Abstract
6-Hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA) is widely used to study the death of catecholaminergic cells related to Parkinson’s disease. Oxidative stress and gene transcription are known to mediate the pro-apoptotic effect of 6-OHDA. As redox mechanisms are involved in activation of the transcription factor NF-κB, we studied the role of NF-κB in 6-OHDA-induced death of PC12 cells.
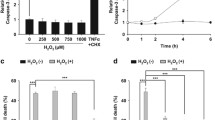
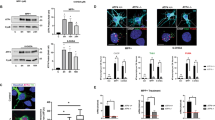
We stably transfected PC12 cells with a doxycycline-regulated expression vector for the NF-κB super-repressor (IκBα mutated at serine-32 and serine-36, IκBα-SR). NF-κB transcriptional activity was evaluated by transient transfection of an NF-κB-driven luciferase reporter gene. Expression of IκBα-SR inhibited NF-κB stimulated by tumor necrosis factor α (TNFα) and 6-OHDA. Apoptosis was quantified by counting cells with condensed nuclei. IκBα-SR inhibited apoptosis induced by 6-OHDA but enhanced apoptosis that was triggered by TNFα. The converse effects of NF-κB could be due to different target genes that are induced in the context of TNFα and 6-OHDA stimulation. Indeed, TNFα stimulated mRNA accumulation of the anti-apoptotic superoxide dismutase 2 through NF-κB whereas 6-OHDA induced mRNA accumulation of the pro-apoptotic c-myc.
These data demonstrate that NF-κB regulates survival of the neuron-like PC12 cells in a stimulus-specific manner. In the context of 6-OHDA stimulation, NF-κB mediates pro-apoptotic effects, suggesting that NF-κB signaling could be a target for drug development in Parkinson-related neurodegeneration.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aggarwal BB (2003) Signalling pathways of the TNF superfamily: a double-edged sword. Nat Rev Immunol 3:745–756
Andrew R, Watson DG, Best SA, Midgley JM, Wenlong H, Petty RKH (1993) The determination of hydroxydopamines and other trace amines in the urine of parkinsonian patients and normal controls. Neurochem Res 18:1175–1177
Beal MF (2001) Experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:325–334
Beg A, Sha W, Bronson R, Ghosh S, Baltimore D (1995) Embryonic lethality and liver degeneration in mice lacking the RelA component of NF-κB. Nature 376:167–170
Blum D, Torch S, Nissou MF, Verna JM (2001) 6-hydroxydopamine-induced nuclear factor-kappa B activation in PC12 cells. Biochem Pharmacol 62:473–481
Borrello S, Demple B (1997) NF kappa B-independent transcriptional induction of the human manganous superoxide dismutase gene. Arch Biochem Biophys 348:289–294
Brockman JA, Scherer DC, McKinsey TA, Hall SM, Qi X, Lee WY, Ballard DW (1995) Coupling of a signal response domain in I kappa B alpha to multiple pathways for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol 15:2809–2818
Curtius HC, Wolhensberger M, Steinmann B, Redweik S (1974) Mass fragmentography of dopamine and 6-OH-dopamine. Application to the determination of dopamine in human brain biopsies from the caudate nucleus. J Chromatogr 99:529–540
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2003) Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:819–822
De Erausquin GA, Hyrc K, Dorsey DA, Mamah D, Dokucu M, Masco DH, Walton T, Dikranian K, Soriano M, Garcia Verdugo JM, Goldberg MP, Dugan LL (2003) Nuclear translocation of nuclear transcription factor-kappa B by alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors leads to transcription of p53 and cell death in dopaminergic neurons. Mol Pharmacol 63:784–790
Duyao MP, Buckler AJ, Sonenshein GE (1990) Interaction of an NF-kappa B-like factor with a site upstream of the c-myc promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:4727–4731
Erlandsson N, Baumann B, Rössler OG, Kaufmann K, Giehl KM, Wirth T, Thiel G (2002) Lack of correlation between NF-κB activation and induction of programmed cell death in PC12 pheochromocytoma cells treated with 6-hydroxydopamine or the cannabinoid receptor 1-agonist CP55,940. Biochem Pharmacol 64:487–495
Ghribi O, Herman MM, Pramoonjago P, Savory J (2003) MPP+ induces the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in rabbit brain involving activation of the ATF-6 and NF-κB signaling pathways. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:1144–1153
Gossen M, Bujard H (1992) Tight control of gene expression in mammalian cells by tetracycline-responsive promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5547–5551
Haviv R, Stein R (1999) Nerve growth factor inhibits apoptosis induced b tumor necrosis factor in PC12 cells. J Neurosci Res 55:269–277
Hayakawa M, Miyashita H, Sakamoto I, Kitagawa M, Tanaka H, Yasuda H, Karin M, Kikugawa K (2003) Evidence that reactive oxygen species do not mediate NF-kappaB activation. EMBO J 22:3356–3366
Herrmann O, Tarabin V, Suzuki S, Attigah N, Prinz S, Schneider A, Coserea I, Monyer H, Brombacher F, Schwaninger M (2003) Regulation of body temperature and neuroprotection by endogenous interleukin-6 in focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:406–415
Holtz WA, O’Malley KL (2003) Parkinsonian mimetics induce aspects of unfolded protein response in death of dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem 278:19367–19377
Hunot S, Brugg B, Ricard D, Michel PP, Muriel MP, Ruberg M, Faucheux BA, Agid Y, Hirsch EC (1997) Nuclear translocation of NF-kappaB is increased in dopaminergic neurons of patients with Parkinson disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:7531–7536
Kaltschmidt B, Kaltschmidt C, Hofmann TG, Hehner SP, Droge W, Schmitz ML (2000) The pro- or anti-apoptotic function of NF-kappaB is determined by the nature of the apoptotic stimulus. Eur J Biochem 267:3828–3835
Karin M, Lin A (2002) NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3:221–227
Karin M, Yamamoto Y, Wang QM (2004) The IKK NF-κB system: a treasure trove for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:17–26
Kiningham KK, Xu Y, Daosukho C, Popova B, St Clair DK (2001) Nuclear factor kappaB-dependent mechanisms coordinate the synergistic effect of PMA and cytokines on the induction of superoxide dismutase 2. Biochem J 353:147–156
Levites Y, Youdim MBH, Maor G, Mandel S (2002) Attenuation of 6-hydroxydopamine (6-OHDA)-induced nuclear factor-kappa (NF-κB) activation and cell death by tea extracts in neuronal cultures. Biochem Pharmacol 63:21–29
Mielke K, Herdegen T (2002) Fatal shift of signal transduction is an integral part of neuronal differentiation: JNKs realize TNFalpha-mediated apoptosis in neuronlike, but not naive, PC12 cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 20:211–224
Nass R, Blakely RD (2003) The caenorhabditis elegans dopaminergic system: opportunities for insight into dopamine transport and neurodegeneration. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:521–544
Packham G, Cleveland JL (1995) c-Myc and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1242:11–28
Panet H, Barzilai A, Daily D, Melamed E, Offen D (2001) Activation of nuclear transcription factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) is essential for dopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells. J Neurochem 77:391–398
Pizzi M, Goffi F, Boroni F, Benarese M, Perkins SE, Liou HC, Spano P (2002) Opposing roles for NF-kappa B/Rel factors p65 and c-Rel in the modulation of neuron survival elicited by glutamate and interleukin-1beta. J Biol Chem 277:20717–20723
Roshak AK, Jackson JR, McGough K, Chabot-Fletcher M, Mochan E, Marshall LA (1996) Manipulation of distinct NFkappaB proteins alters interleukin-1beta-induced human rheumatoid synovial fibroblast prostaglandin E2 formation. J Biol Chem 271:31496–31501
Ryan KM, Ernst MK, Rice NR, Vousden KH (2000) Role of NF-kappaB in p53-mediated programmed cell death. Nature 404:892–897
Ryu EJ, Harding HP, Angelastro JM, Vitolo OV, Ron D, Greene LA (2002) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response in cellular models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 22:10690–10698
Sallmann S, Juttler E, Prinz S, Petersen N, Knopf U, Weiser T, Schwaninger M (2000) Induction of interleukin-6 by depolarization of neurons. J Neurosci 20:8637–8642
Scholzke MN, Potrovita I, Subramaniam S, Prinz S, Schwaninger M (2003) Glutamate activates NF-kappaB through calpain in neurons. Eur J Neurosci 18:3305–3310
Schwaninger M, Sallmann S, Petersen N, Schneider A, Prinz S, Libermann TA, Spranger M (1999) Bradykinin induces interleukin-6 expression in astrocytes through activation of nuclear factor-kappaB. J Neurochem 73:1461–1466
Senoh S, Creveling CR, Udenfriend S, Witkop B (1959) Chemical, enzymatic and metabolic studies on the mechanism of oxidation of dopamine. J Am Chem Soc 81:6236–6240
Teismann P, Schwaninger M, Weih F, Ferger B (2001) Nuclear factor-kappaB activation is not involved in a MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroreport 12:1049–1053
Van Antwerp DJ, Martin SJ, Kafri T, Green DR, Verma IM (1996) Suppression of TNF-α-induced apoptosis by NF-κB. Science 274:787–789
Walkinshaw G, Waters CM (1994) Neurotoxin-induced cell death in neuronal PC12 cells is mediated by induction of apoptosis. Neuroscience 63:975–987
Wang X, Qin ZH, Leng Y, Wang Y, Jin X, Chase TN, Bennett MC (2002) Prostaglandin A1 inhibits rotenone-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurochem 83:1094–1102
Wong GH, Elwell JH, Oberley LW, Goeddel DV (1989) Manganous superoxide dismutase is essential for cellular resistance to cytotoxicity of tumor necrosis factor. Cell 58:923–931
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant of the DFG to M.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tarabin, V., Schwaninger, M. The role of NF-κB in 6-hydroxydopamine- and TNFα-induced apoptosis of PC12 cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 369, 563–569 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-004-0938-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-004-0938-1