Abstract
Rationale
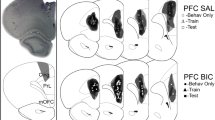
The density of tyrosine hydroxylase-immunoreactive (TH-IR) axons in the prefrontal cortex of schizophrenic subjects may be reduced by as much as 50% in the deep cortical layers (Am J Psychiatry 156:1580–1589, 1999). Previously, we demonstrated that ~60% loss of TH-IR axons in the rat medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) decreases local basal and stress-evoked extracellular dopamine (DA) concentrations, suggesting that moderate loss of DA axons in the mPFC is sufficient to alter the neurochemical activity of the remaining DA neurons (Neuroscience 93:497–505, 1999).
Objectives
To further assess the functional consequences of partial mPFC DA depletion, we examined the effects of 6-hydroxydopamine lesions of the rat mPFC on behavior in a T-maze delayed-response task. We also assessed whether chronic administration of the norepinephrine (NE) uptake inhibitor, desipramine (DMI), attenuates lesion-induced deficits in T-maze performance. Previous research indicates that inhibition of NE transport in the mPFC results in a concomitant increase in extracellular DA and NE.
Results
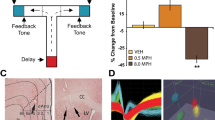
Moderate loss of mPFC DA and NE (~50 and 10% loss, respectively) was sufficient to impair delayed-response behavior, in part due to an increase in perseverative responding. Chronic DMI treatment (3 mg/kg delivered via osmotic pumps) impaired performance of control rats but attenuated the deficits in delayed-response behavior in rats previously sustaining loss of mPFC DA and NE (~75 and 35% loss, respectively).
Conclusion
These data suggest that moderate loss of DA and NE in the prefrontal cortex is sufficient to impair cognitive function, and these behavioral effects are attenuated by inhibition of the NE transporter.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akil M, Pierri JN, Whitehead RE, Edgar CL, Mohila C, Sampson AR, Lewis DA (1999) Lamina-specific alterations in the dopamine innervation of the prefrontal cortex in schizophrenic subjects. Am J Psychiatry 156:1580–1589
Angrist B, Rotrosen J, Gershon S (1980) Responses to apomorphine, amphetamine, and neuroleptics in schizophrenic subjects. Psychopharmacology 67:31–38
Angrist B, Peselow E, Rubenstein M, Wolkin A, Rotrosen J (1985) Amphetamine response and relapse risk after depot neuroleptic discontinuation. Psychopharmacology 85:277–283
Arnsten AF, Goldman-Rakic PS (1985) Alpha 2-adrenergic mechanisms in prefrontal cortex associated with cognitive decline in aged nonhuman primates. Science 230:1273–1276
Arnsten AF, Cai JX, Goldman-Rakic PS (1988) The alpha-2 adrenergic agonist guanfacine improves memory in aged monkeys without sedative or hypotensive side effects: evidence for alpha-2 receptor subtypes. J Neurosci 8:4287–4298
Arnsten AF, Cai JX, Murphy BL, Goldman-Rakic PS (1994) Dopamine D1 receptor mechanisms in the cognitive performance of young adult and aged monkeys. Psychopharmacology 116:143–151
Arnsten AF, Mathew R, Ubriani R, Taylor JR, Li BM (1999) Alpha-1 noradrenergic receptor stimulation impairs prefrontal cortical cognitive function. Biol Psychiatry 45:26–31
Arnsten AFT (1997) Catecholamine regulation of the prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 11:151–162
Aultman JM, Moghaddam B (2001) Distinct contributions of glutamate and dopamine receptors to temporal aspects of rodent working memory using a clinically relevant task. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 153:353–364
Avery RA, Franowicz JS, Studholme C, van Dyck CH, Arnsten AF (2000) The alpha-2A-adrenoceptor agonist, guanfacine, increases regional cerebral blood flow in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of monkeys performing a spatial working memory task. Neuropsychopharmacology 23:240–249
Bell LJ, Iversen LL, Uretsky NJ (1970) Time course of the effects of 6-hydroxydopamine on catecholamine-containing neurones in rat hypothalamus and striatum. Br J Pharmacol 40:790–799
Birnbaum S, Gobeske KT, Auerbach J, Taylor JR, Arnsten AF (1999) A role for norepinephrine in stress-induced cognitive deficits: alpha-1-adrenoceptor mediation in the prefrontal cortex. Biol Psychiatry 46:1266–1274
Bogerts B, Hantsch J, Herzer M (1983) A morphometric study of the dopamine-containing cell groups in the mesencephalon of normals, Parkinson patients, and schizophrenics. Biol Psychiatry 18:951–969
Boyce PJ, Finlay JM (2005) Neonatal depletion of cortical dopamine: Effects on dopamine turnover and motor behavior in juvenile and adult rats. Dev Brain Res 156:167–175
Brozoski TJ, Brown RM, Rosvold HE, Goldman PS (1979) Cognitive deficit caused by regional depletion of dopamine in prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkey. Science 205:929–932
Bubser M, Schmidt WJ (1990) 6-Hydroxydopamine lesion of the rat prefrontal cortex increases locomotor activity, impairs acquisition of delayed alternation tasks, but does not affect uninterrupted tasks in the radial maze. Behav Brain Res 37:157–168
Cai JX, Ma YY, Xu L, Hu XT (1993) Reserpine impairs spatial working memory performance in monkeys: reversal by the alpha 2-adrenergic agonist clonidine. Brain Res 614:191–196
Carboni E, Tanda GL, Frau R, Di Chiara G (1990) Blockade of the noradrenaline carrier increases extracellular dopamine concentrations in the prefrontal cortex: evidence that dopamine is taken up in vivo by noradrenergic terminals. J Neurochem 55:1067–1070
Carlson S, Tanila H, Rama P, Mecke E, Pertovaara A (1992) Effects of medetomidine an α-2 antagonist on spatial memory performance in adult and aged rats. Behav Neural Biol 58:113–119
Chudasama Y, Robbins TW (2004) Dopaminergic modulation of visual attention and working memory in the rodent prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1628–1636
Coull JT, Middleton HC, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (1995) Contrasting effects of clonidine and diazepam on tests of working memory and planning. Psychopharmacology 120:311–321
Daniel DG, Berman KF, Weinberger DR (1989) The effect of apomorphine on regional cerebral blood flow in schizophrenia. J Neurophysiol Clin Neurosci 1:377–384
Daniel DG, Weinberger DR, Jones DW, Zigun JR, Coppola R, Handel S, Bigelow LB, Goldberg TE, Berman KF, Kleinman JE (1991) The effect of amphetamine on regional cerebral blood flow during cognitive activation in schizophrenia. J Neurosci 11:1907–1917
Darlington RB (1990) Regression and linear models. McGraw-Hill, New York
Dolan R, Fletcher P, Frith C, Friston K, Frackowiak R, Grasby P (1995) Dopaminergic modulation of impaired cognitive activation in the anterior cingulate cortex in schizophrenia. Nature 378:180–182
Ellenbroek B, Budde S, Cools A (1996) Prepulse inhibition and latent inhibition the role of dopamine in the medial prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience 75:535–542
Ferguson JM, Wesnes KA, Schwartz GE (2003) Reboxetine versus paroxetine versus placebo: effects on cognitive functioning in depressed patients. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 18:9–14
Fletcher PC, Frith CD, Grasby PM, Friston KJ, Dolan RJ (1996) Local and distributed effects of apomorphine on fronto-temporal function in acute unmedicated schizophrenia. J Neurosci 16:7055–7062
Franowicz JS, Arnsten AF (1998) The alpha-2a noradrenergic agonist, guanfacine, improves delayed response performance in young adult rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 136:8–14
Franowicz JS, Phil M, Arnsten AF (1999) Treatment with the noradrenergic alpha-2 agonist clonidine, but not diazepam, improves spatial working memory in normal young rhesus monkeys. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:611–621
Geraud G, Arne-Bes MC, Guell A, Bes A (1987) Reversibility of hemodynamic hypofrontality in schizophrenia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 7:9–12
Granon S, Passetti F, Thomas KL, Dalley JW, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2000) Enhanced and impaired attentional performance after infusion of D1 dopaminergic receptor agents into rat prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 20:1208–1215
Gresch PJ, Sved AF, Zigmond MJ, Finlay JM (1995) Local influence of endogenous norepinephrine on extracellular dopamine in rat medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurochem 65:111–116
Jaskiw GE, Weinberger DR (1992) Dopamine and schizophrenia—a cortically corrective perspective. Semin Neurosci 4:179–188
Jentsch J, Tran A, Le D, Youngren K, Roth R (1997) Subchronic phencyclidine administration reduces mesoprefrontal dopamine utilization and impairs prefrontal cortical dependent cognition in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 17:92–99
King D, Finlay JM (1995) Effects of selective dopamine depletion in medial prefrontal cortex on basal and evoked extracellular dopamine in neostriatum. Brain Res 685:117–128
King D, Finlay JM (1997) Loss of dopamine terminals in the medial prefrontal cortex increased the ratio of DOPAC to DA in tissue of the nucleus accumbens shell: role of stress. Brain Res 767:192–200
Kirk RE (1982) Experimental design: procedures for the behavioral science. Brooks/Cole, Pacific Grove, CA
Koch M, Bubser M (1994) Deficient sensorimotor gating after 6-hydroxydopamine lesion of the rat medial prefrontal cortex is reversed by haloperidol. Eur J Neurosci 6:1837–1845
Li BM, Mei ZT (1994) Delayed-response deficit induced by local injection of the alpha 2-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine into the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in young adult monkeys. Behav Neural Biol 62:134–139
Mao ZM, Arnsten AF, Li BM (1999) Local infusion of an alpha-1 adrenergic agonist into the prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance in monkeys. Biol Psychiatry 46:1259–1265
Moron JA, Brockington A, Wise RA, Rocha BA, Hope BT (2002) Dopamine uptake through the norepinephrine transporter in brain regions with low levels of the dopamine transporter: evidence from knock-out mouse lines. J Neurosci 22:389–395
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic, New York
Popper CW (2000) Pharmacologic alternatives to psychostimulants for the treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am 9:605–646
Rammsayer TH, Hennig J, Haag A, Lange N (2001) Effects of noradrenergic activity on temporal information processing in humans. Q J Exp Psychol B 54:247–258
Ravard S, Herve D, Thiebot MH, Soubrie P, Tassin JP (1990) Anticonflict-like effect of a prefrontal DA lesion in rats: permissive role of NA neurons. Behav Pharmacol 1:255–259
Robbins TW (1991) Cognitive deficits in schizophrenia and Parkinson’s disease: neural basis and the role of dopamine. In: The mesolimbic dopamine system: from motivation to action. Wiley, Chichester, UK, pp 497–528
Roberts AC, De Salvia MA, Wilkinson LS, Collins P, Muir JL, Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (1994) 6-Hydroxydopamine lesions of the prefrontal cortex in monkeys enhance performance on an analog of the Wisconsin Card Sort Test: possible interactions with subcortical dopamine. J Neurosci 14:2531–2544
Romanides AJ, Duffy P, Kalivas PW (1999) Glutamatergic and dopaminergic afferents to the prefrontal cortex regulate spatial working memory in rats. Neuroscience 92:97–106
Sawaguchi T (1998) Attenuation of delay-period activity of monkey prefrontal neurons by an alpha2-adrenergic antagonist during an oculomotor delayed-response task. J Neurophysiol 80:2200–2205
Sawaguchi T, Goldman-Rakic PS (1991) D1 dopamine receptors in prefrontal cortex: involvement in working memory. Science 251:947–950
Sawaguchi T, Goldman-Rakic RS (1994) The role of D1-dopamine receptor in working memory: local injections of dopamine antagonists into the prefrontal cortex of rhesus monkeys performing an oculomotor delayed-response. J Neurophysiol 71:515–528
Seamans JK, Floresco SB, Phillips AG (1998) D1 receptor modulation of hippocampal–prefrontal cortical circuits integrating spatial memory with executive functions in the rat. J Neurosci 18:1613–1621
Sleipness EP, Bliss CA, Finlay JM (2001) Effects of desipramine on extracellular dopamine and norepinephrine in prefrontal cortex following partial depletion of local dopamine. 31st Annu Meet Soc Neurosci 27:479.16
Stam C, deBruin J, Haelst A, Gugten J, Kalsbeek A (1989) Influence of the mesocortical dopaminergic system on activity, food hoarding, social-agonistic behavior, and spatial delayed alternation in male rats. Behav Neurosci 103:24–35
Taghzouti K, Simon H, Herve D, Blanc G, Studler JM, Glowinski J, LeMoal M, Tassin JP (1988) Behavioural deficits induced by an electrolytic lesion of the rat ventral mesencephalic tegmentum are corrected by a superimposed lesion of the dorsal noradrenergic system. Brain Res 440:172–176
Thomas G, Gash D (1988) Differential effects of hippocampal ablations on dispositional and representational memory in the rat. Behav Neurosci 102:635–642
van Kammen D, Docherty J, Bunney W (1982) Prediction of early relapse after pimozide discontinuation by response to d-amphetamine during pimozide treatment. Biol Psychiatry 17:223–242
Venator DK, Lewis DA, Finlay JM (1999) Effects of partial dopamine loss in the medial prefrontal cortex on local baseline and stress-evoked extracellular dopamine concentrations. Neuroscience 93:497–505
Verma A, Moghaddam B (1996) NMDA receptor antagonists impair prefrontal cortex function as assessed via spatial delayed alternation performance in rats: modulation by dopamine. J Neurosci 16:373–379
Williams GV, Goldman-Rakic PS (1995) Modulation of memory fields by dopamine D1 receptors in prefrontal cortex. Nature 376:572–575
Yamamoto BK, Novotney S (1998) Regulation of extracellular dopamine by the norepinephrine transporter. J Neurochem 71:274–280
Zahrt J, Taylor JR, Matthew RG, Arnsten AFT (1997) Supranormal stimulation of D1 dopamine receptors in the rodent prefrontal cortex impairs spatial working memory performance. J Neurosci 17:8528–8535
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by USPHS grants MH45156 and MH61616 and a Summer Research Grant from WWU Bureau for Faculty Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clinton, S.M., Sucharski, I.L. & Finlay, J.M. Desipramine attenuates working memory impairments induced by partial loss of catecholamines in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 183, 404–412 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0221-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-005-0221-2