molina-Cano JL et al (2008) Patterns of genetic and eco-geographical diversity in Spanish barleys. Theor Appl Genet 116:271–282
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Vroh B, Yamasaki IM et al (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208
Zhao K, Aranzana MJ, Kim S, Lister C, Shindo C et al (2007) An Arabidopsis example of association mapping in structured samples. PLoS Genet 3:e4
Acknowledgments
The above work was funded by the European Union-INCO-MED program (ICA3-CT2002-10026). SCRI received grant in aid from the Scottish Government Rural and Environment Research and Analysis Department.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by A. Kilian.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Comadran, J., Thomas, W.T.B., van Eeuwijk, F.Á. et al. Patterns of genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium in a highly structured Hordeum vulgare association-mapping population for the Mediterranean basin. Theor Appl Genet 119, 175–187 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1027-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1027-0