Abstract
Rationale
Ethanol and caffeine are two of the most widely consumed drugs in the world, often used in the same setting. Animal models may help to understand the conditions under which incidental memories formed just before ethanol intoxication might be lost or become difficult to retrieve.
Objectives
Ethanol-induced retrograde amnesia was investigated using a new odor-recognition test.
Materials and methods
Rats thoroughly explored a wood bead taken from the cage of another rat, and habituated to this novel odor (N1) over three trials. Immediately following habituation, rats received saline, 25 mg/kg pentylenetetrazol (a seizure-producing agent known to cause retrograde amnesia) to validate the test, 1.0 g/kg ethanol, or 3.0 g/kg ethanol. The next day, they were presented again with N1 and also a bead from a new rat’s cage (N2).
Results
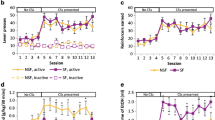
Rats receiving saline or the lower dose of ethanol showed overnight memory for N1, indicated by preferential exploration of N2 over N1. Rats receiving pentylenetetrazol or the higher dose of ethanol appeared not to remember N1, in that they showed equal exploration of N1 and N2. Caffeine (5 mg/kg), delivered either 1 h after the higher dose of ethanol or 20 min prior to habituation to N1, negated ethanol-induced impairment of memory for N1. A combination of a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor and an adenosine A2A antagonist, mimicking two major mechanisms of action of caffeine, likewise prevented the memory impairment, though either drug alone had no such effect. Binge alcohol can induce retrograde, caffeine-reversible disruption of social odor memory storage or recall.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alkana RL, Parker ES (1979) Memory facilitation by post-training injection of ethanol. Psychopharmacology 66:117–119
Angelucci MEM, Vital M, Cesario C, Zadusky CR, Rosalen PL, Da Cunha C (1999) The effect of caffeine in animal models of learning and memory. Eur J Pharmacol 373:135–140
Anthenelli RM, Klein JL, Tsuang JW, Smith TL, Schuckit MA (1994) The prognostic importance of blackouts in young men. J Stud Alcohol 55:290–295
Baratti CM (1987) The impairment of retention induced by pentylenetetrazol in mice may be mediated by a release of opioid peptides in the brain. Behav Neural Biol 48:183–196
Birnbaum IM, Parker ES, Hartley JT, Noble EP (1978) Alcohol and memory—retrieval processes. J Verbal Learn Verbal Behav 17:325–335
Blokland A, Schreiber R, Prickaerts J (2006) Improving memory: a role for phosphodiesterases. Curr Pharm Des 12:2511–2523
Bruce KR, Pihl RO (1997) Forget ‘drinking to forget’: enhanced consolidation of emotionally charged memory by alcohol. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 5:242–250
Buelow G, Harbin J (1996) The influence of blackouts on alcohol use expectancies. J Alcohol Drug Educ 42:25–34
Buelow G, Koeppel J (1995) Psychological consequences of alcohol-induced blackout among college students. J Alcohol Drug Educ 40:10–20
Chandler LJ, Sutton G (2005) Acute ethanol inhibits extracellular signal-regulated kinase, protein kinase B, and adenosine 3′:5′-cyclic monophosphate response element binding protein activity in an age- and brain region-specific manner. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29:672–682
Choi SH, Woodlee MT, Hong JJ, Schallert T (2006) A simple modification of the water maze test to enhance daily detection of spatial memory in rats and mice. J Neurosci Methods 156:182–193
Creeley C, Wozniak DF, Labruyere J, Taylor GT, Olney JW (2006) Low doses of memantine disrupt memory in adult rats. J Neurosci 26:3923–3932
Crews D, Gore AC, Hsu TS, Dangleben NL, Spinetta M, Schallert T, Anway MD, Skinner MK (2007) Transgenerational epigenetic imprints on mate preference. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:5942–5946
Day LB, Schallert T (1996) Anticholinergic effects on acquisition of place learning in the Morris water task: spatial mapping deficit or inability to inhibit non-place strategies? Behav Neurosci 110:1–8
Dohrman DP, Diamond I (1997) The role of the neuromodulator adenosine in alcohol’s actions. Alcohol Health Res World 21:136–140
Ennaceur A, Neave N, Aggleton JP (1997) Spontaneous object recognition and object location memory in rats: the effects of lesions in the cingulate cortices, the medial prefrontal cortex, the cingulum bundle and the fornix. Exp Brain Res 113:509–519
Felt BT, Beard JL, Schallert T, Shao J, Aldridge W, Conner JR, Georgieff MK, Lozoff B (2006) Persistent neurochemical and behavioral abnormalities in adulthood despite early iron supplementation for perinatal iron deficiency anemia in rats. Behav Brain Res 171:261–270
Flexner LB, Stellar E (1965) Memory and cerebral protein synthesis in mice as affected by graded amounts of puromycin. Exp Neurol 13:264–272
Fredholm BB, Battig K, Holmen J, Nehlig A, Zvartau EE (1999) Actions of caffeine in the brain with special reference to factors that contribute to its widespread use. Pharmacol Rev 51:83–133
Gold PE (2006) The many faces of amnesia. Learn Memory 13:506–514
Goodwin DW (1995) Alcohol amnesia. Addiction 90:315–317
Hartzler B, Fromme K (2003) Fragmentary and en bloc blackouts: similarity and distinction among episodes of alcohol-induced memory loss. J Stud Alcohol 64:547–550
Hernandez TD, Schallert T (1988) Seizures and recovery from experimental brain damage. Exp Neurol 102:318–324
Howell LL, Coffin VL, Spealman RD (1997) Behavioral and physiological effects of xanthines in nonhuman primates. Psychopharmacology 129:1–14
Jennison KM, Johnson KA (1994) Drinking-induced blackouts among young adults—results from a national longitudinal study. Int J Addict 29:23–51
Kandel ER (2001) Neuroscience—the molecular biology of memory storage: a dialogue between genes and synapses. Science 294:1030–1038
Lindner MD, Schallert T (1988) Aging and atropine effects on spatial navigation in the Morris water task. Behav Neurosci 102:621–634
Mailliard WS, Diamond I (2004) Recent advances in the neurobiology of alcoholism: the role of adenosine. Pharmacol Ther 101:39–46
Manrique HM, Miquel M, Aragon CMG (2005) Brain catalase mediates potentiation of social recognition memory produced by ethanol in mice. Drug Alcohol Depend 79:343–350
Matthews DB, Silvers JR (2004) The use of acute ethanol administration as a tool to investigate multiple memory systems. Neurobiol Learn Mem 82:299–308
Matthews DB, Ilgen M, White AM, Best PJ (1999) Acute ethanol administration impairs spatial performance while facilitating nonspatial performance in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 72:169–179
McLean JH, Darby-King A, Harley CW (2005) Potentiation and prolongation of long-term odor memory in neonate rats using a phosphodiesterase inhibitor. Neuroscience 135:329–334
Melia KR, Ryabinin AE, Corodimas KP, Wilson MC, Ledoux JE (1996) Hippocampal-dependent learning and experience-dependent activation of the hippocampus are preferentially disrupted by ethanol. Neuroscience 74:313–322
Miller RR, Matzel LD (2006) Retrieval failure versus memory loss in experimental amnesia: definitions and processes. Learn Memory 13:491–497
Miserendino MJD, Sananes CB, Melia KR, Davis M (1990) Blocking of acquisition but not expression of conditioned fear-potentiated startle by NMDA antagonists in the amygdala. Nature 345:716–718
Mumby D (2005) Object recognition. In: Whishaw IQ and Kolb B (ed) The behavior of the laboratory rat. Oxford University Press, New York
Nader K, Wang SH (2006) Fading in. Learn Memory 13:530–535
Nilsson M, Hansson S, Carlsson A, Carlsson ML (2007) Differential effects of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist MK-801 on different stages of object recognition memory in mice. Neuroscience 149:123–130
Parker ES, Birnbaum IM, Weingartner H, Hartley JT, Stillman RC, Wyatt RJ (1980) Retrograde enhancement of human memory with alcohol. Psychopharmacology 69:219–222
Prediger RDS, Takahashi RN (2003) Ethanol improves short-term social memory in rats. Involvement of opioid and muscarinic receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 462:115–123
Prediger RDS, Batista LC, Miyoshi E, Takahashi RN (2004) Facilitation of short-term social memory by ethanol in rats is mediated by dopaminergic receptors. Behav Brain Res 153:149–157
Prediger RDS, Batista LC, Takahashi RN (2005a) Caffeine reverses age-related deficits in olfactory discrimination and social recognition memory in rats—involvement of adenosine A(1) and A(2A) receptors. Neurobiol Aging 26:957–964
Prediger RDS, Fernandes D, Takahashi RN (2005b) Blockade of adenosine A(2A) receptors reverses short-term social memory impairments in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Behav Brain Res 159:197–205
Prediger RDS, Pamplona FA, Fernandes D, Takahashi RN (2005c) Caffeine improves spatial learning deficits in an animal model of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)—the spontaneously hypertensive rat (SHR). Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 8:583–594
Prickaerts J, Steinbusch HWM, Smits JFM, de Vente J (1997) Possible role of nitric oxide-cyclic GMP pathway in object recognition memory: effects of 7-nitroindazole and zaprinast. Eur J Pharmacol 337:125–136
Prickaerts J, Sik A, van Staveren WCG, Koopmans G, Steinbusch HWM, van der Staay FJ, de Vente J, Blokland A (2004) Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibition improves early memory consolidation of object information. Neurochem Int 45:915–928
Riedel G, Platt B, Micheau J (2003) Glutamate receptor function in learning and memory. Behav Brain Res 140:1–47
Rodrigues SM, Schafe GE, LeDoux JE (2001) Intra-amygdala blockade of the NR2B subunit of the NMDA receptor disrupts the acquisition but not the expression of fear conditioning. J Neurosci 21:6889–6896
Ryabinin AE, Miller MN, Durrant S (2002) Effects of acute alcohol administration on object recognition learning in C57BL/6J mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 71:307–312
Sara SJ, Hars B (2006) In memory of consolidation. Learn Memory 13:515–521
Schafe GE, LeDoux JE (2000) Memory consolidation of auditory Pavlovian fear conditioning requires protein synthesis and protein kinase A in the amygdala. J Neurosci 20:RC96
Silvers JM, Tokunaga S, Berry RB, White AM, Matthews DB (2003) Impairments in spatial learning and memory: ethanol, allopregnanolone, and the hippocampus. Brain Res Rev 43:275–284
Simola N, Morelli M, Seeman P (2008) Increase of Dopamine D2High receptors in the striatum of rats sensitized to caffeine motor effects. Synapse 62:394–397
Squire LR (2006) Lost forever or temporarily misplaced? The long debate about the nature of memory impairment. Learn Memory 13:522–529
Steckler T, Drinkenburg W, Sahgal A, Aggleton JP (1998) Recognition memory in rats—I. Concepts and classification. Prog Neurobiol 54:289–311
Sweeney DF (1989) Alcohol versus mnemosyne—blackouts. J Subst Abuse Treat 6:159–162
Tillerson JL, Caudle WM, Parent JM, Gong C, Schallert T, Miller GW (2006) Olfactory discrimination deficits in mice lacking the dopamine transporter or the D2 dopamine receptor. Behav Brain Res 172:97–105
Weitemier AZ, Ryabinin AE (2003) Alcohol-induced memory impairment in trace fear conditioning: a hippocampus-specific effect. Hippocampus 13:305–315
White AM (2003) What happened? Alcohol, memory blackouts, and the brain. Alcohol Res Health 27:186–196
White AM, Matthews DB, Best PJ (2000) Ethanol, memory, and hippocampal function: a review of recent findings. Hippocampus 10:88–93
Wixted JT (2005) A theory about why we forget what we once knew. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 14:6–9
Yang M, Soohoo D, Soelaiman S, Kalla R, Zablocki J, Chu N, Leung K, Yao L, Diamond I, Belardinelli L, Shryock JC (2007) Characterization of the potency, selectivity and pharmacokinetic profile for six adenosine A2A receptor antagonists. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol 375:133–144
Zhang Z, Morse AC, Koob GF, Schulteis G (2007) Dose- and time-dependent expression of anxiety-like behavior in the elevated plus-maze during withdrawal from acute and repeated intermittent ethanol intoxication in rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:1811–1819
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank John Heymann and Whitney O’Connell for their indispensable contributions to the experimental design and tireless efforts with regard to behavioral testing. This work was supported by NIH grants NS19608, HD02023, and NS042345.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary online material
(DOC 986 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spinetta, M.J., Woodlee, M.T., Feinberg, L.M. et al. Alcohol-induced retrograde memory impairment in rats: prevention by caffeine. Psychopharmacology 201, 361–371 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1294-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1294-5