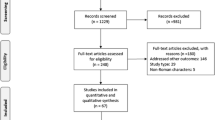
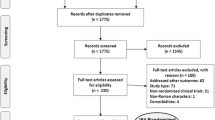
Abstract
Background
About one-half of patients with hepatitis C genotype 1 and one-third with genotype 2/3 have treatment failure with peginterferon alpha and ribavirin. Consensus interferon (CIFN) is an option for retreatment of these patients.
Objective
To summarize comparative safety and efficacy of different regimens of CIFN for the treatment of patients with chronic hepatitis C infection.
Data source
Medline, Scopus, ISI, and Cochran Central Register of Clinical Trials were used.
Study eligibility criteria
Randomized clinical trials (RCTs) were eligible for inclusion in the study.
Participants
HIV and HBV seronegative patients with positive HCV-RNA during the 6 months before the start of the study were eligible for inclusion.
Interventions
Different regimens of CIFN were studied.
Study appraisal and synthesis methods
Studies were appraised based on methods of random sequence generation, allocation concealment, and blinding. The random effects model of DerSimonian and Laird was employed to run the meta-analysis. The end-point was sustained virological response (SVR).
Results
Data of 10 RCTs including 1,600 subjects were extracted. High daily induction dose regimen of CIFN did not yield a higher rate of SVR than low daily induction dose treatment regimen, RR = 0.83 (95% CI 0.58–1.17). A dose of 9 μg thrice weekly (tiw) was associated with a significantly higher rate of SVR compared with 3 μg [RR = 3.14 (95% CI 1.68–5.58)]‹. Withdrawal rate was similar [RR = 1.28 (95% CI 0.65–2.50)] but dose modification was higher in 9 μg [RR = 3.22 (95% CI 1.08–9.60)]. A dose of 18/15 μg tiw was not more effective than 9 μg over a similar treatment duration [RR = 1.02 (95% CI 0. 87–1.19)].
Limitations
Limitations include inadequate reporting of methodological information and side effects, lack of publication bias assessment due to the small number of studies in each analysis.
Conclusions
High dose daily induction therapy with CIFN is not superior to low dose therapy in terms of SVR. It seems that 9 μg tiw is the optimal treatment dose of CIFN for treatment of HCV infection. Optimal duration and safety profile of CIFN therapy have yet been elucidated.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmadipour MH, Alavian SM, Amini S, Azadmanesh K (2005) Hepatitis C virus genotypes. Hepat Mon 5(3):77–82
Arens M (2001) Clinically relevant sequence-based genotyping of HBV, HCV, CMV, and HIV. J Clin Virol 22(1):11–29
Lavanchy D (2009) The global burden of hepatitis C. Liver Int 29(Suppl 1):74–81
Seeff LB (2002) Natural history of chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 36(5 Suppl 1):S35–S46
Berenguer J, Alvarez-Pellicer J, Martin PM, Lopez-Aldeguer J, Von-Wichmann MA, Quereda C et al (2009) Sustained virological response to interferon plus ribavirin reduces liver-related complications and mortality in patients coinfected with human immunodeficiency virus and hepatitis C virus. Hepatology 50(2):407–413
Singal AK, Singh A, Jaganmohan S, Guturu P, Mummadi R, Kuo YF et al (2010) Antiviral therapy reduces risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 8(2):192–199
Breitenstein S, Dimitroulis D, Petrowsky H, Puhan MA, Mullhaupt B, Clavien PA (2009) Systematic review and meta-analysis of interferon after curative treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with viral hepatitis. Br J Surg 96(9):975–981
Poynard T, McHutchison J, Manns M, Trepo C, Lindsay K, Goodman Z et al (2002) Impact of pegylated interferon alfa-2b and ribavirin on liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 122(5):1303–1313
Miyake Y, Takaki A, Iwasaki Y, Yamamoto K (2010) Meta-analysis: interferon-alpha prevents the recurrence after curative treatment of hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. J Viral Hepat 17(4):287–292
Poynard T, Leroy V, Mathurin P, Cohard M, Opolon P, Zarski JP (1996) Treatment of chronic hepatitis C by interferon for longer duration than six months. Dig Dis Sci 41(12 Suppl):99S–102S
Hoofnagle JH, di Bisceglie AM (1997) The treatment of chronic viral hepatitis. N Engl J Med 336(5):347–356
Poynard T, Leroy V, Cohard M, Thevenot T, Mathurin P, Opolon P et al (1996) Meta-analysis of interferon randomized trials in the treatment of viral hepatitis C: effects of dose and duration. Hepatology 24(4):778–789
Lin R, Roach E, Zimmerman M, Strasser S, Farrell GC (1995) Interferon alfa-2b for chronic hepatitis C: effects of dose increment and duration of treatment on response rates. Results of the first multicentre Australian trial. Australia Hepatitis C Study Group. J Hepatol 23(5):487–496
Carithers RL Jr, Emerson SS (1997) Therapy of hepatitis C: meta-analysis of interferon alfa-2b trials. Hepatology 26(3 Suppl 1):83S–88S
McHutchison JG, Gordon SC, Schiff ER, Shiffman ML, Lee WM, Rustgi VK et al (1998) Interferon alfa-2b alone or in combination with ribavirin as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis C. Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group. N Engl J Med 339(21):1485–1492
Poynard T, Marcellin P, Lee SS, Niederau C, Minuk GS, Ideo G et al (1998) Randomised trial of interferon alpha2b plus ribavirin for 48 weeks or for 24 weeks versus interferon alpha2b plus placebo for 48 weeks for treatment of chronic infection with hepatitis C virus. International Hepatitis Interventional Therapy Group (IHIT). Lancet 352(9138):1426–1432
Lai MY, Kao JH, Yang PM, Wang JT, Chen PJ, Chan KW et al (1996) Long-term efficacy of ribavirin plus interferon alfa in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 111(5):1307–1312
Ferenci P, Formann E, Laferl H, Gschwantler M, Hackl F, Brunner H et al (2006) Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of peginterferon alfa-2a (40KD) plus ribavirin with or without amantadine in treatment-naive patients with chronic hepatitis C genotype 1 infection. J Hepatol 44(2):275–282
Bosques-Padilla F, Trejo-Estrada R, Campollo-Rivas O, Cortez-Hernandez C, Dehesa-Violante M, Maldonado-Garza H et al (2003) Peginterferon alfa-2a plus ribavirin for treating chronic hepatitis C virus infection: analysis of Mexican patients included in a multicenter international clinical trial. Ann Hepatol 2(3):135–139
Hadziyannis SJ, Sette H Jr, Morgan TR, Balan V, Diago M, Marcellin P et al (2004) Peginterferon-alpha2a and ribavirin combination therapy in chronic hepatitis C: a randomized study of treatment duration and ribavirin dose. Ann Intern Med 140(5):346–355
Jacobson IM, Brown RS Jr, Freilich B, Afdhal N, Kwo PY, Santoro J et al (2007) Peginterferon alfa-2b and weight-based or flat-dose ribavirin in chronic hepatitis C patients: a randomized trial. Hepatology 46(4):971–981
Gonzalez SA, Keeffe EB (2009) Management of chronic hepatitis C treatment failures: role of consensus interferon. Biologics 3:141–150
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gotzsche PC, Ioannidis JP et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate health care interventions: explanation and elaboration. Ann Intern Med 151(4):W65–W94
Gluud LL (2006) Bias in clinical intervention research. Am J Epidemiol 163(6):493–501
Bax L, Yu LM, Ikeda N, Tsuruta H, Moons KG (2006) Development and validation of MIX: comprehensive free software for meta-analysis of causal research data. BMC Med Res Methodol 6:50
Borenstein M, Hedges LV, Higgins JPT, Rothstein HR (2009) Introduction to meta-analysis, 1st edn. Wiley, London
Petitti DB (2000) Meta-analysis, decision analysis, and cost-effectiveness analysis: methods for quantitative synthesis in medicine, 2nd edn. Oxford University Press, New York
Higgins JP, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 327(7414):557–560
Alaimo G, Di Marco V, Ferraro D, Di Stefano R, Porrovecchio S, D'Angelo F et al (2006) Different doses of consensus interferon plus ribavirin in patients with hepatitis C virus genotype 1 relapsed after interferon monotherapy: a randomized controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol 12(42):6861–6864
Bocher WO, Schuchmann M, Link R, Hillenbrand H, Rahman F, Sprinzl M et al (2006) Consensus interferon and ribavirin for patients with chronic hepatitis C and failure of previous interferon-alpha therapy. Liver Int 26(3):319–325
Cornberg M, Hadem J, Herrmann E, Schuppert F, Schmidt HH, Reiser M et al (2006) Treatment with daily consensus interferon (CIFN) plus ribavirin in non-responder patients with chronic hepatitis C: a randomized open-label pilot study. J Hepatol 44(2):291–301
Fattovich G, Zagni I, Minola E, Felder M, Rovere P, Carlotto A et al (2003) A randomized trial of consensus interferon in combination with ribavirin as initial treatment for chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 39(5):843–849
Gaglio PJ, Rodriguez-Torres M, Herring R, Anand B, Box T, Rabinovitz M et al (2004) Racial differences in response rates to consensus interferon in HCV infected patients naive to previous therapy. J Clin Gastroenterol 38(7):599–604
Heathcote EJ, James S, Mullen KD, Hauser SC, Rosenblate H, Albert DG Jr (1999) Chronic hepatitis C virus patients with breakthroughs during interferon treatment can successfully be retreated with consensus interferon. The Consensus Interferon Study Group. Hepatology 30(2):562–566
Hirashima N, Orito E, Ohba K, Kondo H, Sakamoto T, Matsunaga S et al (2004) A randomized controlled trial of consensus interferon with or without lactoferrin for chronic hepatitis C patients with genotype 1b and high viral load. Hepatol Res 29(1):9–12
Hwang SJ, Lee SD, Chan CY, Lu RH, Chang FY (1999) A randomized, double-blind, controlled trial of consensus interferon in the treatment of Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis C. Am J Gastroenterol 94(9):2496–2500
Jensen DM, Krawitt EL, Keeffe EB, Hollinger FB, James SP, Mullen K et al (1999) Biochemical and viral response to consensus interferon (CIFN) therapy in chronic hepatitis C patients: effect of baseline viral concentration. Consensus Interferon Study Group. Am J Gastroenterol 94(12):3583–3588
Kao JH, Chen PJ, Lai MY, Chen DS (2000) Efficacy of consensus interferon in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15(12):1418–1423
Keeffe EB, Dusheiko GM, James SP, Mullen KD, Everson GT, Pimstone NR et al (1999) Utility of hepatitis C virus serotypes in predicting response to treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Consensus Interferon Study Group. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther 5(4):207–210
Keeffe EB, Dusheiko GM, Tong MJ, Hollinger FB, Heathcote EJ, McHutchison J et al (1999) Genotype does not affect pattern of HCV RNA decrease among responders during interferon treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Consensus Interferon Study Group. Cytokines Cell Mol Ther 5(4):211–216
Layden TJ, Layden JE, Reddy KR, Levy-Drummer RS, Poulakos J, Neumann AU (2002) Induction therapy with consensus interferon (CIFN) does not improve sustained virologic response in chronic hepatitis C. J Viral Hepat 9(5):334–339
Miglioresi L, Bacosi M, Russo F, Patrizi F, Saccenti P, Ursitti A et al (2003) Consensus interferon versus interferon-α 2b plus ribavirin in patients with relapsing HCV infection. Hepatol Res 27(4):253–259
Pockros PJ, Reindollar R, McHutchinson J, Reddy R, Wright T, Boyd DG et al (2003) The safety and tolerability of daily infergen plus ribavirin in the treatment of naive chronic hepatitis C patients. J Viral Hepat 10(1):55–60
Pockros PJ, Tong M, Lee WM, van Leeuwen DJ, Keeffe EB, Bala K et al (1998) Relationship between biochemical and virological responses to interferon therapy in chronic hepatitis C infection. Consensus Interferon Study Group. J Viral Hepat 5(4):271–276
Reddy KR, Hoofnagle JH, Tong MJ, Lee WM, Pockros P, Heathcote EJ et al (1999) Racial differences in responses to therapy with interferon in chronic hepatitis C. Consensus Interferon Study Group. Hepatology 30(3):787–793
Saito H, Tada S, Ebinuma H, Ishii H, Kashiwazaki K, Nishida J et al (2006) Induction therapy with twice-daily interferon-beta does not improve the therapeutic efficacy of consensus interferon monotherapy for chronic hepatitis C. Keio J Med 55(3):111–117
Sjogren MH, Sjogren R, Holtzmuller K, Winston B, Butterfield B, Drake S et al (2005) Interferon alfacon-1 and ribavirin versus interferon alpha-2b and ribavirin in the treatment of chronic hepatitis C. Dig Dis Sci 50(4):727–732
Sjogren MH, Sjogren R Jr, Lyons MF, Ryan M, Santoro J, Smith C et al (2007) Antiviral response of HCV genotype 1 to consensus interferon and ribavirin versus pegylated interferon and ribavirin. Dig Dis Sci 52(6):1540–1547
Suzuki H, Sato K, Takagi H, Kanda D, Sohara N, Kakizaki S et al (2006) Randomized controlled trial of consensus interferon with or without zinc for chronic hepatitis C patients with genotype 2. World J Gastroenterol 12(6):945–950
Suzuki H, Tango T (2002) A multicenter, randomized, controlled clinical trial of interferon alfacon-1 in comparison with lymphoblastoid interferon-alpha in patients with high-titer chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Hepatol Res 22(1):1–12
Tong MJ, Reddy KR, Lee WM, Pockros PJ, Hoefs JC, Keeffe EB et al (1997) Treatment of chronic hepatitis C with consensus interferon: a multicenter, randomized, controlled trial. Consensus Interferon Study Group. Hepatology 26(3):747–754
Yao GB, Fu XX, Tian GS, Xu DZ, Hao LJ, Huangfu YS et al (2000) A multicenter, randomized, controlled trial of interferon alfacon-1 compared with alpha-2a-interferon in Chinese patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 15(10):1165–1170
MacNicholas R, Norris S (2010) Review article: optimizing SVR and management of the haematological side effects of peginterferon/ribavirin antiviral therapy for HCV—the role of epoetin, G-CSF and novel agents. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 31(9):929–937
Kraus MR, Schafer A, Schottker K, Keicher C, Weissbrich B, Hofbauer I et al (2008) Therapy of interferon-induced depression in chronic hepatitis C with citalopram: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Gut 57(4):531–536
Hopewell S, Loudon K, Clarke MJ, Oxman AD, Dickersin K (2009) Publication bias in clinical trials due to statistical significance or direction of trial results. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):MR000006
Turner EH, Matthews AM, Linardatos E, Tell RA, Rosenthal R (2008) Selective publication of antidepressant trials and its influence on apparent efficacy. N Engl J Med 358(3):252–260
Moher D, Jones A, Lepage L (2001) Use of the CONSORT statement and quality of reports of randomized trials: a comparative before-and-after evaluation. JAMA 285(15):1992–1995
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest relevant to the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alavian, SM., Behnava, B. & Tabatabaei, S.V. Comparative efficacy and overall safety of different doses of consensus interferon for treatment of chronic HCV infection: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 66, 1071–1079 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0881-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0881-7