Abstract
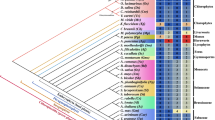
In order to understand the molecular evolution of catalase genes in higher plants, we compared the exon-intron structures of 12 genomic sequences from six plant species. It was assumed that the putative single primordial catalase gene had seven introns, because only those catalase genes having this structure are found in the monocotyledonae and dicotyledonae classes. After the evolutionary divergence of monocots from dicots, consecutive duplication of the primordial gene followed by the differential loss of introns occurred in each class to form three (or possibly four in dicots) diverse isozyme genes. In monocots, three ancestral isozyme genes were formed before the divergence of ancestral rice and maize. One of the rice genes, CatA, has an entirely new short intron which was not found in any other plant catalase gene examined. We have investigated the existence of the intron in the CatA homolog in other rice species by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) analysis. One major PCR product was found with the genomic DNAs from O. sativa (indica and japonica types), O. rufipogon and O. glaberrima. DNAs from several accessions of O. longistaminata showed variation in both the number and size of the DNA fragments amplified. PCR analyses and sequencing of the PCR products revealed that there are several CatA homologs having different sequences in some accessions of O. longistaminata. We have extended our study to other species in the Poaceae. The results suggest that the gain of the intron, most likely by insertion of a retroposon, took place in the ancestral genome of rice after its evolutionary divergence from other ancestral cereals such as barley, wheat and oat.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 November 1997 / Accepted: 5 January 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Iwamoto, M., Maekawa, M., Saito, A. et al. Evolutionary relationship of plant catalase genes inferred from exon-intron structures: isozyme divergence after the separation of monocots and dicots. Theor Appl Genet 97, 9–19 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050861
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001220050861