Abstract
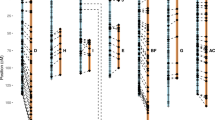
Using single-copy conserved ortholog set (COSII) and simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers, we have constructed two genetic maps for diploid Nicotiana species, N. tomentosiformis and N. acuminata, respectively. N. acuminata is phylogenetically closer to N. sylvestris than to N. tomentosiformis, the latter two of which are thought to contribute the S-genome and T-genome, respectively, to the allotetraploid tobacco (N. tabacum L., 2n = 48). A comparison of the two maps revealed a minimum of seven inversions and one translocation subsequent to the divergence of these two diploid species. Further, comparing the diploid maps with a dense tobacco map revealed that the tobacco genome experienced chromosomal rearrangements more frequently than its diploid relatives, supporting the notion of accelerated genome evolution in allotetraploids. Mapped COSII markers permitted the investigation of Nicotiana–tomato syntenic relationships. A minimum of 3 (and up to 10) inversions and 11 reciprocal translocations differentiate the tomato genome from that of the last common ancestor of N. tomentosiformis and N. acuminata. Nevertheless, the marker/gene order is well preserved in 25 conserved syntenic segments. Molecular dating based on COSII sequences suggested that tobacco was formed 1.0MYA or later. In conclusion, these COSII and SSR markers link the cultivated tobacco map to those of wild diploid Nicotiana species and tomato, thus providing a platform for cross-reference of genetic and genomic information among them as well as other solanaceous species including potato, eggplant, pepper and the closely allied coffee (Rubiaceae). Therefore they will facilitate genetic research in the genus Nicotiana.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bindler G, van der Hoeven R, Gunduz I, Plieske J, Ganal M, Rossi L, Gadani F, Donini P (2007) A microsatellite marker based linkage map of tobacco. Theor Appl Genet 114:341–349
Bogani P, Lio P, Intrieri MC, Buiatti M (1997) A physiological and molecular analysis of the genus Nicotiana. Mol Phylogenet Evol 7:62–70
Chaleff RS, Ray TB (1984) Herbicide-resistant mutants from tobacco cell-cultures. Science 223:1148–1151
Clarkson JJ, Lim KY, Kovarik A, Chase MW, Knapp S, Leitch AR (2005) Long-term genome diploidization in allopolyploid Nicotiana section Repandae (Solanaceae). New Phytol 168:241–252
Clemente T (2006) Nicotiana (Nicotiana tobaccum, Nicotiana benthamiana). Methods Mol Biol 343:143–154
Dadejova M, Lim KY, Souckova-Skalicka K, Matyasek R, Grandbastien MA, Leitch A, Kovarik A (2007) Transcription activity of rRNA genes correlates with a tendency towards intergenomic homogenization in Nicotiana allotetraploids. New Phytol 174:658–668
Daniell H, Streatfield SJ, Wycoff K (2001) Medical molecular farming: production of antibodies, biopharmaceuticals and edible vaccines in plants. Trends Plant Sci 6:219–226
Doganlar S, Frary A, Daunay MC, Lester RN, Tanksley SD (2002a) A comparative genetic linkage map of eggplant (Solanum melongena) and its implications for genome evolution in the Solanaceae. Genetics 161:1697–1711
Doganlar S, Frary A, Daunay MC, Lester RN, Tanksley SD (2002b) Conservation of gene function in the solanaceae as revealed by comparative mapping of domestication traits in eggplant. Genetics 161:1713–1726
Doyle JJ, Flagel LE, Paterson AH, Rapp RA, Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Wendel JF (2008) Evolutionary genetics of genome merger and doubling in plants. Annu Rev Genet 42:443–461
Frary A, Xu YM, Liu JP, Mitchell S, Tedeschi E, Tanksley S (2005) Development of a set of PCR-based anchor markers encompassing the tomato genome and evaluation of their usefulness for genetics and breeding experiments. Theor Appl Genet 111:291–312
Freeling M, Lyons E, Pedersen B, Alam M, Ming R, Lisch D (2008) Many or most genes in Arabidopsis transposed after the origin of the order Brassicales. Genome Res 18:1924–1937
Fulton TM, van der Hoeven R, Eannetta NT, Tanksley SD (2002) Identification, analysis, and utilization of conserved ortholog set markers for comparative genomics in higher plants. Plant Cell 14:1457–1467
Gaeta RT, Pires JC, Iniguez-Luy F, Leon E, Osborn TC (2007) Genomic changes in resynthesized Brassica napus and their effect on gene expression and phenotype. Plant Cell 19:3403–3417
Goodin MM, Zaitlin D, Naidu RA, Lommel SA (2008) Nicotiana benthamiana: its history and future as a model for plant-pathogen interactions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21:1015–1026
Julio E, Verrier JL, de Borne FD (2006) Development of SCAR markers linked to three disease resistances based on AFLP within Nicotiana tabacum L. Theor Appl Genet 112:335–346
Kenton A, Parokonny AS, Gleba YY, Bennett MD (1993) Characterization of the Nicotiana tabacum L. genome by molecular cytogenetics. Mol Gen Genet 240:159–169
Kessler A, Halitschke R (2007) Specificity and complexity: the impact of herbivore-induced plant responses on arthropod community structure. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:409–414
Kessler D, Gase K, Baldwin IT (2008) Field experiments with transformed plants reveal the sense of floral scents. Science 321:1200–1202
Knapp S, Chase MW, Clarkson JJ (2004) Nomenclatural changes and a new sectional classification in Nicotiana (Solanaceae). Taxon 53:73–82
Konieczny A, Ausubel FM (1993) A procedure for mapping Arabidopsis mutations using co-dominant ecotype-specific PCR-based markers. Plant J 4:403–410
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Kovarik A, Matyasek R, Lim KY, Skalicka K, Koukalova B, Knapp S, Chase M, Leitch AR (2004) Concerted evolution of 18-5.8-26S rDNA repeats in Nicotiana allotetraploids. Biol J Linn Soc 82:615–625
Kovarik A, Dadejova M, Lim YK, Chase MW, Clarkson JJ, Knapp S, Leitch AR (2008) Evolution of rDNA in Nicotiana allopolyploids: a potential link between rDNA homogenization and epigenetics. Ann Bot 101:815–823
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
Leitch A, Lim KY, Skalicka K, Kovarik A (2006) Nuclear cytoplasmic interaction hypothesis and the role of translocations in Nicotiana allopolyploids. In: Cigna AA, Durante M (eds) Radiation risk estimates in normal and emergency situations. Springer, The Netherlands, pp 319–326
Lewis RS, Nicholson JS (2007) Aspects of the evolution of Nicotiana tabacum L. and the status of the United States Nicotiana Germplasm Collection. Genet Resour Crop Evol 54:727–740
Lim KY, Matyasek R, Kovarik A, Leitch AR (2004) Genome evolution in allotetraploid Nicotiana. Biol J Linn Soc 82:599–606
Lin TY, Kao YY, Lin S, Lin RF, Chen CM, Huang CH, Wang CK, Lin YZ, Chen CC (2001) A genetic linkage map of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia/Nicotiana longiflora based on RFLP and RAPD markers. Theor Appl Genet 103:905–911
Livingstone KD, Lackney VK, Blauth JR, van Wijk R, Jahn MK (1999) Genome mapping in Capsicum and the evolution of genome structure in the solanaceae. Genetics 152:1183–1202
Melayah D, Lim KY, Bonnivard E, Chalhoub B, De Borne FD, Mhiri C, Leitch A, Grandbastien M (2004) Distribution of the Tnt1 retrotransposon family in the amphidiploid tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) and its wild Nicotiana relatives. Biol J Linn Soc 82:639–649
Neff MM, Neff JD, Chory J, Pepper AE (1998) dCAPS, a simple technique for the genetic analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms: experimental applications in Arabidopsis thaliana genetics. Plant J 14:387–392
Neff MM, Turk E, Kalishman M (2002) Web-based primer design for single nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Trends Genet 18:613–615
Nishi T, Tajima T, Noguchi S, Ajisaka H, Negishi H (2003) Identification of DNA markers of tobacco linked to bacterial wilt resistance. Theor Appl Genet 106:765–770
Okamuro JK, Goldberg RB (1985) Tobacco single-copy DNA is highly homologous to sequences present in the genomes of its diploid progenitors. Mol Gen Genet 198:290–298
Olmstead RG, Sweere JA, Spangler RE (1999) Phylogeny and provisional classification of the Solanaceae based on chloroplast DNA. In: Nee M, Symon DE, Lester RN, Jessop JP (eds) Solanaceae IV. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, pp 111–137
Petit M, Lim KY, Julio E, Poncet C, de Borne FD, Kovarik A, Leitch AR, Grandbastien MA, Mhiri C (2007) Differential impact of retrotransposon populations on the genome of allotetraploid tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum). Mol Gen Genom 278:1–15
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) MODELTEST: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Ren N, Timko MP (2001) AFLP analysis of genetic polymorphism and evolutionary relationships among cultivated and wild Nicotiana species. Genome 44:559–571
Rossi L, Bindler G, Pijnenburg H, Isaac PG, Giraud-Henry I, Mahe M, Orvain C, Gadani F (2001) Potential of molecular marker analysis for variety identification in processed tobacco. Plant Var Seeds 14:89–101
Sanderson MJ (1997) A nonparametric approach to estimating divergence times in the absence of rate constancy. Mol Biol Evol 14:1218–1231
Swofford DL (2003) PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, de Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW, Broun P, Fulton TM, Giovannoni JJ, Grandillo S, Martin GB (1992) High density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
Wang Y, Diehl A, Wu FN, Vrebalov J, Giovannoni J, Siepel A, Tanksley SD (2008) Sequencing and comparative analysis of a conserved syntenic segment in the solanaceae. Genetics 180:391–408
Wendel JF (2000) Genome evolution in polyploids. Plant Mol Biol 42:225–249
Wu FN, Mueller LA, Crouzillat D, Petiard V, Tanksley SD (2006) Combining bioinformatics and phylogenetics to identify large sets of single-copy orthologous genes (COSII) for comparative, evolutionary and systematic studies: a test case in the euasterid plant clade. Genetics 174:1407–1420
Wu FN, Eannetta NT, Xu YM, Durrett R, Mazourek M, Jahn MM, Tanksley SD (2009a) A COSII genetic map of the pepper genome provides a detailed picture of synteny with tomato and new insights into recent chromosome evolution in the genus Capsicum. Theor Appl Genet 118:1279–1293
Wu FN, Eannetta NT, Xu YM, Tanksley SD (2009b) A detailed synteny map of the eggplant genome based on conserved ortholog set II (COSII) markers. Theor Appl Genet 118:927–935
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Philip Morris International, Switzerland. We thank Xiaomin Jia, Ingrid S. Phillips, Doris Kriseleit and Katja Wendehake for technical assistance, Nick J. Van Eck for greenhouse work, and Dr. Lukas A. Mueller (Boyce Thompson Institute for Plant Research, Ithaca, NY, USA) and his bioinformatics group for hosting the maps and the marker data in Solanaceae Genomics Network (http://www.sgn.cornell.edu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Heslop-Harrison.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, F., Eannetta, N.T., Xu, Y. et al. COSII genetic maps of two diploid Nicotiana species provide a detailed picture of synteny with tomato and insights into chromosome evolution in tetraploid N. tabacum . Theor Appl Genet 120, 809–827 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1206-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1206-z