Abstract
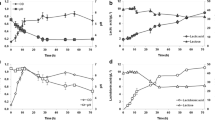
The decarboxylation of tyrosine by certain lactic acid bacteria leads to the undesirable presence of tyramine in fermented foods. Tyramine is the most frequent biogenic amine found in cheese and is also commonly found in other fermented foods and beverages. The tyramine-producing strain Enterococcus durans IPLA 655 was grown in a bioreactor under different conditions to determine the influence of carbon source, tyrosine and tyramine concentrations, and pH on tyramine production. The carbon source appeared to have no significant effect on the production of tyramine. In contrast, tyrosine was necessary for tyramine production, while the presence of tyramine itself in the growth medium inhibited such production. pH showed by far the greatest influence on tyramine synthesis; tyramine was produced in the greatest quantities at pH 5.0, although this was accompanied by a reduced growth rate.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schaffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bearson S, Bearson B, Foster JW (1997) Acid stress responses in enterobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Lett 147:173–180
Connil N, Plissoneau L, Onno B, Pilet MF, Prevost H, Dousset X (2002) Growth of Carnobacterium divergens V41 and production of biogenic amines and divercin V41 in sterile cold-smoked salmon extract at varying temperatures, NaCl levels, and glucose concentrations. J Food Prot 65:333–338
Coton E, Rollan GC, Lonvaud-Funel A (1998) Histidine decarboxylase of Leuconostoc oenos 9204: purification, kinetic properties, cloning and nucleotide sequence of the hdc gene. J Appl Microbiol 84:143–151
Cuesta P (1996) Desarrollo de un cultivo iniciador para el queso Afuega’l Pitu. Ph.D. thesis, University of Oviedo, Oviedo, Spain
Delgado S, Mayo B (2004) Phenotypic and genetic diversity of Lactococcus lactis and Enterococcus spp. strains isolated from Northern Spain starter-free farmhouse cheeses. Int J Food Microbiol 90:309–319
Edwards U, Rogall T, Blocker H, Emde M, Bottger EC (1989) Isolation and direct complete nucleotide determination of entire genes. Characterization of a gene coding for 16S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 17:7843–7853
Eitenmiller RR, Koehler PE, Reagan JO (1978) Tyramine in fermented sausages: factors affecting formation of tyrosine and tyrosine decarboxylase. J Food Sci 43:689–693
Fernández M, Linares DM, Alvarez MA (2004) Sequencing of the tyrosine decarboxylase cluster of Lactococcus lactis IPLA 655 and the development of a PCR method for detecting tyrosine decarboxylating lactic acid bacteria. J Food Prot 67:2521–2529
Fernández M, Flórez AB, Linares DM, Mayo B, Alvarez MA (2006) Early PCR detection of tyramine-producing bacteria during cheese production. J Dairy Res 73:1–4
Foulquie Moreno MR, Sarantinopoulos P, Tsakalidou E, De Vuyst L (2006) The role and application of enterococci in food and health. Int J Food Microbiol 106:1–24
Gale EF (1946) Bacterial amino acid decarboxylases. Adv Enzymol 6:1–32
Gardini F, Martuscelli M, Caruso MC, Galgano F, Crudele MA, Favatti F, Guerzoni ME, Suzzi G (2001) Effects of pH, temperature and NaCl concentration on the growth kinetics, proteolytic activity and biogenic amine production of Enterococcus faecalis. Int J Food Microbiol 64:105–117
Krause I, Bockhardt A, Neckemann H, Henle T, Klostermeyer H (1995) Simultaneous determination of amino acids and biogenic amines by reversed-phase high performance liquid chromatography of the dabsyl derivatives. J Chromatogr A 715:67–79
Landete JM, Ferrer S, Pardo I (2003) Regulación genica y enzimatica de la histidina descarboxilasa (HDC) de Lactobacillus hilgardii Congreso Nacional de Microbiologia (P 42), p 314
Le Jeune C, Lonvaud-Funel A, ten Brink B, Hofstra H, van der Vossen JM (1995) Development of a detection system for histidine decarboxylating lactic acid bacteria based on DNA probes, PCR and activity test. J Appl Bacteriol 78:316–326
Lin J, Smith MP, Chapin KC, Baik HS, Benett GN, Foster JW (1996) Mechanisms of acid resistance in enterohemorragic Escherichia coli. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:3094–3100
Marcobal A, Martin-Alvarez PJ, Moreno-Arribas MV, Muñoz R (2006) A multifactorial design for studying factors influencing growth and tyramine production of the lactic acid bacteria Lactobacillusbrevis CECT 4669 and Enterococcus faecium BIFI-58. Res Microbiol 157:417–424
Moreno-Arribas V, Lonvaud-Funel A (1999) Tyrosine decarboxylase activity of Lactobacillusbrevis IrOEB 9809 isolated from wine and L. brevis ATCC 367. FEMS Microbiol Lett 180:55–60
Novella-Rodríguez S, Veciana-Nogues MT, Izquierdo-Pulido M, Vidal-Carou MC (2003) Distribution of biogenic amines and polyamines in cheese. J Food Sci 68:750–755
Novella-Rodríguez S, Veciana-Nogues MT, Roig-Sagués AX, Trujillo-Mesa AJ, Vidal-Carou MC (2004) Evaluation of biogenic amines and microbial counts throughout the ripening of goat cheeses from pasteurized and raw milk. J Dairy Res 71:245–252
Ordoñez AI, Ibáñez FC, Torre P, Barcina Y (1997) Formation of biogenic amines in Idiazábal ewe’s-milk cheese: effect of ripening, pasteurization, and starter. J Food Prot 60:1371–1375
O’Sullivan E, Condon S (1999) Relationship between acid tolerance, cytoplasmic pH, and ATP and H+-ATPase levels in chemostat cultures of Lactococcus lactis. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:2287–2293
Poolman B, Driessen AJ, Konings WN (1987) Regulation of arginine-ornithine exchange and the arginine deiminase pathway in Streptococcus lactis. J Bacteriol 169:5597–5604
Psoni L, Kotzamanides C, Andrighetto C, Lombardi A, Tzanetakis N, Litopoulou-Tzanetaki E (2006) Genotypic and phenotypic heterogeneity in Enterococcus isolates from Batzos, a raw goat milk cheese. Int J Food Microbiol 119:109–120
Rollan GC, Coton E, Lonvaud-Funel A (1995) Histidine decarboxylase activity of Leuconostoc oenos 9204. Food Microbiol 12:455–461
Sanders JW, Leenhouts K, Burghoorn J, Brands JRl, Venema G, Kok J (1998) A chloride-inducible acid resistance mechanism in Lactococcus lactis and its regulation. Mol Microbiol 27:299–310
Santos-Buelga C, Peña-Egido MJ, Rivas-Gonzalo JC (1986) Changes in tyramine during Chorizo–sausages ripening. J Food Sci 51:518–527
Schelp E, Worley S, Monzingo AF, Ernst S, Robertus JD (2001) pH-induced structural changes regulate histidine decarboxylase activity in Lactobacillus 30a. J Mol Biol 306:727–732
Shalaby AR (1996) Significance of biogenic amines to food safety and human health. Food Res Int 29:675–690
Silla Santos MH (1996) Biogenic amines: their importance in foods. Int J Food Microbiol 29:213–231
Suzzi G, Gardini F (2003) Biogenic amines in dry fermented sausages: a review. Int J Food Microbiol 88:41–54
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by the Commission of the European Communities (QLK1-CT2002-02389). D. M. Linares was the recipient of a fellowship from the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science, and M. Fernández is a beneficiary of a I3P CSIC contract financed by the European Social Fund. We thank Adrian Burton for proofreading the English.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernández, M., Linares, D.M., Rodríguez, A. et al. Factors affecting tyramine production in Enterococcus durans IPLA 655. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 73, 1400–1406 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0596-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-006-0596-y