Abstract
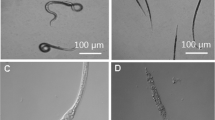
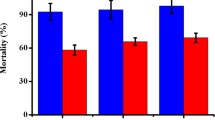
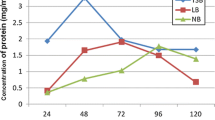
A neutral protease (npr) (designated Bae16) toxic to nematodes was purified to homogeneity from the strain Bacillus nematocida. The purified protease showed a molecular mass of approximately 40 kDa and displayed optimal activity at 55°C, pH 6.5. Bioassay experiments demonstrated that this purified protease could destroy the nematode cuticle and its hydrolytic substrates included gelatin and collagen. The gene encoding Bae16 was cloned, and the deduced amino acid sequence showed 94% sequence identity with npr gene from B. amyloliquefaciens, but had low similarity (13–43%) with the previously reported virulence serine proteases from fungi or bacteria, which reflected their differences. Recombinant mature Bae16 (rm-Bae16) was expressed in Escherichia coli BL21 using pET30 vector system, and its nematicidal activity confirmed that Bae16 could be involved in the infection process. Our present study revealed that the npr besides the known alkaline serine protease could serve as a potential virulence factor in the infection against nematodes, furthermore, the two proteases with different characteristics produced by the same strain co-ordinated efforts to kill nematodes. These data helped to understand the interaction between this bacterial pathogen and its host.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Åhman J, Johansson T, Olsson M, Punt PJ, Hondel CAMJJVD, Tunlid A (2002) Improving the pathogenicity of a nematode-trapping fungus by genetic engineering of a subtilisin with nematotoxic activity. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:3408–3415
Ali NI, Siddiqui IA, Shaukat SS, Zaki MJ (2002) Nematicidal activity of some strains of Pseudomonas spp. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1051–1058
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cheng LR (1998) The apply of PVDF membrane in electroblotting. Biotechnology 8:45–46
Choi N-S, Chang K-T, Maeng PJ, Kim S-H (2004) Cloning, expression, and fibrin (ogen) olytic properties of a subtilisin DJ-4 gene from Bacillus sp. DJ-4. FEMS Microbiol Lett 236:325–331
Cox GN Kusch M Edgar RS (1981) Cuticle of Caenorhabditis elegans: its isolation and partial characterization. J Cell Biol 90:7–17
Decraemer W, Karanastasi E, Brown D, Backeljau T (2003) Review of the ultrastructure of the nematode body cuticle and its phylogentic interpretation. Biol Rev 78:465–510
Elmar WH (1984) Method with haemoglobin, casein and azocoll as substrate. In: Bergmeyer P (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Wiley, New York, pp 270–274
Gray NF (1984) Ecology of nematophagous fungi: comparison of the soil sprinkling method with the Baerman funnel technique in the isolation of endoparasites. Soil Biol Biochem 16:81–83
Huang XW, Zhao NH, Zhang KQ (2004) Extracellular enzymes serving as virulence factors in nematophageous fungi involved in infection of the host. Res Microbiol 155:811–816
Huang XW, Tian BY, Niu QH, Yang JK, Zhang LM, Zhang KQ (2005a) An extracellular protease from Brevibacillus laterosporus G4 without parasporal crystal can serve as a pathogenic factor in infection of nematodes. Res Microbiol 156:719–727
Huang XW, Niu QH, Zhou W, Zhang KQ (2005b) Bacillus nematocida sp.nov, a novel bacterial strain with nematotoxic activity isolated from soil in Yunnan, China. Syst Appl Microbiol 28:323–327
Ioannis OG, Dimitrios GK, Demetra P-A (2004) A novel non-chemical nematicide for the control of root-knot nematodes [J]. Appl Soil Ecol 26:69–79
Laemmli EK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Leger RJ, Richard MC, Charnley AK (1987) Production of cuticle-degrading enzymes by the entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae during infection of cuticles from Calliphora vomitoria and Manduca sexta. J Gen Microbiol 133:1371–1382
Maizels RM, Blaxter ML, Selkirk ME (1993) Forms and functions of nematode surfaces. Exp Parasitol 77:380–384
Mala BR, Aparna MT, Mohini SG, Vasanti VD (1998) Molecular and biotechnological aspects of microbial proteases. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:597–635
Nack-Shick C, Kyu-Tae C, Pil JM, Seung-Ho K (2004) Cloning, expression, and fibrin (ogen) olytic properties of a subtilisin DJ-4 gene from Bacillus sp DJ-4. FEMS Microbiol Lett 336:325–331
Niu Q, Huang X, Tian B, Yang J, Liu J, Zhang L, Zhang K (2006) Bacillus sp B16 kills nematodes with a serine protease identified as a pathogenic factor. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 69:722–730
Nobutaka N, Tomohiro T (2003) A novel system for expressing recombinant proteins over a wide temperature range from 4 to 35°C. Biotechnology and bioengineering 86:136–148
Schroth MN, Hancock JG (1981) Selected topics in biological control. Ann Rev Phytopathol 35:453–476
Siddiqui LA, Oureshi SA, Sultana V, Ehteshamul-Haque S, Ghaffar A (2000) Biological control of root rot-knot disease complex of tomato. Plant Soil 227:163–169
St Leger RJ (1995) The role of cuticle-degrading proteases in fungal pathogenesis of insects. Can J Bot 73:1119–1125
The QIAexprssionistTM (2001) A handbook for high-level expression and purification of 6 * His-tagged proteins, 5th edn
Tunlid A, Rosen S, Ek B, Rask L (1994) Purification and characterization of an extracellular serine protease from the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Microbiology 140:1687–1695
Weller DM (1988) Bio-control of soilborne plant pathogens in the rhizosphere with bacteria. Ann Rev Phytopathol 26:379–407
Yokoyama K, Kunio O, Ohtsuka T et al (2002) In vitro refolding process of urea-denatured microbial transglutaminase without pro-peptide sequence [J]. Protein Exp Purif 26:329–335
Zhao ML, Mo MH, Zhang KQ (2004) Characterization of a neutral serine protease and its full-lenth cDNA from the nematode-trapping fungus Arthrobotrys oligospora. Mycologia 96:16–22
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to W. Zhou for her invaluable help in facilitating the work, H. Luo, J. Xu, B.Y. Tian, H. Sun, L.Q. Dong, J.W. Liu and L.H. Lian for their helpful advice in the study. This work was supported by the projects from National Natural Science Foundation Program of People’s Republic of China (30500338), Department of Science and Technology of Yunnan Province, People’s Republic of China (nos. 2005NG05, 2004C0004Q and 2004C0001Z).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Qiuhong Niu, Xiaowei Huang have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, Q., Huang, X., Zhang, L. et al. A neutral protease from Bacillus nematocida, another potential virulence factor in the infection against nematodes. Arch Microbiol 185, 439–448 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0112-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0112-x