Abstract
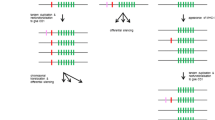
Ly49 genes regulate the cytotoxic activity of natural killer (NK) cells in rodents and provide important protection against virus-infected or tumor cells. About 15 Ly49 genes have been identified in mice, but only a few genes have been reported to date in rats. Here we studied all Ly49 genes in the entire rat genome sequence and identified 17 putative functional and 16 putative non-functional genes together with their genomic locations in a 1.8-Mb region of chromosome 4. Phylogenetic analysis of these genes indicated that the Ly49 gene family expanded rapidly in recent years, and this expansion was mediated by both tandem and genomic block duplication. The joint phylogenetic analysis of mouse and rat genes suggested that the most recent common ancestor of the two species had at least several Ly49 genes, but that the majority of current duplicate genes were generated after divergence of the two species. In both species Ly49 genes are apparently subject to birth-and-death evolution, but the birth and death rates of Ly49 genes are higher in rats than in mice. The rate of gene expansion in the Ly49 gene family in rats is one of the highest among all mammalian multigene families so far studied. The biochemical function of Ly49 genes is essentially the same as that of KIR genes in primates, but the molecular structures of the two groups of NK cell receptors are very different. A hypothesis was presented to explain the origin of the differential use of Ly49 and KIR genes in rodents and primates.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anzai T, Shiina T, Kimura N et al (2003) Comparative sequencing of human and chimpanzee MHC class I regions unveils insertions/deletions as the major path to genomic divergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:7708–7713
Arase H, Lanier LL (2004) Specific recognition of virus-infected cells by paired NK receptors. Rev Med Virol 14:83–93
Brennan J, Mager DL, Jefferies WA, Takei F (1996) Recognition of class I major histocompatibility complex molecules by Ly-49: specificities and domain interactions. J Exp Med 183:1553–1559
Brown MG, Fulmek S, Matsumoto K, Cho R, Lyons PA, Levy ER, Scalzo AA, Yokoyama WM (1997) A 2-Mb YAC contig and physical map of the natural killer gene complex on mouse chromosome 6. Genomics 42:16–25
Brown MG, Dokun AO, Heusel JW, Smith HRC, Beckman DL, Blattenberg EA, Dubbelde CE, Stone LR, Scalzo AA, Yokoyama WM (2001) Vital involvement of a natural killer cell activation receptor in resistance to viral infection. Science 292:934–937
Colonna M, Samaridis J (1995) Cloning of immunoglobulin-superfamily members associated with HLA-C and HLA-B recognition by human natural killer cells. Science 268:405–408
Depatie C, Lee SH, Stafford A, Avner P, Belouchi A, Gros P, Vidal SM (2000) Sequence-ready BAC contig, physical, and transcriptional map of a 2-Mb region overlapping the mouse chromosome 6 host-resistance locus Cmvl. Genomics 66:161–174
Dissen E, Ryan JC, Seaman WE, Fossum S (1996) An autosomal dominant locus, Nka, mapping to the Ly-49 region of a rat natural killer (NK) gene complex, controls NK cell lysis of allogeneic lymphocytes. J Exp Med 183:2197–2207
Dorfman JR, Raulet DH (1996) Major histocompatibility complex genes determine natural killer cell tolerance. Eur J Immunol 26:151–155
Gagnier L, Wilhelm BT, Mager DL (2003) Ly49 genes in non-rodent mammals. Immunogenetics 55:109–115
Gardiner CM, Guethlein LA, Shilling HG, Pando M, Carr WH, Rajalingam R, Vilches C, Parham P (2001) Different NK cell surface phenotypes defined by the DX9 antibody are due to KIR3DL1 gene polymorphism. J Immunol 166:2992–3001
Guethlein LA, Flodin LR, Adams EJ, Parham P (2002) NK cell receptors of the orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus): a pivotal species for tracking the coevolution of killer cell Ig-like receptors with MHC-C. J Immunol 169:220–229
Hershberger KL, Shyam R, Miura A, Letvin NL (2001) Diversity of the killer cell Ig-like receptors of Rhesus Monkeys. J Immunol 166:4380–4390
Hoelsbrekken SE, Nylenna O, Saether PC, Slettedal IO, Ryan JC, Fossum S, Dissen E (2003) Cutting edge: molecular cloning of a killer cell Ig-like receptor in the mouse and rat. J Immunol 170:2259–2263
Hsu K, Liu XR, Selvakumar A, Mickelson E, O’Reilly RJ, Dupont B (2002) Killer Ig-like receptor haplotypes analysis by gene content: evidence for genomic diversity with a minimum of six basic framework haplotypes, each with multiple subsets. J Immunol 169:5118–5129
Idris AH, Smith HR, Mason LH, Ortaldo JR, Scalzo AA, Yokoyama WM (1999) The natural killer gene complex genetic locus Chok encodes Ly-49D, a target recognition receptor that activates natural killing. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6330–6335
Johnson ME, Viggiano L, Bailey JA, Abdul-Rauf M, Goodwin G, Rocchi M, Eichler EE (2001) Positive selection of a gene family during the emergence of humans and African apes. Nature 413:514–515
Kane KP, Silver ET, Hazes B (2001) Specificity and function of activating Ly-49 receptors. Immunol Rev 181:104–114
Klein J, Figueroa F (1986) Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex. Crit Rev Immunol 6:295–386
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Kwon D, Chwae YJ, Choi IH, Park JH, Kim SJ, Kim J (2000) Diversity of the p70 killer cell inhibitory receptor (KIR3DL) family members in a single individual. Mol Cells 10:54–60
Lynch M, Conery JS (2003) The evolutionary demography of duplicate genes. J Struct Funct Genomics 3:35–44
Mager DL, McQueen KL, Wee V, Freeman JD (2001) Evolution of natural killer cell receptors: coexistence of functional Ly49 and KIR genes in baboons. Curr Biol 11:626–630
Makrigiannis AP, Pau AT, Schwartzberg PL, McVicar DW, Beck TW, Anderson SK (2002) A BAC contig map of the Ly49 gene cluster in 129 mice reveals extensive differences in gene content relative to C57BL/6 mice. Genomics 79:437–444
Martin A, Freitas EM, Witt CS, Christiansen FT (2000) The genomic organization and evolution of the natural killer immunoglobulin-like receptor (KIR) gene cluster. Immunogenetics 51:268–280
Mason LH, Anderson SK, Smith HR, Yokoyama WM, Winkler-Pickett R, Ortaldo JR (1996) The Ly49D receptor activates murine natural killer cells. J Exp Med 184:2119–2128
Mason LH, Gosselin P, Anderson SK, Fosler WE, Ortaldo JR, McVicar DW (1997) Differential tyrosine phosphorylation of inhibitory versus activating Ly49 receptors and their recruitment of SHP-1 phosphatase. J Immunol 159:4187–4196
Matsuda F, Shin EK, Nagaoka H et al (1993) Structure and physical map of 64 variable segments in the 3′ 0.8-megabase region of the human immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus. Nat Genet 3:88–94
McQueen KL, Lohwasser S, Takei F, Mager DL (1999) Expression analysis of new Ly49 genes: most transcripts of Ly49j lack the transmembrane domain. Immunogenetics 49:685–691
McQueen KL, Wilhelm BT, Harden KD, Mager DL (2002) Evolution of NK receptors: a single Ly49 and multiple KIR genes in the cow. Eur J Immunol 32:810–817
Nam J, Kim J, Lee S, An G, Ma H, Nei M (2004) Type I MADS-box genes have experienced faster birth-and-death evolution than type II MADS-box genes in angiosperms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:1910–1915
Naper C, Hayashi S, Joly E, Butcher GW, Rolstad B, Vaage JT, Ryan JC (2002a) Ly49i2 is an inhibitory rat natural killer cell receptor for an MHC class Ia molecule (RT1-A1c). Eur J Immunol 32:2031–2036
Naper C, Hayashi S, Kveberg L, Niemi EC, Lanier LL, Vaage JT, Ryan JC (2002b) Ly49-s3 is a promiscuous activating rat NK cell receptor for nonclassical MHC class I-encoded target ligands. J Immunol 169:22–30
Nei M (1969) Gene duplication and nucleotide substitution in evolution. Nature 221:40–42
Nei M, Kumar S (2000) Molecular evolution and phylogenetics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Nei M, Xu P, Glazko G (2001) Estimation of divergence times from multiprotein sequences for a few mammalian species and several distantly related organisms. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:2497–2502
Niimura Y, Nei M (2003) Evolution of olfactory receptor gene clusters in the human genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12235–12240
Piontkivska H, Nei M (2003) Birth-and-death evolution in primate MHC class I genes: divergence time estimates. Mol Biol Evol 20:601–609
Rat Genome Sequencing Project Consortium (RGSC) (2004) Genome sequence of the Brown Norway rat yields insights into mammalian evolution. Nature 428:493–521
Renedo M, Arce I, Montgomery K, Roda-Navarro P, Lee EE, Kucherlapati R, Fernandez-Ruiz E (2000) A sequence-ready physical map of the region containing the human natural killer gene complex on chromosome 12p12.3–p13.2. Genomics 65:129–136
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Satta Y, Mayer WE, Klein J (1996) Evolutionary relationship of HLA–DRB genes inferred from intron sequences. J Mol Evol 42:648–657
Schable KF, Zachau HG (1993) The variable genes of the human immunoglobulin k locus. Biol Chem Hoppe Seyler 374:1001–1022
Schwartz S, Zhang Z, Frazer KA, Smit A, Riemer C, Bouck J, Gibbs R, Hardison R, Miller W (2000) PipMaker—a web server for aligning two genomic DNA sequences. Genome Res 10:577–586
Storset AK, Slettedeal IO, Williams JL, Law A, Dissen E (2003) Natural killer cell receptors in cattle: a bovine killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptor multigene family contains members with divergent signaling motifs. Eur J Immunol 33:980–990
Su C, Nei M (2001) Evolutionary dynamics of the T-cell receptor VB gene family as inferred from the human and mouse genomic sequences. Mol Biol Evol 18:503–513
Swofford DL (1998) PAUP: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony. Sinauer, Sunderland, Mass.
Takahashi K, Rooney AP, Nei M (2000) Origins and divergence times of mammalian class II MHC gene clusters. J Hered 19:198–204
Takahashi T, Yawata M, Raudsepp T, Lear TL, Chowdhary BP, Antczak DF, Kasahara M (2004) Natural killer cell receptors in the horse: evidence for the existence of multiple transcribed Ly49 genes. Eur J Immunol 34:773–784
Takei F, Brennan J, Mager DL (1997) The Ly-49 family: genes, proteins and recognition of class I MHC. Immunol Rev 155:67–77
Takezaki N, Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1995) Phylogenetic test of the molecular clock and linearized trees. Mol Biol Evol 12:823–833
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface, flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Trowsdale J, Barten R, Haude A, Stewart CA, Beck S, Wilson MJ (2001) The genomic context of natural killer receptor extended gene families. Immunol Rev 181:20–38
Welch AY, Kasahara M, Spain LM (2003) Identification of the mouse killer immunoglobulin-like receptor-like (Kir1) gene family mapping to chromosome X. Immunogenetics 54:782–790
Wilhelm BT, Gagnier L, Mager DL (2002) Sequence analysis of the Ly49 cluster in C57BL/6 mice: a rapidly evolving multigene family in the immune system. Genomics 80:646–661
Wilhelm BT, Mager DL (2004) Rapid expansion of the Ly49 gene cluster in rat. Genomics 84:218–221
Wilson MJ, Torkar M, Haude A, Milne S, Jones T, Sheer D, Beck S, Trowsdale J (2000) Plasticity in the organization and sequences of human KIR/ILT gene families. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:4778–4783
Zhang Z, Schaffer AA, Miller W, Madden TL, Lipman DJ, Koonin EV, Altschul SF (1998a) Protein sequence similarity searches using patterns as sees. Nucleic Acids Res 26:3986–3990
Zhang J, Rosenberg HF, Nei M (1998b) Positive Darwinian selection after gene duplication in primate ribonuclease genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:3708–3713
Acknowledgements
We thank Jan Klein, Jongmin Nam, Yoshihito Niimura, and Nikolas Nikolaidis for their discussion. This work was supported by NIH grant GM20293 (to M.N.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, L., Nei, M. Genomic organization and evolutionary analysis of Ly49 genes encoding the rodent natural killer cell receptors: rapid evolution by repeated gene duplication. Immunogenetics 56, 343–354 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-004-0703-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-004-0703-0