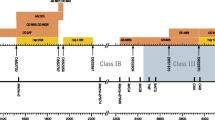
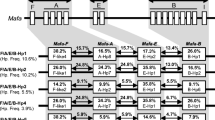
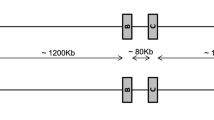
Abstract
A thoroughly characterized breeding colony of 172 pedigreed rhesus macaques was used to analyze exon 2 of the polymorphic Mamu-DPB1, -DQA1, -DQB1, and -DRB loci. Most of the monkeys or their ancestors originated in India, though the panel also included animals from Burma and China, as well as some of unknown origin and mixed breeds. In these animals, mtDNA appears to correlate with the aforementioned geographic origin, and a large number of Mamu class II alleles were observed. The different Mamu-DPB1 alleles were largely shared between monkeys of different origin, whereas in humans particular alleles appear to be unique for ethnic populations. In contrast to Mamu-DPB1, the highly polymorphic -DQA1/DQB1 alleles form tightly linked pairs that appear to be about two-thirds population specific. For most of the DQA1/DQB1 pairs, Mamu-DRB region configurations present on the same chromosome have been ascertained, resulting in 41 different -DQ/DRB haplotypes. These distinct DQ/DRB haplotypes seem to be specific for monkeys of a determined origin. Thus, in evolutionary terms, the Mamu-DP, -DQ, and -DR regions show increasing instability with regard to allelic polymorphism, such as for -DP/DQ, or gene content and allelic polymorphism, such as for -DR, resulting in population-specific class II haplotypes. Furthermore, novel haplotypes are generated by recombination-like events. The results imply that mtDNA analysis in combination with Mhc typing is a helpful tool for selecting animals for biomedical experiments.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen TM, Mothe BR, Sidney J, Jing P, Dzuris JL, Liebl ME, Vogel TU, O’Connor DH, Wang X, Wussow MC, Thomson JA, Altman JD, Watkins DI, Sette A (2001) CD8(+) lymphocytes from simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus macaques recognize 14 different epitopes bound by the major histocompatibility complex class I molecule mamu-A*01: implications for vaccine design and testing. J Virol 75:738–749
Balla-Jhagjhoorsingh SS, Koopman G, Mooij P, Haaksma, TG, Teeuwsen VJ, Bontrop RE, Heeney JL (1999) Conserved CTL epitopes shared between HIV-infected human long-term survivors and chimpanzees. J Immunol 162: 2308–2314
Bakker NP, van Erck MG, Otting N, Lardy NM, Noort RC, ‘t Hart BA, Jonker M, Bontrop RE (1992) Resistance to collagen-induced arthritis in a nonhuman primate species maps to the major histocompatibility complex class I region. Exp Med 75:933–937
Balner H, Van Rood JJ (1971) Transplantation antigens in rhesus monkeys. Nature 232:121
Bontrop RE (2001) Non-human primates: essential partners in biomedical research. Immunol Rev 183:5–9
Bontrop RE, Otting N, de Groot NG, Doxiadis GG (1999) Major histocompatibility complex class II polymorphisms in primates. Immunol Rev 167:339–350
Boyson JE, Iwanaga KK, Golos TG, Watkins DI (1996) Identification of the rhesus monkey HLA-G ortholog. Mamu-G is a pseudogene. J Immunol 157:5428–5437
Brok HP, Uccelli A, Kerlero De Rosbo N, Bontrop RE, Roccatagliata L, de Groot NG, Capello E, Laman JD, Nicolay K, Mancardi GL, Ben-Nun A, Hart BA (2000) Myelin/oligodendrocyte glycoprotein-induced autoimmune encephalomyelitis in common marmosets: the encephalitogenic T cell epitope pMOG24–36 is presented by a monomorphic MHC class II molecule. J Immunol 165:1093–1101
Doxiadis GG, Otting N, de Groot NG, Noort R, Bontrop RE (2000) Unprecedented polymorphism of Mhc-DRB region configurations in rhesus macaques. J Immunol 164:3193–3199
Doxiadis GG, Otting N, de Groot NG, Bontrop RE (2001) Differential evolutionary MHC class II strategies in humans and rhesus macaques: relevance for biomedical studies. Immunol Rev 183:76–85
Evans DT, Knapp LA, Jing P, Piekarczyk MS, Hinshaw V S, Watkins DI (1999) Three different MHC class I molecules bind the same CTL epitope of the influenza virus in a primate species with limited MHC class I diversity. J Immunol 162:3970–3977
Fooden J (2000) Systematic review of the rhesus macaque, Macaca mulatta (Zimmermann, 1780). Field Museum of Natural History, Chicago
Furchner M, Erickson AL, Allen T, Watkins DI, Sette A, Johnson PR, Walker CM (1999) The simian immunodeficiency virus envelope glycoprotein contains two epitopes presented by the Mamu-A*01 class I molecule. J Virol 73:8035–8039
Hashiba KMST (2000) Evolution of Catarrhini DPB1 exon 2 under intragenic recombination. In: Kasahara ME (ed) Major Histocompatibility Complex. Springer-Verlag, Tokyo, pp 386–397
Hayasaka K, Fujii K, Horai S (1996) Molecular phylogeny of macaques: implications of nucleotide sequences from an 896-base pair region of mitochondrial DNA. Mol Biol Evol 13:1044–1053
Horton H, Rehrauer W, Meek EC, Shultz MA, Piekarczyk, MS, Jing P, Carter DK, Steffen SR, Calore B, Urvater JA, Vogel TU, Wilson NA, Watkins DI (2001) A common rhesus macaque MHC class I molecule which binds a cytotoxic T-lymphocyte epitope in Nef of simian immunodeficiency virus. Immunogenetics 53:423–426
Jonker M, van de Hout Y, Neuhaus P, Ringers J, Kuhn EM, Bruijn JA, Noort R, Doxiadis G, Otting N, Bontrop RE, Claas FH, van Rood JJ (1998) Complete withdrawal of immunosuppression in kidney allograft recipients: a prospective study in rhesus monkeys. Transplantation 66:925–927
Kenter M, Otting N, Anholts J, Jonker M, Schipper R, Bontrop RE (1992) Mhc-DRB diversity of the chimpanzee (Pan troglodytes). Immunogenetics 37:1–11
Khazand M, Peiberg C, Nagy M, Sauermann U (1999) Mhc-DQ-DRB haplotype analysis in the rhesus macaque: evidence for a number of different haplotypes displaying a low allelic polymorphism. Tissue Antigens 54:615–624
Knapp LA, Cadavid LF, Eberle ME, Knechtle SJ, Bontrop RE, Watkins DI (1997) Identification of new Mamu-DRB alleles using DGGE and direct sequencing. Immunogenetics 45:171–179
Kocher TD, Thomas WK, Meyer A, Edwards SV, Paabo S, Villablanca FX, Wilson AC (1989) Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 6196–200
Lobashevsky A, Smith JP, Kasten-Jolly J, Horton H, Knapp L, Bontrop RE, Watkins D, Thomas J (1999) Identification of DRB alleles in rhesus monkeys using polymerase chain reaction-sequence-specific primers (PCR-SSP) amplification. Tissue Antigens 54:254–263
Melnick DJ, Hoelzer GA, Absher R, Ashley MV (1993) mtDNA diversity in rhesus monkeys reveals overestimates of divergence time and paraphyly with neighboring species. Mol Biol Evol 10:282–295
Morales JC, Melnick DJ (1998) Phylogenetic relationships of the macaques (Cercopithecidae: Macaca), as revealed by high resolution restriction site mapping of mitochondrial ribosomal genes. J Hum Evol 34:1–23
Mothe BR, Weinfurter J, Wang C, Rehrauer W, Wilson N, Allen TM, Allison DB, Watkins DI (2003) Expression of the major histocompatibility complex class I molecule Mamu-A*01 is associated with control of simian immunodeficiency virus SIVmac239 replication. J Virol 77:2736–2740
Muhl T, Krawczak M, Ten Haaft P, Hunsmann G, Sauermann U (2002) MHC class I alleles influence set-point viral load and survival time in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected rhesus monkeys. J Immunol 169:3438–3446
Nepom GT, Kwok WW (1998) Molecular basis for HLA-DQ associations with IDDM. Diabetes 47:1177–1184
Otting N, Doxiadis GG, Versluis L, de Groot NG, Anholts J, Verduin W, Rozemuller E, Claas F, Tilanus MG, Bontrop RE (1998) Characterization and distribution of Mhc-DPB1 alleles in chimpanzee and rhesus macaque populations. Hum Immunol 59:656–664
Otting N, de Groot NG, Noort MC, Doxiadis GG, Bontrop RE (2000) Allelic diversity of Mhc-DRB alleles in rhesus macaques. Tissue Antigens 56:58–68
Otting N, de Groot NG, Doxiadis GG, Bontrop RE (2002) Extensive Mhc-DQB variation in humans and non-human primate species. Immunogenetics 54:230–239
Reichstetter S, Kwok WW, Kochik S, Koelle DM, Beaty JS, Nepom GT (1999) MHC-peptide ligand interactions establish a functional threshold for antigen-specific T-cell recognition. Hum Immunol 60:608–618
Robinson J, Waller MJ, Parham P, de Groot N, Bontrop R, Kennedy LJ, Stoehr P, Marsh SG (2003) IMGT/HLA and IMGT/MHC: sequence databases for the study of the major histocompatibility complex. Nucleic Acids Res 31:311–314
Rozemuller EH, Bouwens AG, Bast BE, Tilanus MG (1993) Assignment of HLA-DPB alleles by computerized matching based upon sequence data. Hum Immunol 37:207–212
Rozemuller EH, Kropveld A, Kreyveld E, Leppers FG, Scheidel KC, Slootweg PJ, Tilanus MG (2001) Sensitive detection of p53 mutation: analysis by direct sequencing and multisequence analysis. Cancer Detect Prev 25:109–116
Sauermann U, Stahl-Hennig C, Stolte N, Muhl T, Krawczak M, Spring M, Fuchs D, Kaup FJ, Hunsmann G, Sopper S (2000) Homozygosity for a conserved Mhc class II DQ-DRB haplotype is associated with rapid disease progression in simian immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques: results from a prospective study. J Infect Dis 182:716–724
Slierendregt BL, Hall M, t Hart B, Otting N, Anholts J, Verduin W, Claas F, Jonker M, Lanchbury JS, Bontrop RE (1995a) Identification of an Mhc-DPB1 allele involved in susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rhesus macaques. Int Immunol 7:1671–1679
Slierendregt BL, Otting N, Kenter M, Bontrop RE (1995b) Allelic diversity at the Mhc-DP locus in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Immunogenetics 41:29–37
Swafford DL (2002) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods), version 4. Sinauer, Sunderland, Massachusetts
t Hart BA, Brok HP, Amor S, Bontrop RE (2001) The major histocompatibility complex influences the ethiopathogenesis of MS-like disease in primates at multiple levels. Hum Immunol 62:1371–1381
Tosi AJ, Morales JC, Melnick DJ (2000) Comparison of Y chromosome and mtDNA phylogenies leads to unique inferences of macaque evolutionary history. Mol Phylogenet Evol 17:133–144
Tosi AJ, Morales JC, Melnick DJ (2002) Y-chromosome and mitochondrial markers in Macaca fascicularis indicate introgression with Indochinese M. mulatta and a biogeogrphic barrier in the Isthmus of Kra. Int J Primatol 23:161–178
van der Kuyl AC, Kuiken CL, Dekker JT, Goudsmit J (1995) Phylogeny of African monkeys based upon mitochondrial 12S rRNA sequences. J Mol Evol 40:173–180
van der Kuyl AC, van Gennep DR, Dekker JT, Goudsmit J (2000) Routine DNA analysis based on 12S rRNA gene sequencing as a tool in the management of captive primates. J Med Primatol 29:309–317
Versluis LF, Rozemuller E, Tonks S, Marsh SG, Bouwens AG, Bodmer JG, Tilanus MG (1993) High-resolution HLA-DPB typing based upon computerized analysis of data obtained by fluorescent sequencing of the amplified polymorphic exon 2. Hum Immunol 38:277–283
Vigon N, Sauermann U (2002) Sequence-based typing techniques for rhesus macaque MhcMamu-DQB1 allow the identification of more than 35 alleles. Tissue Antigens 59:88–94
Wood KJ, Jones ND, Bushell AR, Morris PJ (2001) Alloantigen-induced specific immunological unresponsiveness. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 356:665–680
Zhang YP, Shi LM (1993) Phylogenetic relationships of macaques as inferred from restriction endonuclease analysis of mitochondrial DNA. Folia Primatol (Basel) 60:7–17
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank D. Devine for editing the manuscript and Henk van Westbroek for preparing the figures. The work was financed in part by the European Union project IMGT-QLG2-CT-2000-01287 and the NIH project 1-R24-RR16038-01 (CFDA no. 93.306).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The sequences reported in this paper have been deposited in the EMBL database (accession nos. AJ534296–AJ534304, AJ 564564, and AJ557455–AJ557511)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doxiadis, G.G.M., Otting, N., de Groot, N.G. et al. Evolutionary stability of MHC class II haplotypes in diverse rhesus macaque populations. Immunogenetics 55, 540–551 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-003-0590-9
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-003-0590-9