Abstract
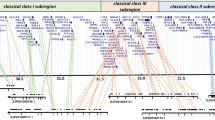
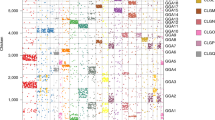
The present day structure of the vertebrate major histocompatibility complex (MHC) and its three paralogous regions has always been a focus of interest. In a recent study, nine human anchor genes located in the MHC region were cloned from a Branchiostoma floridae (amphioxus) cosmid library. The identification and analysis of 31 surrounding genes led to the most probable model of two rounds of en bloc duplication giving rise to these regions. These events were estimated to have occurred after the cephalochordata-craniata divergence [approximately 766 million years ago (Mya)] and before the Gnathostomata radiation (approximately 528 Mya). Furthermore, it was also shown that after this large-scale duplication one of these regions, corresponding to the human 9q33-q34, had retained an ancestral organisation. In the present study, four new cosmids in the amphioxus proto-MHC region were identified by the chromosomal walking technique. These cosmids were sequenced, and their structural annotation was performed, leading to the prediction of eleven genes. Their phylogenetic relationships among species corroborate the results obtained previously and provide more evidence for the plesiomorphic state of the human chromosome 9q33-34 MHC paralogous region.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abi-Rached L, Gilles A, Shiina T, Pontarotti P, Inoko H (2002) Evidence of en bloc duplication in vertebrate genomes. Nature Genetics 31:100–105
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bateman A, Birney E, Cerruti L, Durbin R, Etwiller L, Eddy SR, Griffiths-Jones S, Howe KL, Marshall M, Sonnhammer EL (2002) The Pfam Protein Families Database. Nucleic Acids Res 30:276–280
Caron H, van Schaik B, van der Mee M, Baas F, Riggins G, van Sluis P, Hermus MC, van Asperen R, Boon K, Voute PA, Heisterkamp S, van Kampen A, Versteeg R (2001) The human transcriptome map: clustering of highly expressed genes in chromosomal domains. Science 291:1289–1292
Cremer T, Cremer C (2001) Chromosome territories, nuclear architecture and gene regulation in mammalian cells. Nat Rev Genet 2:292–301
Doolittle RF (1995) The multiplicity of domains in proteins. Annu Rev Biochem 6:287–314
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Gu X, Wang Y, Gu J (2002) Age distribution of human gene families shows significant roles of both large-and small-scale duplications in vertebrate evolution. Nat Genet 31:205–209
Kasahara M, Hayashi M, Tanaka K, Inoko H, Sugaya K, Ikemura T, Ishibashi T (1996) Chromosomal localization of the proteasome Z subunit gene reveals an ancient chromosomal duplication involving the major histocompatibility complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:9096–9101
Katsanis M, Fitzgibbon J, Fisher EMC (1996) Paralogy mapping: identification of a region in the human MHC triplicated onto human chromosomes 1 and 9 allows the prediction and isolation of novel PBX and NOTCH loci. Genomics 35:101–108
Ku HM, Vision T, Liu J, Tanksley SD (2000) Comparing sequenced segments of tomato and Arabidopsis genomes: large-scale duplication followed by selective gene loss creates a network of syntheny. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:9121–9126
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Lundin LG (1993) Evolution of the vertebrate genome as reflected in paralogous chromosomal regions in man and the house mouse. Genomics 16:1-19
Minguillón C, Ferrier DEK, Cebrián C, Garcia-Fernàndez J (2002) Gene duplications in the prototypical cephalochordate amphioxus. Gene 287:121–128
Philippe H (1993) MUST, a computer package of Management Utilities for Sequences and Trees. Nucleic Acids Res 21:5264–5272
Shiina T, Ando A, Suto Y, Kasai F, Shigenari A, Takishima N, Kikkawa E, Iwata K, Kuwano Y, Kitamura Y, Matsuzawa Y, Sano K, Nogami M, Kawata H, Li S, Fukuzumi Y, Yamazaki M, Tashiro H, Tamiya G, Kohda A, Okumura K, Ikemura T, Soeda E, Mizuki N, Kimura M, Bahram S, Inoko H (2001) Genomic anatomy of a premier major histocompatibility complex paralogous region on chromosome 1q21-q22. Genome Res 11:789–802
Strimmer K, Haeseler A (1996) Quartet puzzling: a quartet maximum likelihood method for reconstructing tree topologies. Mol Biol Evol 13:964–969
Swofford DL (2000) PAUP*. Phylogenetic Analysis Using Parsimony (*and other Methods), version 4. Sinauer, Sunderland, Massachusetts
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Zdobnov EM, von Mering C, Letunic I, Torrents D, Suyama M, Copley RR, Christophides GK, Thomasova D, Holt RA, Subramanian GM, Mueller HM, Dimopoulos G, Law JH, Wells MA, Birney E, Charlab R, Halpern AL, Kokoza E, Kraft CL, Lai Z, Lewis S, Louis C, Barillas-Mury C, Nusskern D, Rubin GM, Salzberg SL, Sutton GG, Topalis P, Wides R, Wincker P, Yandell M, Collins FH, Ribeiro J, Gelbart WM, Kafatos FC, Bork P (2002) Comparative genome and proteome analysis of Anopheles gambiae and Drosophila melanogaster. Science 298:149–159
Acknowledgements
We thank André Gilles, Philippe Gouret, Etienne Danchin, and Vincent Dubut for their advises. A great thanks to Jeffrey Rasmussen and Michael McDermott for critical reading and helpful comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00251-004-0653-6
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vienne, A., Shiina, T., Abi-Rached, L. et al. Evolution of the proto-MHC ancestral region: more evidence for the plesiomorphic organisation of human chromosome 9q34 region. Immunogenetics 55, 429–436 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-003-0601-x
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-003-0601-x