Abstract
Rationale
Mesolimbic dopamine (DA), particularly in the nucleus accumbens, importantly regulates activational aspects of maternal responsiveness. DA antagonism and accumbens DA depletions interfere with early postpartum maternal motivation by selectively affecting most forms of active maternal behaviors, while leaving nursing behavior relatively intact. Considerable evidence indicates that there is a functional interaction between DA D2 and adenosine A2A receptors in striatal areas, including the nucleus accumbens.
Objective
This study was conducted to determine if adenosine A2A receptor antagonism could reverse the effects of DA receptor antagonism on early postpartum maternal behavior.
Methods
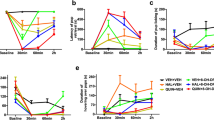
The adenosine A2A receptor antagonist MSX-3 (0.25–2.0 mg/kg, IP) was investigated for its ability to reverse the effects of the DA D2 receptor antagonist haloperidol (0.1 mg/kg, IP) on the maternal behavior of early postpartum female rats.
Results
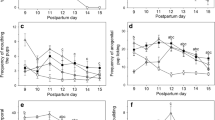
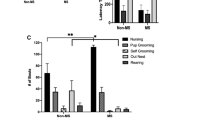
Haloperidol severely impaired the expression of active maternal components, including retrieval and grouping the pups at the nest site, pup licking, and nest building. Co-administration of MSX-3 (0.25–2.0 mg/kg, IP) with haloperidol produced a dose-related attenuation of the haloperidol-induced behavioral deficits in early postpartum females. Doses of MSX-3 that effectively reversed the effects of haloperidol (0.5, 1.0 mg/kg), when administered in the absence of haloperidol, did not affect maternal responding or locomotor activity.
Conclusions
Adenosine and DA systems interact to regulate early postpartum maternal responsiveness. This research may potentially contribute to the development of strategies for treatments of psychiatric disorders during the postpartum period, with particular emphasis in maintaining or restoring the mother–infant relationship.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberman JE, Salamone JD (1999) Nucleus accumbens dopamine depletions make rats more sensitive to high ratio requirements but do not impair primary food reinforcement. Neuroscience 92:545–552
Azdad K, Gall D, Woods AS, Ledent C, Ferré S, Schiffmann SN (2009) Dopamine D2 and adenosine A2A receptors regulate NMDA-mediated excitation in accumbens neurons through A2A–D2 receptor heteromerization. Neuropsychopharmacology 34(4):972–986
Bardgett ME, Depenbrock M, Downs N, Points M, Green L (2009) Dopamine modulates effort-based decision making in rats. Behav Neurosci 123:463–467
Barraco RA, Martens KA, Parizon M, Normile HJ (1993) Adenosine A2A receptors in the nucleus accumbens mediate locomotor depression. Brain Res Bull 31:397–404
Boegman RJ, Vincent SR (1996) Involvement of adenosine and glutamate receptors in the induction of c-fos in the striatum by haloperidol. Synapse 22:70–77
Bosanac P, Buist A, Burrows G (2003) Motherhood and schizophrenic illnesses: a review of the literature. Aust N Z J Psychiatry 37(1):24–30
Campbell SB, Matestic P, von Stauffenberg C, Mohan R, Kirchner T (2007) Trajectories of maternal depressive symptoms, maternal sensitivity, and children’s functioning at school entry. Dev Psychol 43(5):1202–1215
Carter AS, Garrity-Rokous FE, Chazan-Cohen R, Little C, Briggs-Gowan MJ (2001) Maternal depression and comorbidity: predicting early parenting, attachment security, and toddler social-emotional problems and competencies. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40(1):18–26
Champagne FA, Chretien P, Stevenson CW, Zhang TY, Gratton A, Meaney MJ (2004) Variations in nucleus accumbens dopamine associated with individual differences in maternal behavior in the rat. J Neurosci 24(17):4113–4123
Chen JF, Moratalla R, Impagnatiello F, Grandy DK, Cuellar B, Rubinstein M, Beilstein MA, Hacket E, Fink JS, Low MJ, Ongini E, Schwarzschild MA (2001) The role of the D2 dopamine receptor (D2R) in A2A adenenosine-receptor (A2AR) mediated behavioral and cellular responses as revealed by A2A and D2 receptor knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1970–1975
Correa M, Wisniecki A, Betz A, Dobson DR, O’Neill MF, O’Neill MJ, Salamone JD (2004) The adenosine A2A antagonist KF17837 reverses the locomotor suppression and tremulous jaw movements induced by haloperidol in rats: possible relevance to Parkinsonism. Behav Brain Res 148:47–54
D'Aquila PS, Collu M, Gessa GL, Serra G (2000) The role of dopamine in the mechanism of action of antidepressant drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 405(1–3):365–373
DeMet EM, Chicz-DeMet A (2002) Localization of adenosine A2A receptors in rat brain with [3H]ZM-241385. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 366:478–481
Demyttenaere K, De Fruyt J, Stahl SM (2005) The many faces of fatigue in major depressive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 8(1):93–105
Dunlop BW, Nemeroff CB (2007) The role of dopamine in the pathophysiology of depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64(3):327–337
El Yacoubi M, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Costentin J, Vaugeois J (2000) SCH 58261 and ZM 241385 differentially prevent the motor effects of CGS 21680 in mice: evidence for a functional ‘atypical’ adenosine A2A receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 401(1):63–77
Farrar AM, Pereira M, Velasco F, Hockemeyer J, Müller CE, Salamone JD (2007) Adenosine A2A receptor antagonism reverses the effects of dopamine receptor antagonism on instrumental output and effort-related choice in the rat: implications for studies of psychomotor slowing. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 191:579–586
Farrar AM, Segovia KN, Randall PA, Nunes EJ, Collins LE, Stopper CM, Port RG, Hockemeyer J, Müller CE, Correa M, Salamone JD (2010) Nucleus accumbens and effort-related functions: behavioral and neural markers of the interactions between adenosine A2A and dopamine D2 receptors. Neuroscience 166(4):1056–1067
Ferré S (1997) Adenosine-dopamine interactions in the ventral striatum. Implications for the treatment of schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 133:107–120
Ferré S, Fredholm BB, Morelli M, Popoli P, Fuxe K (1997) Adenosine-dopamine receptor-receptor interactions as an integrative mechanism in the basal ganglia. Trends Neurosci 20:482–487
Ferré S, Quiroz C, Woods AS, Cunha R, Popoli P, Ciruela F, Lluis C, Franco R, Azdad K, Schiffmann SN (2008) An update on adenosine A2A-dopamine D2 receptor interactions: implications for the function of G protein-coupled receptors. Curr Pharm Des 14:1468–1474
Field T (2010) Postpartum depression effects on early interactions, parenting, and safety practices: a review. Infant Behav Dev 33(1):1–6
Fink JS, Weaver DR, Rivkees SA, Peterfreund RA, Pollack AE, Adler EM, Reppert SM (1992) Molecular cloning of the rat A2 adenosine receptor: selective co-expression with D2 dopamine receptors in rat striatum. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 14:186–195
Floresco SB, St Onge JR, Ghods-Sharifi S, Winstanley CA (2008) Cortico-limbic-striatal circuits subserving different forms of cost-benefit decision making. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 8(4):375–389
Font L, Mingote S, Farrar AM, Pereira M, Worden L, Stopper C, Port RG, Salamone JD (2008) Intra-accumbens injections of the adenosine A2A agonist CGS 21680 affect effort-related choice behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 199:515–526
Fuxe K, Agnati LF, Jacobsen K, Hillion J, Canals M, Torvinen M, Tinner-Staines B, Staines W, Rosin D, Terasmaa A, Popoli P, Leo G, Vergoni V, Lluis C, Ciruela F, Franco R, Ferre S (2003) Receptor heteromerization in adenosine A2A receptor signaling: relevance for striatal function and Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 61:S19–S23
Goodman SH, Gotlib IH (1999) Risk for psychopathology in children of depressed mothers: a developmental model for understanding mechanisms of transmission. Psychol Rev 106:458–490
Hansen S, Harthon C, Wallin E, Löfberg L, Svensson K (1991a) Mesotelencephalic dopamine system and reproductive behavior in the female rat: effects of ventral tegmental 6-hydroxydopamine lesions on maternal and sexual responsiveness. Behav Neurosci 105(4):588–598
Hansen S, Harthon C, Wallin E, Löfberg L, Svensson K (1991b) The effects of 6-OHDA-induced dopamine depletions in the ventral or dorsal striatum on maternal and sexual behavior in the female rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 39(1):71–77
Hansen S, Bergvall AH, Nyiredi S (1993) Interaction with pups enhances dopamine release in the ventral striatum of maternal rats: a microdialysis study. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 45(3):673–676
Hauber W, Münkle M (1997) Motor depressant effects mediated by dopamine D2 and adenosine A2A receptors in the nucleus accumbens and the caudate-putamen. Eur J Pharmacol 323:127–131
Hauber W, Neuscheler P, Nagel J, Müller CE (2001) Catalepsy induced by a blockade of dopamine D1 or D2 receptors was reversed by a concomitant blockade of adenosine A2A receptors in the caudate-putamen of rats. Eur J Neurosci 14:1287–1293
Hettinger BD, Lee A, Linden J, Rosin DL (2001) Ultrastructural localization of adenosine A2A receptors suggests multiple cellular sites for modulation of GABAergic neurons in rat striatum. J Comp Neurol 431:331–346
Hockemeyer J, Burbiel JC, Müller CE (2004) Multigram-scale syntheses, stability, and photoreactions of A2A adenosine receptor antagonists with 8-styrylxanthine structure: potential drugs for Parkinson’s disease. J Org Chem 69(10):3308–3318
Ikemoto S, Panksepp J (1999) The role of nucleus accumbens dopamine in motivated behavior: a unifying interpretation with special reference to reward-seeking. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 31(1):6–41
Ishiwari K, Madson LJ, Farrar AM, Mingote SM, Valenta JP, DiGianvittorio MD, Frank LE, Correa M, Hockemeyer J, Müller C, Salamone JD (2007) Injections of the selective adenosine A2A antagonist MSX-3 into the nucleus accumbens core attenuate the locomotor suppression induced by haloperidol in rats. Behav Brain Res 178:190–199
Jameson PB, Gelfand DM, Kulcsar E, Teti DM (1997) Mother–toddler interaction patterns associated with maternal depression. Dev Psychopathol 9(3):537–550
Kapur S, VanderSpek SC, Brownlee BA, Nobrega JN (2003) Antipsychotic dosing in preclinical models is often unrepresentative of the clinical condition: a suggested solution based on in vivo occupancy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305(2):625–631
Keer SE, Stern JM (1999) Dopamine receptor blockade in the nucleus accumbens inhibits maternal retrieval and licking, but enhances nursing behavior in lactating rats. Physiol Behav 67(5):659–669
Lavi-Avnon Y, Weller A, Finberg JP, Gispan-Herman I, Kinor N, Stern Y, Schroeder M, Gelber V, Bergman SY, Overstreet DH, Yadid G (2008) The reward system and maternal behavior in an animal model of depression: a microdialysis study. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 196(2):281–291
Li M, Davidson P, Budin R, Kapur S, Fleming AS (2004) Effects of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on maternal behavior in postpartum female rats. Schizophr Res 70(1):69–80
Lyons-Ruth K (2008) Contributions of the mother–infant relationship to dissociative, borderline, and conduct symptoms in young adulthood. Infant Ment Health J 29(3):203–218
MacGibbon GA, Lawlor PA, Bravo R, Dragunow M (1994) Clozapine and haloperidol produce a differential pattern of immediate early gene expression in rat caudate-putamen, nucleus accumbens, lateral septum and islands of Calleja. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 23:21–32
McCormick PN, Kapur S, Graff-Guerrero A, Raymond R, Nobrega JN, Wilson AA (2010) The antipsychotics olanzapine, risperidone, clozapine, and haloperidol are D2-selective ex vivo but not in vitro. Neuropsychopharmacology 35(8):1826–1835
Mingote S, Font L, Farrar AM, Vontell R, Worden LT, Stopper CM, Port RG, Sink KS, Bunce JG, Chrobak JJ, Salamone JD (2008a) Nucleus accumbens adenosine A2A receptors regulate exertion of effort by acting on the ventral striatopallidal pathway. J Neurosci 28:9037–9046
Mingote S, Pereira M, Farrar AM, McLaughlin PJ, Salamone JD (2008b) Systemic administration of the adenosine A2A agonist CGS 21680 induces sedation at doses that suppress lever pressing and food intake. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 89(3):345–351
Mott AM, Nunes EJ, Collins LE, Port RG, Sink KS, Hockemeyer J, Müller CE, Salamone JD (2009) The adenosine A2A antagonist MSX-3 reverses the effects of the dopamine antagonist haloperidol on effort-related decision making in a T-maze cost/benefit procedure. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 204:103–112
Murray L, Fiori-Cowley A, Hooper R, Cooper P (1996) The impact of postnatal depression and associated adversity on early mother–infant interactions and later infant outcome. Child Dev 67(5):2512–2526
Nagel J, Schladebach H, Koch M, Schwienbacher I, Müller CE, Hauber W (2003) Effects of an adenosine A2A receptor blockade in the nucleus accumbens on locomotion, feeding, and prepulse inhibition in rats. Synapse 49(4):279–286
Numan M, Numan MJ, Pliakou N, Stolzenberg DS, Mullins OJ, Murphy JM, Smith CD (2005) The effects of D1 or D2 dopamine receptor antagonism in the medial preoptic area, ventral pallidum, or nucleus accumbens on the maternal retrieval response and other aspects of maternal behavior in rats. Behav Neurosci 119(6):1588–1604
Numan M, Stolzenberg DS, Dellevigne AA, Correnti CM, Numan MJ (2009) Temporary inactivation of ventral tegmental area neurons with either muscimol or baclofen reversibly disrupts maternal behavior in rats through different underlying mechanisms. Behav Neurosci 123(4):740–751
Nunes EJ, Randall PA, Santerre JL, Given AB, Sager TN, Correa M, Salamone JD (2010) Differential effects of selective adenosine antagonists on the effort-related impairments induced by dopamine D1 and D2 antagonism. Neuroscience 170(1):268–280
O’Neill M, Brown VJ (2006) The effect of the adenosine A2A antagonist KW-6002 on motor and motivational processes in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 184(1):46–55
Overstreet DH (1993) The Flinders sensitive line rats: a genetic animal model of depression. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 17(1):51–68
Parada M, King S, Li M, Fleming AS (2008) The roles of accumbal dopamine D1 and D2 receptors in maternal memory in rats. Behav Neurosci 122(2):368–376
Paris R, Bolton RE, Weinberg MK (2009) Postpartum depression, suicidality, and mother–infant interactions. Arch Womens Ment Health 12(5):309–321
Pereira M, Ferreira A (2006) Demanding pups improve maternal behavioral impairments in sensitized and haloperidol-treated lactating female rats. Behav Brain Res 175(1):139–148
Pinna A, Wardas J, Cozzolino A, Morelli M (1999) Involvement of adenosine A2A receptors in the induction of c-fos expression by clozapine and haloperidol. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:44–51
Pinna A, Wardas J, Simola N, Morelli M (2005) New therapies for the treatment of parkinson’s disease: adenosine A2A receptor antagonists. Life Sci 77:3259–3267
Robertson GS, Fibiger HC (1992) Neuroleptics increase c-fos expression in the forebrain: contrasting effects of haloperidol and clozapine. Neuroscience 46:315–328
Salamone JD, Correa M (2009) Dopamine/adenosine interactions involved in effort-related aspects of food motivation. Appetite 53:422–425
Salamone JD, Correa M, Mingote SM, Weber SM, Farrar AM (2006) Nucleus accumbens dopamine and the forebrain circuitry involved in behavioral activation and effort-related decision making: implications for understanding anergia and psychomotor slowing in depression. Curr Psych 2:267–280
Schiffmann SN, Jacobs O, Vanderhaeghen JJ (1991) Striatal restricted adenosine A2 receptor (RDC8) is expressed by enkephalin but not by substance P neurons: an in situ hybridization histochemistry study. J Neurochem 57:1062–1067
Schotte A, Janssen PF, Bonaventure P, Leysen JE (1996) Endogenous dopamine limits the binding of antipsychotic drugs to D3 receptors in the rat brain: a quantitative autoradiographic study. Histochem J 28(11):791–799
Seip KM, Morrell JI (2009) Transient inactivation of the ventral tegmental area selectively disrupts the expression of conditioned place preference for pup- but not cocaine-paired contexts. Behav Neurosci 123(6):1325–1338
Siegel S (1956) Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences. McGraw-Hill, New York
Silva MR, Bernardi MM, Felicio LF (2001) Effects of dopamine receptor antagonists on ongoing maternal behavior in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 68(3):461–8
Silva MR, Bernardi MM, Cruz-Casallas PE, Felicio LF (2003) Pimozide injections into the Nucleus accumbens disrupt maternal behaviour in lactating rats. Pharmacol Toxicol 93(1):42–47
Spielewoy C, Roubert C, Hamon M, Nosten-Bertrand M, Betancur C, Giros B (2000) Behavioural disturbances associated with hyperdopaminergia in dopamine-transporter knockout mice. Behav Pharmacol 11(3–4):279–290
Stahl SM (2002) The psychopharmacology of energy and fatigue. J Clin Psychiatry 63(1):7–8
Stern JM, Keer SE (1999) Maternal motivation of lactating rats is disrupted by low dosages of haloperidol. Behav Brain Res 99(2):231–239
Stern JM, Protomastro M (2000) Effects of low dosages of apomorphine on maternal responsiveness in lactating rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66(2):353–359
Svenningsson P, Le Moine C, Fisone G, Fredholm BB (1999) Distribution, biochemistry and function of striatal adenosine A2A receptors. Prog Neurobiol 59:355–396
Wan MW, Green J (2009) The impact of maternal psychopathology on child-mother attachment. Arch Womens Ment Health 12(3):123–134
Weinberg MK, Tronick EZ (1998) The impact of maternal psychiatric illness on infant development. J Clin Psychiatry 59(2):53–61
Worden LT, Shahriari M, Farrar AM, Sink KS, Hockemeyer J, Müller CE, Salamone JD (2009) The adenosine A2A antagonist MSX-3 reverses the effort-related effects of dopamine blockade: differential interaction with D1 and D2 family antagonists. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 203(3):489–499
Zhang W, Bymaster FP (1999) The in vivo effects of olanzapine and other antipsychotic agents on receptor occupancy and antagonism of dopamine D1, D2, D3, 5HT2A and muscarinic receptors. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 141(3):267–278
Zhao C, Li M (2010) c-Fos identification of neuroanatomical sites associated with haloperidol and clozapine disruption of maternal behavior in the rat. Neuroscience 166(4):1043–1055
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by NARSAD Young Investigator Award and NIH SOAR DA027945 awarded to MP, NIMH MH078023 awarded to JDS, and NIH DA014025 awarded to JIM. The authors thank the Laboratory Animal Facility staff at Rutgers University, Newark Campus, for animal breeding and care.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pereira, M., Farrar, A.M., Hockemeyer, J. et al. Effect of the adenosine A2A receptor antagonist MSX-3 on motivational disruptions of maternal behavior induced by dopamine antagonism in the early postpartum rat. Psychopharmacology 213, 69–79 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2015-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2015-4