Abstract
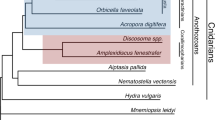
C3, C4, and C5 are thiolester-containing proteins (TEPs) of vertebrate complement. The identification of the molecular origin of the TEP family, and more specifically the ancestor protein of complement components C3, C4, and C5, remains a fundamental question. The prevailing paradigm suggests that duplication and divergence of these proteins occurred after the deuterostome split in phylogeny. It is believed that the ancestor of thiolester-containing complement proteins was alpha-2-macroglobulin (A2M)-like, a noncomplement-related protein. Here we describe a C3-like cDNA from a gorgonian coral, Swiftia exserta. This study provides evidence for the origins of a complement-related C3-like gene in the Precambrian period, predating both protostomes and deuterostomes. Furthermore, one may speculate that complement-like opsonic reactions were evolving at the earliest stages of metazoan evolution. This calls for a reassessment of the present concepts concerning the origins and evolution of TEPs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams MD et al (2000) The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 287:2185–2195
Adoutte A, Balavoine G, Lartillot N, Lespinet O, Prud'homme B, de Rosa R (2000) Special feature: the new animal phylogeny: reliability and implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:4453–4456
Ainscough R et al (1998) Genome sequence of the nematode C. elegans: a platform for investigating biology. The C. elegans Sequencing Consortium. Science 282:2012–2018
Al-Sharif WZ, Sunyer JO, Lambris JD, Smith LC (1998) Sea urchin coelomocytes specifically express a homologue of the complement component C3. J Immunol 160:2983–2997
Armstrong PB, Quigley JP (1999) Alpha2-macroglobulin: an evolutionarily conserved arm of the innate immune system. Dev Comp Immunol 23:375–390
Ayala FJ, Rzhetsky A, Ayala FJ (1998) Origin of the metazoan phyla: molecular clocks confirm paleontological estimates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:606–611
Barrington R, Zhang M, Fischer M, Carroll MC (2001) The role of complement in inflammation and adaptive immunity. Immunol Rev 180:5–15
Bertheussen K (1979) The cytotoxic reaction in allogeneic mixtures of echinoid phagocytes. Exp Cell Res 120:373–381
Bertheussen K (1982) Receptors for complement on echinoid phagocytes. II. Purified human complement mediates echinoid phagocytosis. Dev Comp Immunol 6:635–642
Bertheussen K (1983) Complement-like activity in sea urchin coelomic fluid. Dev Comp Immunol 7:21–31
Bertheussen K, Seijelid R (1978) Echinoid phagocytes in vitro. Exp Cell Res 111:401–412
Bertheussen K, Seljelid R (1982) Receptors for complement on echinoid phagocytes. I. The opsonic effect of vertebrae sera on echinoid phagocytosis. Dev Comp Immunol 6:423–431
Bokischi VA, Dierich MP, Muller-Eberhard HJ (1975) Third component of complement (C3): structural properties in relation to functions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 72:1989–1993
Campbell RD, Law SKA, Reid KBM, Sim RB (1988) Structure, organization, and regulation of the complement genes. Annu Rev Immunol 6:161–195
Carroll MC (1998) The role of complement and complement receptors in induction and regulation of immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 16:545–568
Christophides GK, Zdobnov E, Barillas-Mury C, Birney E, Blandin S, Blass C, Brey PT, Collins FH, Danielli A, Dimopoulos G, Hetru C, Hoa NT, Hoffmann JA, Kanzok SM, Letunic I, Levashina EA, Loukeris TG, Lycett G, Meister S, Michel K, Moita LF, Muller HM, Osta MA, Paskewitz SM, Reichhart JM, Rzhetsky A, Troxler L, Vernick KD, Vlachou D, Volz J, von Mering C, Xu J, Zheng L, Bork P, Kafatos FC (2002) Immunity-related genes and gene families in Anopheles gambiae. Science 298:159–165
Dempsey PW, Allison MED, Akkaraju S, Goodnow CC, Fearon DT (1996) C3d of complement as a molecular adjuvant: bridging innate and acquired immunity. Science 271:348–350
Dodds AW, Law SKA (1998) The phylogeny and evolution of the thioester bond-containing proteins C3, C4, and alpha2-macroglobulin. Immunol Rev 166:15–26
Doolittle RF, Feng D-F, Tsang S, Cho G, Little E (1996) Determining divergence times of the major kingdoms of living organisms with a protein clock. Science 271:470–477
Fearon DT, Locksley RM (1996) The instructive role of innate immunity in the acquired immune response. Science 272:50–54
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenetics: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Fujita T (2002) Evolution of the lectin-complement pathway and its role in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 2:346–353
Gadjeva M, Dodds AW, Taniguchi-Sidle A, Willis AC, Isenman DE, Law SKA (1998) The covalent binding reaction of complement component C3. J Immunol 161:985–990
Gonnet GH, Cohen MA, Benner SA (1992) Exhaustive matching of the entire protein sequence database. Science 256:1443–1445
Guex N, Peitsch MC (1997) SWISS-MODEL and the Swiss-Pdb Viewer: an environment for comparative protein modelling. Electrophoresis 18:2714–2723
Hall TA (1999) BioEdit: a user-friendly biological sequence alignment editor and analysis program for Windows 95/98/NT. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser 41:95–98
Hammond JA, Nakao M, Smith VJ (2005) Cloning of a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored alpha-2-macroglobulin cDNA from the ascidian, Ciona intestinalis, and its possible role in immunity. Mol Immunol 42:683–694
Holt RA, Subramanian GM, Halpern A, Sutton GG, Charlab R, Nusskern DR, Wincher P, Clark AG et al (2002) The genome sequence of the malaria mosquito Anopheles gambiae. Science 298:129–159
Huber R, Scholze H, Paques EP, Deisenhofer J (1980) Crystal structure analysis and molecular model of human C3a anaphylatoxin. Hoppe-Seyler Z Physiol Chem 361:1389–1399
Jones DT (1999) Protein secondary structure prediction based on position-specific scoring matrices. J Mol Biol 292:195–202
Karp DR, Parker KL, Shreffler DC, Capra JD (1981) Characterization of the murine C4 precursor (pro-C4): evidence that the carboxyterminal subunit is the C4 gamma-chain. J Immunol 126:2060–2061
Karplus K, Barrett C, Hughey R (1998) Hidden Markov models for detecting remote protein homologies. Bioinformatics 14:846–856
Kortschak RD, Samuel G, Saint R, Miller D (2003) EST analysis of the Cnidarian Acropora millepora reveals extensive gene loss and rapid sequence divergence in the model invertebrates. Curr Biol 13:2190–2195
Krumlauf R (1996) Northern blot analysis. In: Harwood AJ (ed) Basic DNA and RNA protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, NJ
Kumar S (1996) A stepwise algorithm for finding minimum evolution trees. Mol Biol Evol 13:584–593
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen IB, Nei M (2001) Mega2: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis software. Bioinformatics 17:1244–1245
Lachmann P (1979) An evolutionary view of the complement system. Behring-Inst-Mitt 63:25–37
Law SK, Dodds AW (1997) The internal thioester and the covalent binding properties of the complement proteins C3 and C4. Protein Sci 6:263–274
Law SK, Levine RP (1977) Interaction between the third complement protein and cell surface macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 74:2701–2705
Law SK, Lichtenberg NA, Levin RP (1979) Evidence for an ester linkage between the labile binding site of C3b and receptive surfaces. J Immunol 123:1388–1394
Levashina EA, Moita LF, Blandin S, Vriend G, Lagueux M, Kafatos FC (2001) Conserved role of a complement-like protein in phagocytosis revealed by dsRNA knockout in cultured cells of the mosquito, Anopheles gambiae. Cell 104:709–718
Levashina EA, Blandin S, Moita LF, Lagueux M, Kafatos FC (2003) Thioester-containing proteins of protostomes. In: Ezekowitz RAB, Hoffmann JA (eds) Innate immunity. Humana Press Inc., Totowa, NJ, pp 155–174
Lin M, Sutherland DR, Horsfall W, Totty N, Yeo E, Nayar R, Wu X-F, Schuh AC (2002) Cell surface antigen CD109 is a novel member of the alpha2-macroglobulin/C3, C4, C5 family of thioester-containing proteins. Blood 99:1683–1691
Liu J, Rost B (2003) NORSp: predictions of long regions without regular secondary structure. Nucleic Acids Res 31:3833–3835
Liu J, Tan H, Rost B (2002) Loopy proteins appear conserved in evolution. J Mol Biol 322:53–64
Marino R, Kimura Y, De Santis R, Lambris JD, Pinto MR (2002) Complement in urochordates: cloning and characterization of two C3-like genes in the ascidian Ciona intestinalis. Immunogenetics 53:1055–1064
Mastellos D, Lambris JD (2002) Complement: more than a ‘guard’ against invading pathogens? Trends Immunol 23:485–491
McGuffin LJ, Jones DT (2003) GenTHREADER: an efficient and reliable protein fold recognition method for genomic sequences. Bioinformatics 19:874–881
McGuffin LJ, Bryson K, Jones DT (2000) The PSIPRED protein structure prediction server. Bioinformatics 16:404–405
McMenamin MAS, McMenamin DLS (1990) The emergence of animals: the Cambrian breakthrough. Columbia University Press, New York
Morley BJ, Walport MJ (2000) The complement facts book. Academic, New York
Muto Y, Fukumoto Y, Arata Y (1985) Proton nuclear magnetic resonance study of the third component of complement: solution conformation of the carboxyl-terminal segment of C3a fragment. Biochemistry 24:6659–6665
Nagar B, Jones RG, Diefenbach RJ, Isenman DE, Rini JM (1998) X-ray crystal structure of C3d: a C3 fragment and ligand for complement receptor 2. Science 280:1277–1281
Nicholas KB, Nicholas HB Jr (1997) GeneDoc: a tool for annotating and editing multiple sequence alignments. Distributed by author
Nonaka M (1994) Molecular analysis of the lamprey complement system. Fish Shellfish Immunol 4:437–446
Nonaka M, Azumi K, Ji X, Namikawa-Yamada C, Sasaki M, Saiga H, Dodds AW, Sekine H, Homma MK, Matsushita M, Endo Y, Fujita T (1999) Opsonic complement component C3 in the solitary ascidian, Halocynthia roretzi. J Immunol 162:387–391
Page RDM (2001) TreeView ver 1.6.5. Distributed by author
Peitsch MC, Schwede T, Guex N (2000) Automated protein modelling—the proteome in 3D. Pharmacogenomics 1:257–266
Rost B (1996) PHD: predicting one-dimensional protein structure by profile based neural networks. Methods Enzymol 266:525–539
Rzhetsky A, Nei M (1993) Theoretical foundation of the minimum-evolution method of phylogenetic inference. Mol Biol Evol 10:1073–1095
Sahu A, Lambris JD (2001) Structure and biology of complement protein C3, a connecting link between innate and acquired immunity. Immunol Rev 180:35–48
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY
Saravanna T, Wiese C, Sojka D, Kopacek P (2003) Molecular cloning, structure, and bait region splice variants of alpha2-macroglobulin from the soft tick Ornithodoros moubata. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:841–851
Smith LC, Azumi K, Nonaka M (1999) Complement systems in invertebrates: the ancient alternative and lectin pathways. Immunopharmacology 42:107–120
Sottrup-Jensen L, Stepanik TM, Kristensen T, Lonblad PB, Jones CM, Wierzbicki DM, Magnusson S, Domdey H, Wetsel RA, Lundwall A, Tack BF, Fey GH (1985) Common evolutionary origin of alpha2-macroglobulin and complement components C3 and C4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 82:9–13
Stothard P (2000) The sequence manipulation suite: JavaScript programs for analyzing and formatting protein and DNA sequences. BioTechniques 28:1102–1104
Suzuki MM, Satoh N, Nonaka M (2002) C6-like and C3-like molecules from the cephalochordate, amphioxus, suggests a cytolytic complement system in invertebrates. J Mol Evol 54:671–679
Swofford DL (1998) PAUP*: phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (and other methods). Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, MA
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Valenzuela JG, Francischetti IM, Pham VM, Garfield MK, Mather TN, Ribeiro JM (2002) Exploring the sialome of the tick Ixodes scapularis. J Exp Biol 205:2843–2864
Vik DP, Amiguet P, Moffat GJ, Fey M, Amiguet-Barras F, Wetsel RA, Tack BF (1991) Structural features of the Human C3 gene: intron/exon organization, transcriptional start site, and promoter region sequence. Biochemistry 30:1080–1085
Vogel CW, Bredehorst R, Fritzinger DC, Grunwald T, Ziegelmuller P, Kock MA (1996) Structure and function of cobra venom factor, the complement-activating protein in cobra venom. Adv Exp Med Biol. 391:97–114
Zdobnov EM et al (2002) Comparative genome and proteome analysis of Anopheles gambiae and Drosophila melanogaster. Science 298:149–159
Zhang Y, Frohman MA (1997) Using rapid amplification of cDNA ends (RACE) to obtain full-length cDNAs. In: Cowell IG, Austin CA (eds) cDNA library protocols. Humana Press Inc, Totowa, NJ, pp 61–88
Zhu Y, Thangamani S, Ho B, Ding JL (2005) The ancient origin of the complement system. EMBO J 24:382–394
Acknowledgements
We thank Dr. M. Nonaka and Dr. M. Nakao for critical comments on an early version of the manuscript. M.L. Herrera, A.S. Goyos, and M. Gomez provided excellent technical assistance. This is contribution FIU-CII-001 from the FIU Comparative Immunology Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dishaw, L.J., Smith, S.L. & Bigger, C.H. Characterization of a C3-like cDNA in a coral: phylogenetic implications. Immunogenetics 57, 535–548 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-005-0005-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-005-0005-1