Abstract
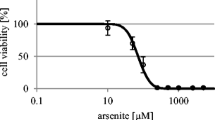
Increases in the glutathione (GSH) level in cultured Chinese hamster V79 cells incubated with arsenic compounds were investigated in terms of changes in the activity of γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase (γ-GCS), rate of cystine uptake, and utilization of cysteine. Arsenite at subtoxic concentrations caused a marked increase of the GSH level at 8 h after addition and then declined. Increase in the GSH level caused by arsenite was associated with an increase in the rate of cystine uptake, but not in γ-GCS activity. Increase in the rate of uptake of cystine was attributed mainly to an increase in the utilization of cysteine in the synthesis of GSH. Dimethylarsinic acid (DMAA) also caused an increase in the GSH level in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. Increase in the GSH level was accompanied by increases in γ-GCS activity and in the uptake of cystine. DMAA caused a reduction in the rate of utilization of cysteine for protein synthesis while enhancing the rate of cysteine utilization for GSH synthesis. Cycloheximide inhibited increases in γ-GCS activity caused by DMAA and in the rate of cystine uptake caused by arsenite and DMAA. The cystine transport system is suggested to be induced by arsenite and DMAA with γ-GCS induced in cells incubated with DMAA. Among the arsenic compounds, methylarsonic acid (MAA) was not effective in causing an increase in the GSH level. Accordingly, increases in the GSH level caused by arsenite and DMAA may be specific phenomena in which the cells responded to the arsenicals by increasing the GSH level.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 9 April 1997 / Accepted: 22 April 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ochi, T. Arsenic compound-induced increases in glutathione levels in cultured Chinese hamster V79 cells and mechanisms associated with changes in γ-glutamylcysteine synthetase activity, cystine uptake and utilization of cysteine. Arch Toxicol 71, 730–740 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050454
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002040050454