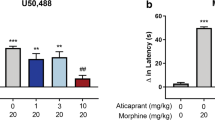
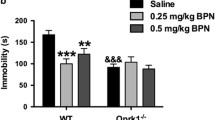
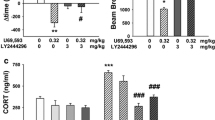
Abstract
Rationale
Recent evidence suggests a role for the dynorphin/kappa-opioid receptor (KOR) system in the expression of stress-induced behaviors. Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats exhibit increased depression-like and anxiety-like responses in behavioral tests compared to other strains and may be a model of comorbid depression and anxiety characterized by increased activity within the dynorphin/KOR system. Though KOR antagonists produce antidepressant-like effects in WKY rats, their effects in tests of anxiety-like behavior have not been examined in the WKY strain.
Objective
The aim of the current study was to investigate the effects of the KOR antagonist 2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-N-methyl-N-[(1S)-1-(3-isothiocyanatophenyl)-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)ethyl]acetamide hydrochloride (DIPPA) on the behavior of WKY rats and Sprague Dawley (SD) rats in tests of anxiety-like behavior.
Methods
The novelty-induced hypophagia and defensive burying tests were used to measure anxiety-like behavior in WKY and SD rats and determine the effects of DIPPA on anxiety-like behavior in both strains.
Results
WKY rats displayed greater amounts of anxiety-like behavior compared to SD rats. DIPPA produced anxiolytic-like effects in both tests in both strains.
Conclusions
WKY rats display more anxiety-like behavior at baseline compared to SD rats, and DIPPA produced anxiolytic-like effects in both WKY and SD rats. These findings support previous research suggesting that KOR antagonists possess anxiolytic-like properties and may potentially represent a novel class of treatments for mood disorders.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadiyeh N, Churchill GA, Shimomura K, Solberg LC, Takahashi JS, Redei EE (2003) X-linked and lineage-dependent inheritance of coping responses to stress. Mamm Genome 14:748–757
Armario A, Gavalda A, Marti J (1995) Comparison of the behavioural and endocrine response to forced swimming stress in five inbred strains of rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 20:879–890
Bechtholt AJ, Valentino RJ, Lucki I (2008) Overlapping and distinct brain regions associated with the anxiolytic effects of chlordiazepoxide and chronic fluoxetine. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2117–2130
Bodnoff SR, Suranyi-Cadotte B, Aitken DH, Quirion R, Meaney MJ (1988) The effects of chronic antidepressant treatment in an animal model of anxiety. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 95:298–302
Borsini F, Podhorna J, Marazziti D (2002) Do animal models of anxiety predict anxiolytic-like effects of antidepressants? Psychopharmacology (Berl) 163:121–141
Britton DR, Britton KT (1981) A sensitive open field measure of anxiolytic drug activity. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:577–582
Bruchas MR, Land BB, Chavkin C (2009) The dynorphin/kappa opioid system as a modulator of stress-induced and pro-addictive behaviors. Brain Res 1314:44–55
Carr GV, Bangasser DA, Bethea T, Young M, Valentino RJ, Lucki I (2010) Antidepressant-like effects of kappa opioid receptor antagonists in Wistar-Kyoto rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:752–763
Chang AC, Takemori AE, Portoghese PS (1994) 2-(3, 4-Dichlorophenyl)-N-methyl-N-[(1S)-1-(3-isothiocyanatophenyl)-2-(1-py rrolidinyl)ethyl]acetamide: an opioid receptor affinity label that produces selective and long-lasting kappa antagonism in mice. J Med Chem 37:1547–1549
Chartoff EH, Papadopoulou M, MacDonald ML, Parsegian A, Potter D, Konradi C, Carlezon WA Jr (2009) Desipramine reduces stress-activated dynorphin expression and CREB phosphorylation in NAc tissue. Mol Pharmacol 75:704–712
Cooper SJ, Jackson A, Kirkham TC (1985) Endorphins and food intake: kappa opioid receptor agonists and hyperphagia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:889–901
De Boer SF, Koolhaas JM (2003) Defensive burying in rodents: ethology, neurobiology and psychopharmacology. Eur J Pharmacol 463:145–161
De La Garza R 2nd, Mahoney JJ 3rd (2004) A distinct neurochemical profile in WKY rats at baseline and in response to acute stress: implications for animal models of anxiety and depression. Brain Res 1021:209–218
Dulawa SC, Holick KA, Gundersen B, Hen R (2004) Effects of chronic fluoxetine in animal models of anxiety and depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1321–1330
Fava M, Rush AJ, Alpert JE, Balasubramani GK, Wisniewski SR, Carmin CN, Biggs MM, Zisook S, Leuchter A, Howland R, Warden D, Trivedi MH (2008) Difference in treatment outcome in outpatients with anxious versus nonanxious depression: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry 165:342–351
Grillon C, Levenson J, Pine DS (2007) A single dose of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram exacerbates anxiety in humans: a fear-potentiated startle study. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:225–231
Gutierrez-Mariscal M, de Gortari P, Lopez-Rubalcava C, Martinez A, Joseph-Bravo P (2008) Analysis of the anxiolytic-like effect of TRH and the response of amygdalar TRHergic neurons in anxiety. Psychoneuroendocrinology 33:198–213
Howard O, Carr GV, Hill TE, Valentino RJ, Lucki I (2008) Differential blockade of CRF-evoked behaviors by depletion of norepinephrine and serotonin in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 199:569–582
Jiao X, Pare WP, Tejani-Butt S (2003) Strain differences in the distribution of dopamine transporter sites in rat brain. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:913–919
Joffe RT, Bagby RM, Levitt A (1993) Anxious and nonanxious depression. Am J Psychiatry 150:1257–1258
Knoll AT, Carlezon WA Jr (2009) Dynorphin, stress, and depression. Brain Res 1314:56–73
Knoll AT, Meloni EG, Thomas JB, Carroll FI, Carlezon WA (2007) Anxiolytic-like effects of {kappa}-opioid receptor antagonists in models of unlearned and learned fear in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 323:838–845
Land BB, Bruchas MR, Lemos JC, Xu M, Melief EJ, Chavkin C (2008) The dysphoric component of stress is encoded by activation of the dynorphin kappa-opioid system. J Neurosci 28:407–414
Lopez-Rubalcava C, Lucki I (2000) Strain differences in the behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs in the rat forced swimming test. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:191–199
Marshall RD, Printz D, Cardenas D, Abbate L, Liebowitz MR (1995) Adverse events in PTSD patients taking fluoxetine. Am J Psychiatry 152:1238–1239
McLaughlin JP, Marton-Popovici M, Chavkin C (2003) Kappa opioid receptor antagonism and prodynorphin gene disruption block stress-induced behavioral responses. J Neurosci 23:5674–5683
McLaughlin JP, Li S, Valdez J, Chavkin TA, Chavkin C (2006) Social defeat stress-induced behavioral responses are mediated by the endogenous kappa opioid system. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1241–1248
Merali Z, Levac C, Anisman H (2003) Validation of a simple, ethologically relevant paradigm for assessing anxiety in mice. Biol Psychiatry 54:552–565
Pardon MC, Ma S, Morilak DA (2003) Chronic cold stress sensitizes brain noradrenergic reactivity and noradrenergic facilitation of the HPA stress response in Wistar Kyoto rats. Brain Res 971:55–65
Pare WP (1989) Stress ulcer susceptibility and depression in Wistar Kyoto (WKY) rats. Physiol Behav 46:993–998
Pare WP (1992) The performance of WKY rats on three tests of emotional behavior. Physiol Behav 51:1051–1056
Pare WP (1994) Open field, learned helplessness, conditioned defensive burying, and forced-swim tests in WKY rats. Physiol Behav 55:433–439
Pare WP, Kluczynski J (1997) Differences in the stress response of Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats from different vendors. Physiol Behav 62:643–648
Pearson KA, Stephen A, Beck SG, Valentino RJ (2006) Identifying genes in monoamine nuclei that may determine stress vulnerability and depressive behavior in Wistar-Kyoto rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2449–2461
Pfeiffer PN, Ganoczy D, Ilgen M, Zivin K, Valenstein M (2009) Comorbid anxiety as a suicide risk factor among depressed veterans. Depress Anxiety 26:752–757
Ramos A, Berton O, Mormede P, Chaouloff F (1997) A multiple-test study of anxiety-related behaviours in six inbred rat strains. Behav Brain Res 85:57–69
Rittenhouse PA, Lopez-Rubalcava C, Stanwood GD, Lucki I (2002) Amplified behavioral and endocrine responses to forced swim stress in the Wistar-Kyoto rat. Psychoneuroendocrinology 27:303–318
Sareen J, Cox BJ, Afifi TO, de Graaf R, Asmundson GJ, ten Have M, Stein MB (2005) Anxiety disorders and risk for suicidal ideation and suicide attempts: a population-based longitudinal study of adults. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:1249–1257
Servatius RJ, Jiao X, Beck KD, Pang KC, Minor TR (2008) Rapid avoidance acquisition in Wistar-Kyoto rats. Behav Brain Res 192:191–197
Shephard RA, Broadhurst PL (1982) Effects of diazepam and picrotoxin on hyponeophagia in rats. Neuropharmacology 21:771–773
Sibille E, Sarnyai Z, Benjamin D, Gal J, Baker H, Toth M (1997) Antisense inhibition of 5-hydroxytryptamine2a receptor induces an antidepressant-like effect in mice. Mol Pharmacol 52:1056–1063
Silva RM, Grossman HC, Hadjimarkou MM, Rossi GC, Pasternak GW, Bodnar RJ (2002) Dynorphin A(1-17)-induced feeding: pharmacological characterization using selective opioid antagonists and antisense probes in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 301:513–518
Sipols AJ, Bayer J, Bennett R, Figlewicz DP (2002) Intraventricular insulin decreases kappa opioid-mediated sucrose intake in rats. Peptides 23:2181–2187
Solberg LC, Baum AE, Ahmadiyeh N, Shimomura K, Li R, Turek FW, Churchill GA, Takahashi JS, Redei EE (2004) Sex- and lineage-specific inheritance of depression-like behavior in the rat. Mamm Genome 15:648–662
Sullivan PF, Neale MC, Kendler KS (2000) Genetic epidemiology of major depression: review and meta-analysis. Am J Psychiatry 157:1552–1562
Terlecki LJ, Pinel JPJ, Treit D (1979) Conditioned and unconditioned defensive burying in the rat. Learn Motiv 10:337–350
Treit D (1990) A comparison of anxiolytic and nonanxiolytic agents in the shock-probe/burying test for anxiolytics. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 36:203–205
Treit D, Pesold C (1990) Septal lesions inhibit fear reactions in two animal models of anxiolytic drug action. Physiol Behav 47:365–371
Treit D, Pinel JP, Fibiger HC (1981) Conditioned defensive burying: a new paradigm for the study of anxiolytic agents. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 15:619–626
Van Bockstaele EJ, Reyes BA, Valentino RJ (2009) The locus coeruleus: a key nucleus where stress and opioids intersect to mediate vulnerability to opiate abuse. Brain Res 1314:162–174
Wittmann W, Schunk E, Rosskothen I, Gaburro S, Singewald N, Herzog H, Schwarzer C (2009) Prodynorphin-derived peptides are critical modulators of anxiety and regulate neurochemistry and corticosterone. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:775–785
Zinner SH (1994) Panic attacks precipitated by sertraline. Am J Psychiatry 151:147–148
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the valuable technical assistance of Matthew Young. This research was supported by funds from AstraZeneca and the National Institute of Mental Health (T32 MH14652).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carr, G.V., Lucki, I. Comparison of the kappa-opioid receptor antagonist DIPPA in tests of anxiety-like behavior between Wistar Kyoto and Sprague Dawley rats. Psychopharmacology 210, 295–302 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1832-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-1832-9