Abstract
Rationale
Chronic antidepressant treatment increases glucocorticoid-mediated negative feedback on the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, and thus reduces HPA axis activity, in depressed patients and healthy controls. In contrast, acute antidepressant treatment induces an activation of basal HPA axis activity.
Objectives
We examined the effects of 4 days of treatment with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor, citalopram, on basal salivary cortisol and on suppression of salivary cortisol by prednisolone.
Methods
We used a single-blind, placebo-controlled, repeated-measure design. Salivary cortisol was measured from 0900 to 1700 hours. In the first phase of the study, basal salivary cortisol secretion was measured on 2 study days, before and after 4 days of treatment with citalopram (orally, 20 mg/day). In the second phase, salivary cortisol secretion after suppression by prednisolone (5 mg, given at 2200 hours the night before) was measured on 2 study days, again before and after 4 days of treatment with citalopram (orally, 20 mg/day). Eight volunteers participated to the study.
Results
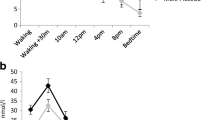
Citalopram increased basal salivary cortisol in the morning (0900–1100 hours) by approximately 47% (P=0.003). Moreover, citalopram increased suppression by prednisolone in the morning (0900–1100 hours): suppression was approximately 22% before citalopram and 45% after citalopram (P=0.05).
Conclusions
Citalopram increases glucocorticoid-mediated negative feedback on the HPA axis after as little as 4 days of treatment. This effect could be due to an increased function of the corticosteroid receptors. Our findings further support the notion that one of the mechanisms by which antidepressants exert their therapeutic effects is by normalizing HPA axis hyperactivity in depressed patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arana GW, Baldessarini RJ, Ornsteen M (1985) The dexamethasone suppression test for diagnosis and prognosis in psychiatry. Commentary and review. Arch Gen Psychiatry 42:1193–1204
Attenburrow MJ, Mitter PR, Whale R, Terao T, Cowen PJ (2001) Low-dose citalopram as a 5-HT neuroendocrine probe. Psychopharmacology 155:323–326
von Bardeleben U, Steiger A, Gerken A, Holsboer F (1989) Effects of fluoxetine upon pharmacoendocrine and sleep-EEG parameters in normal controls. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 4(Suppl 1):1–5
Bazire S (2003) Psychotropic drug directory 2003/04. Fipevin, Salisbury
Bhagwagar Z, Hafizi S, Cowen PJ (2002a) Acute citalopram administration produces correlated increases in plasma and salivary cortisol. Psychopharmacology 163:118–120
Bhagwagar Z, Whale R, Cowen PJ (2002b) State and trait abnormalities in serotonin function in major depression. Br J Psychiatry 180:24–28
Bouwer C, Claassen J, Dinan TG, Nemeroff CB (2000) Prednisone augmentation in treatment-resistant depression with fatigue and hypocortisolaemia: a case series. Depress Anxiety 12:44–50
Brady LS, Gold PW, Herkenham M, Lynn AB, Whitfield HJ Jr (1992) The antidepressants fluoxetine, idazoxan and phenelzine alter corticotropin-releasing hormone and tyrosine hydroxylase mRNA levels in rat brain: therapeutic implications. Brain Res 572:117–125
Chakraborty J, English J, Marks V, Dumasia MC, Chapman DJ (1976) A radioimmunoassay method for prednisolone: comparison with the competitive protein binding method. Br J Clin Pharmacol 3:903–906
DeBattista C, Posener JA, Kalehzan BM, Schatzberg AF (2000) Acute antidepressant effects of intravenous hydrocortisone and CRH in depressed patients: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Am J Psychiatry 157:1334–1337
Delbende C, Contesse V, Mocaer E, Kamoun A, Vaudry H (1991) The novel antidepressant, tianeptine, reduces stress-evoked stimulation of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenal axis. Eur J Pharmacol 202:391–396
Deuschle M, Schmider J, Weber B, Standhardt H, Korner A, Lammers CH, Schweiger U, Hartmann A, Heuser I (1997) Pulse-dosing and conventional application of doxepin: effects on psychopathology and hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) system. J Clin Psychopharmacol 17:156–160
Dinan TG, Lavelle E, Cooney J, Burnett F, Scott L, Dash A, Thakore J, Berti C (1997) Dexamethasone augmentation in treatment-resistant depression. Acta Psychiatr Scand 95:58–61
Ebrecht M, Buske-Kirschbaum A, Hellhammer D, Kern S, Rohleder N, Walker B, Kirschbaum C (2000) Tissue specificity of glucocorticoid sensitivity in healthy adults. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:3733–3739
Harmer CJ, Bhagwagar Z, Shelley N, Cowen PJ (2003) Contrasting effects of citalopram and reboxetine on waking salivary cortisol. Psychopharmacology 167:112–114
Harris B, Watkins S, Cook N, Walker RF, Read GF, Riad-Fahmy D (1990) Comparisons of plasma and salivary cortisol determinations for the diagnostic efficacy of the dexamethasone suppression test. Biol Psychiatry 27:897–904
Hennig J, Lange N, Haag A, Rohrmann S, Netter P (2000) Reboxetine in a neuroendocrine challenge paradigm: evidence for high cortisol responses in healthy volunteers scoring high on subclinical depression. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 3:193–201
Heuser IJ, Schweiger U, Gotthardt U, Schmider J, Lammers CH, Dettling M, Yassouridis A, Holsboer F (1996) Pituitary-adrenal-system regulation and psychopathology during amitriptyline treatment in elderly depressed patients and normal comparison subjects. Am J Psychiatry 153:93–99
Karssen AM, Meijer OC, van der Sandt I, Lucassen PJ, de Lange EC, de Boer AG, de Kloet ER (2001) Multidrug resistance p-glycoprotein hampers the access of cortisol but not of corticosterone to mouse and human brain. Endocrinology 142:2686–2694
Laakmann G, Wittmann M, Gugath M, Mueller OA, Treusch J, Wahlster U, Stalla GK (1984) Effects of psychotropic drugs (desimipramine, chlorimipramine, sulpiride and diazepam) on the human HPA axis. Psychopharmacology 84:66–70
Laakmann G, Hinz A, Voderholzer U, Daffner C, Muller OA, Neuhauser H, Neulinger E, Wittmann M (1990) The influence of psychotropic drugs and releasing hormones on anterior pituitary hormone secretion in healthy subjects and depressed patients. Pharmacopsychiatry 23:18–26
Linkowski P, Mendlewicz J, Kerkhofs M, Leclercq R, Golstein J, Brasseur M, Copinschi G, Van Cauter E (1987) 24-Hour profiles of adrenocorticotropin, cortisol, and growth hormone in major depressive illness: effect of antidepressant treatment. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 65:141–152
Meijer OC, de Lange EC, Breimer DD, de Boer AG, Workel JO, de Kloet ER (1998) Penetration of dexamethasone into brain glucocorticoid targets is enhanced in mdr1A p-glycoprotein knockout mice. Endocrinology 139:1789–1793
Michelson D, Galliven E, Hill L, Demitrack M, Chrousos G, Gold P (1997) Chronic imipramine is associated with diminished hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis responsivity in healthy humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 82:2601–2606
Montkowski A, Barden N, Wotjak C, Stec I, Ganster J, Meaney M, Engelmann M, Reul JM, Landgraf R, Holsboer F (1995) Long-term antidepressant treatment reduces behavioural deficits in transgenic mice with impaired glucocorticoid receptor function. J Neuroendocrinol 7:841–845
Muller MB, Keck ME, Binder EB, Kresse AE, Hagemeyer TP, Landgraf R, Holsboer F, Uhr M (2003) ABCB1 (MDR1)-type p-glycoproteins at the blood-brain barrier modulate the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical system: implications for affective disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1991–1999
Orth D, Kovacs W (1998) The adrenal cortex. In: Wilson J, Foster D, Kronenberg H, Larsen P (eds) Williams textbook of endocrinology. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 517–664
Pariante CM (2003) Depression, stress and the adrenal axis. J Neuroendocrinol 15:811–812
Pariante CM, Miller AH (2001) Glucocorticoid receptors in major depression: relevance to pathophysiology and treatment. Biol Psychiatry 49:391–404
Pariante CM, Makoff A, Lovestone S, Feroli S, Heyden A, Miller AH, Kerwin RW (2001) Antidepressants enhance glucocorticoid receptor function in vitro by modulating the membrane steroid transporters. Br J Pharmacol 134:1335–1343
Pariante CM, Papadopoulos AS, Poon L, Checkley SA, English J, Kerwin RW, Lightman S (2002) A novel prednisolone suppression test for the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. Biol Psychiatry 51:922–930
Pariante CM, Hye A, Williamson R, Makoff A, Lovestone S, Kerwin RW (2003a) The antidepressant clomipramine regulates cortisol intracellular concentrations and glucocorticoid receptor expression in fibroblasts and rat primary neurones. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1553–1561
Pariante CM, Kim RB, Makoff A, Kerwin RW (2003b) Antidepressant fluoxetine enhances glucocorticoid receptor function in vitro by modulating membrane steroid transporters. Br J Pharmacol 139:1111–1118
Pariante CM, Thomas SA, Lovestone S, Makoff A, Kerwin RW (2004) Do antidepressants regulate how cortisol affects the brain? 2003 Curt Richter Award Paper. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29:423–447
Reul JM, Stec I, Soder M, Holsboer F (1993) Chronic treatment of rats with the antidepressant amitriptyline attenuates the activity of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenocortical system. Endocrinology 133:312–320
Reynolds RM, Bendall HE, Whorwood CB, Wood PJ, Walker BR, Phillips DI (1998) Reproducibility of the low dose dexamethasone suppression test: comparison between direct plasma and salivary cortisol assays. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 49:307–310
Schlosser R, Wetzel H, Dorr H, Rossbach W, Hiemke C, Benkert O (2000) Effects of subchronic paroxetine administration on night-time endocrinological profiles in healthy male volunteers. Psychoneuroendocrinology 25:377–388
Schule C, Baghai T, Schmidbauer S, Bidlingmaier M, Strasburger CJ, Laakmann G (2004) Reboxetine acutely stimulates cortisol, ACTH, growth hormone and prolactin secretion in healthy male subjects. Psychoneuroendocrinology 29:185–200
Seifritz E, Baumann P, Muller MJ, Annen O, Amey M, Hemmeter U, Hatzinger M, Chardon F, Holsboer-Trachsler E (1996) Neuroendocrine effects of a 20-mg citalopram infusion in healthy males. A placebo-controlled evaluation of citalopram as 5-HT function probe. Neuropsychopharmacology 14:253–263
Varis T, Kivisto KT, Neuvonen PJ (2000) The effect of itraconazole on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of oral prednisolone. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 56:57–60
Veith RC, Lewis N, Langohr JI, Murburg MM, Ashleigh EA, Castillo S, Peskind ER, Pascualy M, Bissette G, Nemeroff CB, Raskind MA (1993) Effect of desipramine on cerebrospinal fluid concentrations of corticotropin-releasing factor in human subjects. Psychiatry Res 46:1–8
Yau JL, Noble J, Hibberd C, Seckl JR (2001) Short-term administration of fluoxetine and venlafaxine decreases corticosteroid receptor mRNA expression in the rat hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 306:161–164
Yehuda R, Boisoneau D, Lowy MT, Giller EL Jr (1995) Dose–response changes in plasma cortisol and lymphocyte glucocorticoid receptors following dexamethasone administration in combat veterans with and without posttraumatic stress disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 52:583–593
Yehuda R, Halligan SL, Grossman R, Golier JA, Wong C (2002) The cortisol and glucocorticoid receptor response to low dose dexamethasone administration in aging combat veterans and holocaust survivors with and without posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry 52:393–403
Acknowledgements
This research has been funded by a UK Medical Research Council (MRC) Clinical Training Fellowship, and a NARSAD Young Investigator Award, both to C.M. Pariante.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pariante, C.M., Papadopoulos, A.S., Poon, L. et al. Four days of citalopram increase suppression of cortisol secretion by prednisolone in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 177, 200–206 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1925-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1925-4