Abstract
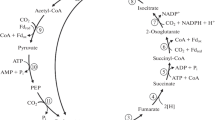
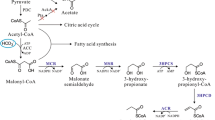
The 3-hydroxypropionate cycle, a pathway for autotrophic carbon dioxide fixation, is reviewed with special emphasis on the biochemistry of CO2 fixing enzymes in Acidianus brierleyi, a thermophilic and acidophilic archeon. In the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle, two enzymes, acetyl-CoA carboxylase and propionyl-CoA carboxylase, catalyze CO2 fixation. It has been shown in A. brierleyi, and subsequently in Metallosphaera sedula, that acetyl-CoA carboxylase is promiscuous, acting equally well on acetyl-CoA and propionyl-CoA. The subunit structure of the acyl-CoA carboxylase was shown to be α4β4γ4. Gene cloning revealed that the genes encoding the three subunits are adjacent to each other. accC encodes the β-subunit (59 kDa subunit, biotin carboxylase subunit), accB encodes the γ-subunit (20 kDa subunit, biotin carboxyl carrier protein), and pccB encodes the α-subunit (62 kDa subunit, carboxyltransferase subunit). Sequence analyses showed that accC and accB are co-transcribed and that pccB is transcribed separately. Potential biotechnological applications for the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle are also presented.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alber BE, Fuchs G (2002) Propionyl-coenzyme A synthase from Chloroflexus aurantiacus, a key enzyme of the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle for autotrophic CO2 fixation. J Biol Chem 277:12137–12143
Bell SD, Jackson SP (1998) Transcription and translation in archaea: a mosaic of eukaryal and bacterial features. Trends Microbiol 6:222–228
Best EA, Knauf VC (1993) Organization and nucleotide sequences of the genes encoding the biotin carboxyl carrier protein and biotin carboxylase protein of Pseudomonas aeruginosa acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase. J Bacteriol 175:6881–6889
Burton NP, Williams TD, Norris PR (1999) Carboxylase genes of Sulfolobus metallicus. Arch Microbiol 172:349–353
Chuakrut S, Arai H, Ishii M, Igarashi Y (2003) Characterization of a bifunctional archaeal acyl coenzyme A carboxylase. J Bacteriol 185:938–947
Davis MS, Cronan JE Jr (2001) Inhibition of Escherichia coli acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase by acyl-acyl carrier protein. J Bacteriol 183:1499–1503
Dennis PP (1997) Ancient ciphers: translation in Archaea. Cell 89:1007–1010
Gornicki P, Scappino LA, Haselkorn R (1993) Genes for two subunits of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase of Anabaena sp. Strain PCC 7120: biotin carboxylase and biotin carboxyl carrier protein. J Bacteriol 175:5268–5272
Herter S, Farfsing J, Gad’on N, Rieder C, Eisenreich W, Bacher A, Fuchs G (2001) Autotrophic CO2 fixation by Chloroflexus aurantiacus: study of glyoxylate formation and assimilation via the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle. J Bacteriol 183:4305–4316
Herter S, Fuchs G, Bacher A, Eisenreich W (2002a) A bicyclic autotrophic CO2 fixation pathway in Chloroflexus aurantiacus. J Biol Chem 277:20277–20283
Herter S, Busch A, Fuchs G (2002b) l-Malyl-CoA lyase/β-methylmalyl-coenzyme A lyase from Chloroflexus aurantiacus, a bifunctional enzyme involved in autotrophic CO2 fixation. J Bacteriol 184:5999–6006
Holo H (1989) Chloroflexus aurantiacus secretes 3-hydroxypropionate, a possible intermediate in the assimilation of CO2 and acetate. Arch Microbiol 151:252–256
Holo H, Sirevåg R (1986) Autotrophic growth and CO2 fixation of Chloroflexus aurantiacus. Arch Microbiol 145:173–180
Hügler M, Menendez C, Schagger H, Fuchs G (2002) Malonyl-coenzyme A reductase from Chloroflexus aurantiacus, a key enzyme of the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle for autotrophic CO2 fixation. J Bacteriol 184:2404–2410
Hügler M, Huber H, Stetter KO, Fuchs G (2003a) Autotrophic CO2 fixation pathways in archaea (Crenarchaeota). Arch Microbiol 179:160–173
Hügler M, Krieger RS, Jahn M, Fuchs G (2003b) Characterization of acetyl-CoA/propionyl-CoA carboxylase in Metallosphaera sedula. Eur J Biochem 270:736–744
Ishii M, Miyake T, Satoh T, Sugiyama H, Oshima Y, Kodama T, Igarashi Y (1997) Autotrophic carbon dioxide fixation in Acidianus brierleyi. Arch Microbiol 166:368–371
Kandler O, Stetter KO (1981) Evidence for autotrophic CO2 assimilation in Sulfolobus brierleyi via a reductive carboxylic acid pathway. Zentralbl Bakteriol Infektionskr Hyg Abt I Orig 2:111–121
Kazuta Y, Tokunaga E, Aramaki E, Kondo H (1998) Identification of lysine-238 of Escherichia coli biotin carboxylase as an ATP-binding residue. FEBS Lett 427:377–380
Kimura Y, Miyake R, Tokumasu Y, Sato M (2000) Molecular cloning and characterization of two genes for the biotin carboxylase and carboxyltransferase subunits of acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol 182:5462–5469
Levert KL, Lloyd RB, Waldrop GL (2000) Do cysteine 230 and lysine 238 of biotin carboxylase play a role in the activation of biotin? Biochemistry 39:4122–4128
Li SJ, Cronan JE Jr (1992a) The gene encoding the biotin carboxylase subunit of Escherichia coli acetyl-CoA carboxylase. J Biol Chem 267:855–863
Li SJ, Cronan JE Jr (1992b) The genes encoding the two carboxyltransferase subunits of Escherichia coli acetyl-CoA carboxylase. J Biol Chem 267:16841–16847
Marini P, Li SJ, Gardiol D, Cronan JE Jr, de Mendoza D (1995) The genes encoding the biotin carboxyl carrier protein and biotin carboxylase subunits of Bacillus subtilis acetyl coenzyme A carboxylase, the first enzyme of fatty acid synthesis. J Bacteriol 177:7003–7006
Reiter WD, Palm P, Zillig W (1988) Transcription termination in the archaebacterium Sulfolobus: signal structures and linkage to transcription initiation. Nucleic Acids Res 16:2445–2459
Samols D, Thornton CG, Murtif VL, Kumar GK, Haase FC, Wood HG (1988) Evolutionary conservation among biotin enzymes. J Biol Chem 263:6461–6464
Shorrosh BS, Dixon RA, Ohlrogge JB (1994) Molecular cloning, characterization, and elicitation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase from alfalfa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4323–4327
Sloane V, Blanchard CZ, Guillot F, Waldrop GL (2001) Site-directed mutagenesis of ATP binding residues of biotin carboxylase. J Biol Chem 276:24991–24996
Strauss G, Fuchs G (1993) Enzymes of a novel autotrophic CO2 fixation pathway in the phototrophic bacterium Chloroflexus aurantiacus, the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle. Eur J Biochem 215:633–643
Strauss G, Eisenreich W, Bacher A, Fuchs G (1992) 13C-NMR study of autotrophic CO2 fixation pathways in the sulfur-reducing Archaebacterium Thermoproteus neutrophilus and in the phototrophic Eubacterium Chloroflexus aurantiacus. Eur J Biochem 205:853–866
Thomm M, Wich G (1988) An archaebacterial promoter element for stable RNA genes with homology to TATA box of higher eukaryotes. Nucleic Acids Res 16:151–163
Wich G, Hummel H, Jarsch M, Bar U, Bock A (1986) Transcription signals for stable RNA genes in Methanococcus. Nucleic Acids Res 14:2459–2479
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishii, M., Chuakrut, S., Arai, H. et al. Occurrence, biochemistry and possible biotechnological application of the 3-hydroxypropionate cycle. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 64, 605–610 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1540-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-003-1540-z