Abstract
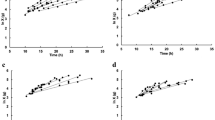
Saccharomyces bayanus, being of interest for wine-making, is not as well known as S. cerevisiae and, due to many changes in the yeast classification, accurate data concerning its metabolic activity are difficult to find. In order to produce this yeast as an active dry yeast to be used as a starter in wine-making, its sensitivity to glucose was determined as the objective of our work. Using the pulse technique in continuous culture, it was found that growth in a synthetic medium was not limited by vitamins or mineral salts. We determined the critical dilution rate of a continuous culture and performed an aerobic continuous culture, measuring the respiratory quotient on-line in order to observe the metabolic shift from respiratory to fermentative metabolism. The S. bayanus var. uvarum strain studied was Crabtree-positive (glucose-sensitive) but had a weaker respiratory capacity than S. cerevisiae since the dilution rate of the metabolic shift was only 0.15 h−1. These new data provide essential information for the biomass production of this yeast strain for wine-making.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiba S, Nagai S, Nishizawa Y (1976) Fed batch culture of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a perspective of computer control to enhance the productivity in baker's yeast cultivation. Biotechnol Bioeng 18:1001–1016
Bailey JE, Ollis DF (1986) Design and analysis of biological reactors. In: Verma K, Marti CC (eds) Biochemical engineering fundamentals 2nd edn. McGraw–Hill, New York, pp 554–561
Barnett JA, Payne RW, Yarrow D (1990) Yeasts: characteristics and identification, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Bertolini L, Zambonelli C, Giudici P, Castellari L (1996) Higher alcohol production by cryotolerant Saccharomyces strains. Am J Enol Vitic 47:343–345
Caridi A, Corte V (1997) Inhibition of malolactic fermentation by cryotolerant yeasts. Biotechnol Lett 19:723–726
Castellari L, Ferruzi M, Magrini A, Giudici P, Passarelli P, Zambonelli C (1994) Unbalanced wine fermentation by cryotolerant vs non-cryotolerant Saccharomyces strains. Vitis 33:49–52
Cooney CL, Wang HY, Wang DIC (1977) Computer-aided material balancing for prediction of fermentation parameters. Biotechnol Bioeng 19:55–67
Enfors SO (1998) Modes of process operation. In: Enfors SO, Haggstrom L (eds) Bioprocess technology: fundamentals and applications. Royal Institute of Technology, Stockholm, pp 105–158
Fiechter A, Fuhrmann GF, Kappeli O (1981) Regulation of glucose metabolism in growing yeast cells. Adv Microb Physiol 22:123–183
Kishimoto M, Goto S (1995) Growth temperatures and electrophoretic karyotyping as tools for practical discrimination of Saccharomyces bayanus and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Appl Microbiol 41:239–247
Kreger-van Rij NJW (1984) The yeast: a taxonomic study, 3rd edn. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Kuhn H, Friederich U, Fietcher A (1979) Defined minimal medium for a thermophilic Bacillus sp. developed by a chemostat pulse and shift technique. Microbiol Biotechnol 6:341–349
Larsson C, Stockar U von, Marison I, Gustafsson L (1993) Growth and metabolism of Saccharomyces cerevisiae in chemostat cultures under carbon-, nitrogen-, or carbon- and nitrogen-limitation conditions. J Bacteriol 175:4809–4816
Naumov GI (1996) Genetic identification of biological species in the Saccharomyces sensu stricto complex. J Ind Microbiol 17:295–302
Naumov GI (2000) New variety Saccharomyces bayanus var. uvarum comb. nov. revealed by genetic analysis. Microbiology 69:338–342
Posten CH, Cooney CL (1993) Growth of microorganisms. In: Rehm J, Reed G (eds) Biotechnology, 2nd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 113–162
Postma E, Verduyn C, Scheffers WA, Van Dijken JP (1989) Enzymic analysis of the Crabtree effect in glucose-limited chemostat cultures of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 55:468–477
Rainieri S, Zambonelli C, Tini V, Castellari L, Giudici P (1998) The enological traits of thermotolerant Saccharomyces strains. Am J Enol Vitic 49:319–324
Rainieri S, Zambonelli C, Hallsworth JE, Pulvirenti A, Giudici P (1999) Saccharomyces uvarum, a distinct group within Saccharomyces sensu stricto. FEMS Microbiol Lett 177:177–185
Rieger M, Kappeli O, Fiechter A (1983) The role of limited respiration in the incomplete oxidation of glucose by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol 129:653–661
Vaughan-Martini A, Martini A (1998) Saccharomyces Meyen ex Reess. In: Kurtzman CP, Fell JW (eds) The yeasts: a taxonomic study. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 58–371
Wang HY, Cooney CHL, Wang DI (1979) Computer control of baker's yeast. Biotechnol Bioeng 21:975–995
Acknowledgements.
The authors thank the Faculty of Enology of Bordeaux for providing the yeast strain and LAFFORT Oenologie (Bordeaux, France) for supporting the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serra, A., Strehaiano, P. & Taillandier, P. Characterization of the metabolic shift of Saccharomyces bayanus var. uvarum by continuous aerobic culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 62, 564–568 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1288-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1288-5