Abstract
Rationale
The placebo effect is a fascinating yet puzzling phenomenon, which has challenged investigators over the past 50 years. In previous studies, the investigators only focused on the placebo effect obtained within a single domain, and pain is the field in which most of the placebo research has been performed. However, recent research by our laboratory (Zhang and Luo in Psychophysiology 46:626–634, 2009; Zhang et al. 2011) showed that, in human subjects, the placebo effect can be transferred from one domain to the other, namely from pain to emotion.
Objectives
The scope of this study was to investigate whether placebo analgesia could affect the depressive behavior in mice.
Materials and methods
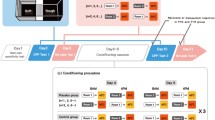
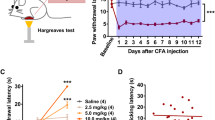
Female C57/BL6 mice were trained to associate the context cue with elevated pain tolerance via a set of procedures. Then the forced swim test and tail suspension test were used to measure the depressive-like behaviors on the test day. Plasma concentrations of adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) and corticosterone were also detected.
Results
Our results showed that the placebo analgesia, which was established by a set of procedures in mice, was transferable and could produce a significant antidepressant effect on depressive test. Plasma levels of corticosterone and ACTH further proved that the placebo analgesia that was established from pain-reducing training not only induced a significant placebo effect on pain, but also decreased significantly the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal axis (HPA) response to stress and produced a stress-alleviating effect.
Conclusions
These data show that placebo analgesia affects the behavioral despair tests and hormonal secretions in mice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amanzio M, Benedetti F (1999) Neuropharmacological dissection of placebo analgesia: expectation-activated opioid systems versus conditioning-activated specific subsystems. J Neurosci 19:484–494
Aulakh CS, Hill JL, Murphy DL (1993) Attenuation of hypercortisolemia in fawn-hooded rats by antidepressant drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 240:85–88
Benedetti F (2007) Placebo and endogenous mechanisms of analgesia. Handb Exp Pharmacol 177:393–413
Benedetti F, Arduino C, Amanzio M (1999) Somatotopic activation of opioid systems by target-directed expectations of analgesia. J Neurosci 19:3639–3648
Benedetti F, Pollo A, Lopiano L, Lanotte M, Vighetti S, Rainero I (2003a) Conscious expectation and unconscious conditioning in analgesic, motor, and hormonal placebo/nocebo responses. J Neurosci 23:4315–4323
Benedetti F, Rainero I, Pollo A (2003b) New insights into placebo analgesia. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 16:515–519
Bespalov AY, Zvartau EE, Beardsley PM (2001) Opioid-NMDA receptor interactions may clarify conditioned (associative) components of opioid analgesic tolerance. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 25:343–353
Bourin M, Chenu F, Ripoll N, David DJ (2005) A proposal of decision tree to screen putative antidepressants using forced swim and tail suspension tests. Behav Brain Res 164:266–269
Bryant CD, Roberts KW, Culbertson CS, Le A, Evans CJ, Fanselow MS (2009) Pavlovian conditioning of multiple opioid-like responses in mice. Drug Alcohol Depend 103:74–83
Carbajal D, Ravelo Y, Molina V, Mas R, Arruzazabala Mde L (2009) D-004, a lipid extract from royal palm fruit, exhibits antidepressant effects in the forced swim test and the tail suspension test in mice. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:465–468
Colloca L, Petrovic P, Wager TD, Ingvar M, Benedetti F (2010) How the number of learning trials affects placebo and nocebo responses. Pain 151:430–439
Cryan JF, Holmes A (2005) The ascent of mouse: advances in modelling human depression and anxiety. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:775–790
Drago F, Nicolosi A, Micale V, Lo Menzo G (2001) Placebo affects the performance of rats in models of depression: is it a good control for behavioral experiments? Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 11:209–213
Eippert F, Bingel U, Schoell ED, Yacubian J, Klinger R, Lorenz J, Buchel C (2009) Activation of the opioidergic descending pain control system underlies placebo analgesia. Neuron 63:533–543
Fanselow MS, Poulos AM (2005) The neuroscience of mammalian associative learning. Annu Rev Psychol 56:207–234
Gehlert DR, Rasmussen K, Shaw J, Li X, Ardayfio P, Craft L, Coskun T, Zhang HY, Chen Y, Witkin JM (2009) Preclinical evaluation of melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 antagonism for the treatment of obesity and depression. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 329:429–438
Gourley SL, Kiraly DD, Howell JL, Olausson P, Taylor JR (2008) Acute hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor restores motivational and forced swim performance after corticosterone. Biol Psychiatry 64:884–890
Guo JY, Li CY, Ruan YP, Sun M, Qi XL, Zhao BS, Luo F (2009) Chronic treatment with celecoxib reverses chronic unpredictable stress-induced depressive-like behavior via reducing cyclooxygenase-2 expression in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 612:54–60
Guo JY, Wang JY, Luo F (2010) Dissection of placebo analgesia in mice: the conditions for activation of opioid and non-opioid systems. J Psychopharmacol 24:1561–1567
Ide S, Fujiwara S, Fujiwara M, Sora I, Ikeda K, Minami M, Uhl GR, Ishihara K (2010) Antidepressant-like effect of venlafaxine is abolished in mu-opioid receptor-knockout mice. J Pharmacol Sci 114:107–110
Johnson SA, Fournier NM, Kalynchuk LE (2006) Effect of different doses of corticosterone on depression-like behavior and HPA axis responses to a novel stressor. Behav Brain Res 168:280–288
Kirsch I (2004) Conditioning, expectancy, and the placebo effect: comment on Stewart-Williams and Podd. Psychol Bull 130:341–343, discussion 344–5
Klinger R, Soost S, Flor H, Worm M (2007) Classical conditioning and expectancy in placebo hypoalgesia: a randomized controlled study in patients with atopic dermatitis and persons with healthy skin. Pain 128:31–39
Levine JD, Gordon NC, Fields HL (1978) The mechanism of placebo analgesia. Lancet 2:654–657
Maier SF, Watkins LR (2005) Stressor controllability and learned helplessness: the roles of the dorsal raphe nucleus, serotonin, and corticotropin-releasing factor. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:829–841
Martin AL, Brown RE (2009) The lonely mouse: verification of a separation-induced model of depression in female mice. Behav Brain Res 207:196–207
Marzouk HF, Zuyderwijk J, Uitterlinden P, van Koetsveld P, Blijd JJ, Abou-Hashim EM, el-Kannishy MH, de Jong FH, Lamberts SW (1991) Caffeine enhances the speed of the recovery of the hypothalamo-pituitary-adrenocortical axis after chronic prednisolone administration in the rat. Neuroendocrinology 54:439–446
Millan MJ (2002) Descending control of pain. Prog Neurobiol 66:355–474
Montgomery GH, Kirsch I (1997) Classical conditioning and the placebo effect. Pain 72:107–113
Petrovic P, Dietrich T, Fransson P, Andersson J, Carlsson K, Ingvar M (2005) Placebo in emotional processing–induced expectations of anxiety relief activate a generalized modulatory network. Neuron 46:957–969
Pollo A, Benedetti F (2009) The placebo response: neurobiological and clinical issues of neurological relevance. Prog Brain Res 175:283–294
Porsolt RD (1979) Animal model of depression. Biomedicine 30:139–140
Porsolt RD, Bertin A, Jalfre M (1977) Behavioral despair in mice: a primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Thér 229:327–336
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N, Jalfre M (1978) Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 47:379–391
Price DD, Milling LS, Kirsch I, Duff A, Montgomery GH, Nicholls SS (1999) An analysis of factors that contribute to the magnitude of placebo analgesia in an experimental paradigm. Pain 83:147–156
Rescorla RA (1988) Behavioral studies of Pavlovian conditioning. Annu Rev Neurosci 11:329–352
Roberts WA, Feeney MC, Macpherson K, Petter M, McMillan N, Musolino E (2008) Episodic-like memory in rats: is it based on when or how long ago? Science 320:113–115
Siegel S (1977) Morphine tolerance acquisition as an associative process. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 3:1–13
Steru L, Chermat R, Thierry B, Simon P (1985) The tail suspension test: a new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 85:367–370
Stewart-Williams S, Podd J (2004) The placebo effect: dissolving the expectancy versus conditioning debate. Psychol Bull 130:324–340
Tanke MA, Fokkema DS, Doornbos B, Postema F, Korf J (2008) Sustained release of corticosterone in rats affects reactivity, but does not affect habituation to immobilization and acoustic stimuli. Life Sci 83:135–141
Thompson WG (2000) Placebos: a review of the placebo response. Am J Gastroenterol 95:1637–1643
Wager TD, Nitschke JB (2005) Placebo effects in the brain: linking mental and physiological processes. Brain Behav Immun 19:281–282
Wager TD, Rilling JK, Smith EE, Sokolik A, Casey KL, Davidson RJ, Kosslyn SM, Rose RM, Cohen JD (2004) Placebo-induced changes in FMRI in the anticipation and experience of pain. Science 303:1162–1167
Wager TD, Scott DJ, Zubieta JK (2007) Placebo effects on human mu-opioid activity during pain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:11056–11061
Zhang W, Luo J (2009) The transferable placebo effect from pain to emotion: changes in behavior and EEG activity. Psychophysiology 46:626–634
Zhang W, Qin S, Guo J, Luo J (2011) A follow-up fMRI study of a transferable placebo anxiolytic effect. Psychophysiology. doi:10.1111/j.1469-8986.2011.01178.x
Zhao ZQ, Gao YJ, Sun YG, Zhao CS, RWt Gereau, Chen ZF (2007) Central serotonergic neurons are differentially required for opioid analgesia but not for morphine tolerance or morphine reward. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:14519–14524
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Professor Fabrizio Benedetti (University of Turin Medical School, Torino, Italy) for his review and helpful comments on this article. This work was supported by the project from the Key Laboratory of Mental Health, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Young Scientist project from IPCAS (08CX043004), National Hi-Tech Research and Development Program of China (grant nos. 2006AA02Z431, 2008AA021204, and 2008AA022604), National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 30800301, 30970890), Knowledge Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (grant nos. KSCX2-YW-R-28, KSCX2-YW-R-254, KSCX2-EW-Q-18, and KSCX2-EW-J-8), and National Basic Research Program of China (grant no. 2010CB833904).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, JY., Yuan, XY., Sui, F. et al. Placebo analgesia affects the behavioral despair tests and hormonal secretions in mice. Psychopharmacology 217, 83–90 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2259-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2259-7