Abstract
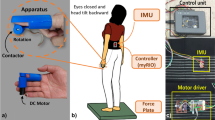
The present paper introduces an original biofeedback system for improving human balance control, whose underlying principle consists in providing additional sensory information related to foot sole pressure distribution to the user through a tongue-placed tactile output device. To assess the effect of this biofeedback system on postural control during quiet standing, ten young healthy adults were asked to stand as immobile as possible with their eyes closed in two conditions of No-biofeedback and Biofeedback. Centre of foot pressure (CoP) displacements were recorded using a force platform. Results showed reduced CoP displacements in the Biofeedback relative to the No-biofeedback condition. The present findings evidenced the ability of the central nervous system to efficiently integrate an artificial plantar-based, tongue-placed tactile biofeedback for controlling control posture during quiet standing.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bach-y-Rita P, Collins CC, Saunders F, White B, Scadden L (1969) Vision substitution by tactile image projection. Nature 221:963–964
Bach-y-Rita P, Kaczmarek KA, Tyler ME, Garcia-Lara J (1998) Form perception with a 49-point electrotactile stimulus array on the tongue. J Rehabil Res Dev 35:427–430
Bach-y-Rita P, Tyler ME, Kaczmarek KA (2003) Seeing with the brain. Int J Hum-Comput Int 15:285–295
Bernard-Demanze L, Vuillerme N, Berger L, Rougier P (2006) Magnitude and duration of the effects of plantar sole massages. Int SportMed J 7:154–169
van Boven RW, Johnson KO (1994) The limit of tactile spatial resolution in humans: grating orientation discrimination at the lips, tongue, and finger. Neurology 44:2361–2366
Chiari L, Dozza M, Cappello A, Horak FB, Macellari V, Giansanti D (2005) Audio-biofeedback for balance improvement: an accelerometry-based system. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52:2108–2111
Clapp S, Wing AM (1999) Light touch contribution to balance in normal bipedal stance. Exp Brain Res 125:521–524
Dozza M, Chiari L, Horak FB (2005) Audio-biofeedback improves balance in patients with bilateral vestibular loss. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:1401–1403
Essick GK, Chopra A, Guest S, McGlone F (2003) Lingual tactile acuity, taste perception, and the density and diameter of fungiform papillae in female subjects. Physiol Behav 80:289–302
Gurfinkel VS, Ivanenko YP, Levik YS (1995) The influence of head rotation on human upright posture during balanced bilateral vibration. Neuroreport 7:137–140
Hegeman J, Honneger F, Kupper M, Allum JH (2005) The balance control of bilateral peripheral vestibular loss subjects and its improvement with auditory prosthetic feedback. J Vest Res 15:109–117
Horak FB, Hlavacka F (2001) Somatosensory loss increases vestibulospinal sensitivity. J Neurophysiol 86:575–585
Isableu B, Ohlmann T, Crémieux J, Amblard B (1997) Selection of spatial frame of reference and postural control variability. Exp Brain Res 114:584–589
Isableu B, Vuillerme N (2006) Differential integration of kinesthetic signals to postural control. Exp Brain Res DOI 10.1007/s0021–006–0630–4
Kaczmareck KA, Webster JG, Bach-y-Rita P, Tompkins WJ (1991) Electrotactile and vibrotactile displays for sensory substitution systems. IEEE Trans Rehabil Eng 38:1–16
Kavounoudias A, Roll R, Roll JP (1998) The plantar sole is a “dynamometric map” for human balance control. Neuroreport 9:3247–3252
Kenshalo DR (1986) Somesthetic sensitivity in young and elderly humans. J Gerontol 41:632–642
Lajoie Y (2004) Effect of computerized feedback postural training on posture and attentional demands in older adults. Aging Clin Exp Res 16:363–368
Lord SR, Clark RD, Webster IW (1991) Physiological factors associated with falls in an elderly population. J Am Geriatr Soc 39:1194–1200
Maki BE, Perry SD, Norrie RG, McIlroy WE (1999) Effect of facilitation of sensation from plantar foot-surface boundaries on postural stabilization in young and older adults. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 54:M281-M287
Massion J (1994) Postural control system. Curr Opin Neurobiol 4:877–887
Meyer PF, Oddsson LIE, De Luca CJ (2004). The role of plantar cutaneous sensation in unperturbed stance. Exp Brain Res 156:505–512
Okubo J, Watanabe I, Baron JB (1980) Study on influences of the plantar mechanoreceptor on body sways. Agressologie 21:61–69
Patton JL, Lee WA, Pai YC (2000) Relative stability improves with experience in a dynamic standing task. Exp Brain Res 135:117–126
Petersen H, Magnusson M, Johansson R, Fransson PA (1996) Auditory feedback regulation of perturbed stance in stroke patients. Scand J Rehabil Med 28:217–223
Picard C, Olivier A (1983) Sensory cortical tongue representation in man. J Neurosurg 59:781–789
Priplata A, Niemi J, Salen M, Harry J, Lipsitz LA, Collins JJ (2002) Noise-enhanced human balance control. Phys Rev Lett 89:23101
Priplata A, Niemi J, Salen M, Harry J, Lipsitz LA, Collins JJ (2003) Vibrating insoles and balance control in elderly people. Lancet 362:1123–1124
Sampaio E, Maris S, Bach-y-Rita P (2001) Brain plasticity: ‘visual’ acuity of blind persons via the tongue. Brain Res 908:204–207
Shumway-Cook A, Anson D, Haller S (1988) Postural sway biofeedback: its effect on reestablishing stance stability in hemiplegic patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 69:395–400
Skinner HB, Barrack RL, Cook SD (1984) Age-related decline in proprioception. Clin Orthop 184:208–211
Tagaki A, Fujimura E, Suehiro S (1985) A new method of statokinesigram area measurement. Application of a statistically calculated ellipse. In: Igarashi M, Black O (eds) Vestibular and visual control on posture and locomotor equilibrium. Karger, Bâle, pp 74–79
Tinetti ME, Speechley M (1989) Prevention of falls among the elderly. N Engl J Med 320:1055–1059
Trulsson M, Essick GK (1997) Low-threshold mechanoreceptive afferents in the human lingual nerve. J Neurophysiol 77:737–748
Tyler M, Danilov Y, Bach-y-Rita P (2003) Closing an open-loop control system: vetibular substitution through the tongue. J Integr Neurosci 2:159–164
Van Erp JBF, van Veen HAHC (2006) Touch down: the effect of artificial touch cues on orientation in microgravity. Neurosci Lett 404:78–82
Vuillerme N, Nougier V (2003) Effect of light finger touch on postural sway after lower-limb muscular fatigue. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 84:1560–1563
Vuillerme N, Chenu O, Demongeot J, Payan Y (2006a) Improving human ankle joint position sense using an artificial tongue-placed tactile biofeedback. Neurosci Lett 405:19–23
Vuillerme N, Chenu O, Fleury, J, Demongeot J, Payan Y (2006b) Optimizing the use of an artificial tongue-placed tactile biofeedback for improving ankle joint position sense in humans. 28th annual international conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBS), New York, USA
Wall C, Weinberg MS, Schmidt PB, Krebs DE (2001) Balance prosthesis based on micromechanical sensors using vibrotactile feedback of tilt. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 48:1153–1161
Winter DA, Prince F, Frank JS, Powell C, Zabjek KF (1996) Unified theory regarding A/P and M/L balance in quiet stance. J Neurophysiol 75:2334–2343
Wong MS, Mak AF, Luk KD, Evans JH, Brown B (2001) Effectiveness of audio-biofeedback in postural training for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis patients. Prosthet Orthot Int 25:60–70
Wu G (1997) Real-time feedback of body center of gravity for postural training of elderly patients with peripheral neuropathy. IEEE Trans Rehabil Eng 5:399–402
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to Professor Paul Bach-y-Rita for introducing us to the TDU and for discussions about sensory substitution. The authors would like to thank subject volunteers. The company Vista Medical is acknowledged for supplying the FSA Inshoe Foot pressure mapping system. This research was supported by the Fondation Garches, the company IDS and Floralis (Université Joseph Fourier, Grenoble). Special thanks also are extended to P. Lashatte and F. Rerberthom for various contributions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vuillerme, N., Chenu, O., Demongeot, J. et al. Controlling posture using a plantar pressure-based, tongue-placed tactile biofeedback system. Exp Brain Res 179, 409–414 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0800-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0800-4