Abstract
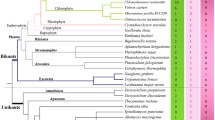
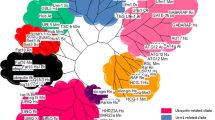
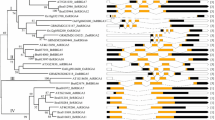
The patterns of emergence and disappearance in animal species of genes encoding RBR ubiquitin ligases are described. RBR genes can be classified into subfamilies (Parkin, Ariadne, Dorfin, ARA54, etc.) according to sequence and structural data. Here, I show that most animal-specific RBR subfamilies emerged early in animal evolution, and that ancient animals, before the cnidarian/bilaterian split, had a set of RBR genes, which was as complex as the one currently found in mammals. However, some lineages (nematodes, dipteran insects) have recently suffered multiple losses, leading to a highly simplified set of RBR genes. Genes of a particular RBR subfamily, characterized by containing a helicase domain and so far found only in plants, are present also in some animal species. The meaning of these patterns of diversification and streamlining are discussed at the light of functional data. Extreme evolutionary conservation may be related to gene products having housekeeping functions.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilera M, Oliveros M, Martínez-Padrón M, Barbas JA, Ferrús A (2000) Ariadne-1: a vital Drosophila gene is required for development and defines a new conserved family of RING-finger proteins. Genetics 155:1231–1244
Beasley SA, Hristova VA, Shaw GS (2007) Structure of the Parkin in-between-ring domain provides insights for E3-ligase dysfunction in autosomal recessive Parkinson’s disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:3095–3100
Bieri T, Blasiar D, Ozersky P, Antoshechkin I, Bastiani C, Canaran P, Chan J, Chen N, Chen WJ, Davis P, Fiedler TJ, Girard L, Han M, Harris TW, Kishore R, Lee R, McKay S, Müller HM, Nakamura C, Petcherski A, Rangarajan A, Rogers A, Schindelman G, Schwarz EM, Spooner W, Tuli MA, Van Auken K, Wang D, Wang X, Williams G, Durbin R, Stein LD, Sternberg PW, Spieth J (2007) WormBase: new content and better access. Nucleic Acids Res 35(Database issue):D506–D510
Capili AD, Edghill EL, Wu K, Borden KLB (2004) Structure of the C-terminal RING finger from a RING-IBR-RING/TRIAD motif reveals a novel zinc-binding domain distinct from a RING. J Mol Biol 340:1117–1129
Chintapalli VR, Wang J, Dow JAT (2007) Using FlyAtlas to identify better Drosophila melanogaster models of human disease. Nat Genet 39:715–730
Clark IE, Dodson MW, Jiang C, Cao JH, Huh JR, Seol JH, Yoo SJ, Hay BA, Guo M (2006) Drosophila pink1 is required for mitochondrial function and interacts genetically with parkin. Nature 441:1162–1166
Dietzl G, Chen D, Schnorrer F, Su KC, Barinova Y, Fellner M, Gasser B, Kinsey K, Oppel S, Scheiblauer S, Couto A, Marra V, Keleman K, Dickson BJ (2007) A genome-wide transgenic RNAi library for conditional gene inactivation in Drosophila. Nature 448:151–156
Eisenhaber B, Chumak N, Eisenhaber F, Hauser MT (2007) The ring between ring fingers (RBR) protein family. Genome Biol 8:209
Glickman MH, Ciechanover A (2002) The ubiquitin-proteasome proteolytic pathway: destruction for the sake of construction. Physiol Rev 82:373–428
Goldberg MS, Fleming SM, Palacino JJ, Cepeda C, Lam HA, Bhatnagar A, Meloni EG, Wu N, Ackerson LC, Klapstein GJ, Gajendiran M, Roth BL, Chesselet MF, Maidment NT, Levine MS, Shen J (2003) Parkin-deficient mice exhibit nigrostriatal deficits but not loss of dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem 278:43628–43635
Greene JC, Whitworth AJ, Kuo I, Andrews LA, Feany MB, Pallanck LJ (2003) Mitochondrial pathology and apoptotic muscle degeneration in Drosophila parkin mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4078–4083
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Ikeda F, Dikic I (2008) Atypical ubiquitin chains: new molecular signals. EMBO Rep 9:536–542
Itier JM, Ibanez P, Mena MA, Abbas N, Cohen-Salmon C, Bohme GA, Laville M, Pratt J, Corti O, Pradier L, Ret G, Joubert C, Periquet M, Araujo F, Negroni J, Casarejos MJ, Canals S, Solano R, Serrano A, Gallego E, Sanchez M, Denefle P, Benavides J, Tremp G, Rooney TA, Brice A, Garcia de Yebenes J (2003) Parkin gene inactivation alters behaviour and dopamine neurotransmission in the mouse. Hum Mol Genet 12:2277–2291
Kerscher O, Felberbaum R, Hochstrasser M (2006) Modification of proteins by ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 22:159–180
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392:605–608
Krylov DM, Wolf YI, Rogozin IB, Koonin EV (2003) Gene loss, protein sequence divergence, gene dispensability, expression level, and interactivity are correlated in eukaryotic evolution. Genome Res 13:222–2235
Kusserow A, Pang K, Sturm C, Hrouda M, Lentfer J, Schmidt HA, Technau U, von Haeseler A, Hobmayer B, Martindale MQ, Holstein TW (2005) Unexpected complexity of the Wnt gene family in a sea anemone. Nature 433:156–160
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Lucas JI, Marín I (2007) A new evolutionary paradigm for the Parkinson disease gene DJ-1. Mol Biol Evol 24:551–561
Lucas JI, Arnau V, Marín I (2006) Comparative genomics and protein domain graph analyses link ubiquitination and RNA metabolism. J Mol Biol 357:9–17
Marín I (2008) Ancient origin of the Parkinson disease gene LRRK2. J Mol Evol 67:41–50
Marín I, Ferrús A (2002) Comparative genomics of the RBR family, including the Parkinson’s disease-related gene parkin and the genes of the ariadne subfamily. Mol Biol Evol 19:2039–2050
Marín I, Lucas JI, Gradilla AC, Ferrús A (2004) Parkin and relatives: the RBR family of ubiquitin ligases. Physiol Genomics 17:253–263
Mukhopadhyay D, Riezman H (2007) Proteasome-independent functions of ubiquitin in endocytosis and signaling. Science 315:201–205
Nicholas KB, Nicholas HB Jr (1997) GeneDoc: a tool for editing and annotating multiple sequence alignments. Distributed by the author
Palacino JJ, Sagi D, Goldberg MS, Krauss S, Motz C, Wacker M, Klose J, Shen J (2004) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative damage in parkin-deficient mice. J Biol Chem 279:18614–18622
Park J, Lee SB, Lee S, Kim Y, Song S, Kim S, Bae E, Kim J, Shong M, Kim JM, Chung J (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction in Drosophila PINK1 mutants is complemented by parkin. Nature 441:1157–1161
Perez FA, Palmiter RD (2005) Parkin-deficient mice are not a robust model of parkinsonism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:2174–2179
Pesah Y, Pham T, Burgess H, Middlebrooks B, Verstreken P, Zhou Y, Harding M, Bellen H, Mardon G (2004) Drosophila parkin mutants have decreased mass and cell size and increased sensitivity to oxygen radical stress. Development 131:2183–2194
Putnam NH, Srivastava M, Hellsten U, Dirks B, Chapman J, Salamov A, Terry A, Shapiro H, Lindquist E, Kapitonov VV, Jurka J, Genikhovich G, Grigoriev IV, Lucas SM, Steele RE, Finnerty JR, Technau U, Martindale MQ, Rokhsar DS (2007) Sea anemone genome reveals ancestral eumetazoan gene repertoire and genomic organization. Science 317:86–94
Qiu X, Fay DS (2006) ARI-1, an RBR family ubiquitin-ligase, functions with UBC-18 to regulate pharyngeal development in C. elegans. Dev Biol 291:239–252
Schwartz AL, Ciechanover A (2009) Targeting protein for destruction by the ubiquitin system: implications for human pathobiology. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 49:73–96
Springer W, Hoppe T, Schmidt E, Baumeister R (2005) A Caenorhabditis elegans Parkin mutant with altered solubility couples alpha-synuclein aggregation to proteotoxic stress. Hum Mol Genet 14:3407–3423
Srivastava M, Begovic E, Chapman J, Putnam NH, Hellsten U, Kawashima T, Kuo A, Mitros T, Salamov A, Carpenter ML, Signorovitch AY, Moreno MA, Kamm K, Grimwood J, Schmutz J, Shapiro H, Grigoriev IV, Buss LW, Schierwater B, Dellaporta SL, Rokhsar DS (2008) The Trichoplax genome and the nature of placozoans. Nature 454:955–960
Su AI, Cooke MP, Ching KA, Hakak Y, Walker JR, Wiltshire T, Orth AP, Vega RG, Sapinoso LM, Moqrich A, Patapoutian A, Hampton GM, Schultz PG, Hogenesch JB (2002) Large-scale analysis of the human and mouse transcriptomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:4465–4470
Su AI, Wiltshire T, Batalov S, Lapp H, Ching KA, Block D, Zhang J, Soden R, Hayakawa M, Kreiman G, Cooke MP, Walker JR, Hogenesch JB (2004) A gene atlas of the mouse and human protein-encoding transcriptomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6062–6067
Swofford DL (2003) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (* and other methods). Version 4. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Weake VM, Workman JL (2008) Histone ubiquitination: triggering gene activity. Mol Cell 29:653–663
Welchman RL, Gordon C, Mayer RJ (2005) Ubiquitin and ubiquitin-like proteins as multifunctional signals. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:599–609
Wilson RJ, Goodman JL, Strelets VB, FlyBase Consortium (2008) FlyBase: integration and improvements to query tools. Nucleic Acids Res 36(Database issue):D588–D593
Yang Y, Gehrke S, Imai Y, Huang Z, Ouyang Y, Wang JW, Yang L, Beal MF, Vogel H, Lu B (2006) Mitochondrial pathology and muscle and dopaminergic neuron degeneration caused by inactivation of Drosophila Pink1 is rescued by Parkin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:10793–10798
Zdobnov EM, Apweiler R (2001) InterProScan—an integration platform for the signature-recognition methods in InterPro. Bioinformatics 17:847–848
Acknowledgments
Research supported by grant 200720I021 (Proyectos intramurales especiales, CSIC, Spain) and grant BIO2008-05067 (Programa Nacional de Biotecnología; Ministerio de Ciencia e Innovación, Spain).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary material 1
This contains the alignment of RBR sequences (indicating species and accession numbers) in FASTA format (TXT 288 kb)
This file is unfortunately not in the Publisher's archive anymore:
Supplementary material 2. This contains the NJ phylogenetic tree with bootstrap values that corresponds to Fig. 1 in the paper. It can be visualized with MEGA 4 (MTS 1201 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marín, I. RBR Ubiquitin Ligases: Diversification and Streamlining in Animal Lineages. J Mol Evol 69, 54–64 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-009-9252-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-009-9252-3