Abstract
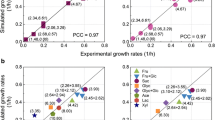
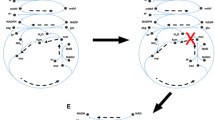
To understand the metabolic characteristics of Clostridium acetobutylicum and to examine the potential for enhanced butanol production, we reconstructed the genome-scale metabolic network from its annotated genomic sequence and analyzed strategies to improve its butanol production. The generated reconstructed network consists of 502 reactions and 479 metabolites and was used as the basis for an in silico model that could compute metabolic and growth performance for comparison with fermentation data. The in silico model successfully predicted metabolic fluxes during the acidogenic phase using classical flux balance analysis. Nonlinear programming was used to predict metabolic fluxes during the solventogenic phase. In addition, essential genes were predicted via single gene deletion studies. This genome-scale in silico metabolic model of C. acetobutylicum should be useful for genome-wide metabolic analysis as well as strain development for improving production of biochemicals, including butanol.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amore R, Kotter P, Kuster C, Ciriacy M, Hollenberg CP (1991) Cloning and expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of the NAD(P)H-dependent xylose reductase-encoding gene (XYL1) from the xylose-assimilating yeast Pichia stipitis. Gene 109:89–97
Atsumi S, Cann AF, Connor MR, Shen CR, Smith KM, Brynildsen MP, Chou KJ, Hanai T, Liao JC (2008) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for 1-butanol production. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/jymben200708003
Bailey JE (1991) Toward a science of metabolic engineering. Science 252:1668–1675
Becker SA, Palsson BØ (2005) Genome-scale reconstruction of the metabolic network in Staphylococcus aureus N315: an initial draft to the two-dimensional annotation. BMC Microbiol 5:8–19
Bonarius H, Schmid G, Tramper J (1997) Flux analysis of underdetermined metabolic networks: the quest for the missing constraints. Trends Biotechnol 15:308–314
Borodina I, Krabben P, Nielsen J (2005) Genome-scale analysis of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) metabolism. Genome Res 15:820–829
Breitling R, Vitkup D, Barrett MP (2008) New surveyor tools for charting microbial metabolic maps. Nat Rev Microbiol 6:156–161
Caspi R, Foerster H, Fulcher CA, Hopkinson R, Ingraham J, Kaipa P, Krummenacker M, Paley S, Pick J, Rhee SY, Tissier C, Zhang P, Karp PD (2006) MetaCyc: a multiorganism database of metabolic pathways and enzymes. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D511–D516
Desai RP, Harris LM, Welker NE, Papoutsakis ET (1999a) Metabolic flux analysis elucidates the importance of the acid-formation pathways in regulating solvent production by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Metab Eng 1:206–213
Desai RP, Nielsen LK, Papoutsakis ET (1999b) Stoichiometric modeling of Clostridium acetobutylicum fermentations with non-linear constraints. J Biotechnol 71:191–205
Duarte NC, Herrgard MJ, Palsson BØ (2004) Reconstruction and validation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae iND750, a fully compartmentalized genome-scale metabolic model. Genome Res 14:1298–1309
Dürre P (2007) Biobutanol: an attractive biofuel. Biotechnol J 2:1525–1534
Edwards JS, Palsson BØ (2000) The Escherichia coli MG1655 in silico metabolic genotype: its definition, characteristics, and capabilities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:5528–5533
Edwards JS, Ramakrishna R, Schilling CH, Palsson BØ (1999) Metabolic flux balance analysis. In: Lee SY, Papoutsakis ET (eds) Metabolic engineering. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 13–57
Feist AM, Palsson BO (2008) The growing scope of applications of genome-scale metabolic reconstructions using Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 26:659–667
Feist AM, Scholten JC, Palsson BØ, Brockman FJ, Ideker T (2006) Modeling methanogenesis with a genome-scale metabolic reconstruction of Methanosarcina barkeri. Mol Syst Biol 2:20060004
Feist AM, Henry CS, Reed JL, Krummenacker M, Joyce AR, Karp PD, Broadbelt LJ, Hatzimanikatis V, Palsson BØ (2007) A genome-scale metabolic reconstruction for Escherichia coli K-12 MG1655 that accounts for 1260 ORFs and thermodynamic information. Mol Syst Biol 3:121–138
Francke C, Siezen RJ, Teusink B (2005) Reconstructing the metabolic network of a bacterium from its genome. Trends Microbiol 13:550–558
Fuhrer T, Chen L, Sauer U, Vitkup D (2007) Computational prediction and experimental verification of the gene encoding the NAD+/NADP+-dependent succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 189:8073–8078
Green EM, Bennett GN (1996) Inactivation of an aldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase gene from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 57–58:213–221
Green EM, Boynton ZL, Harris LM, Rudolph FB, Papoutsakis ET, Bennett GN (1996) Genetic manipulation of acid formation pathways by gene inactivation in Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Microbiology 142(Pt 8):2079–2086
Harris LM, Desai RP, Welker NE, Papoutsakis ET (2000) Characterization of recombinant strains of the Clostridium acetobutylicum butyrate kinase inactivation mutant: need for new phenomenological models for solventogenesis and butanol inhibition? Biotechnol Bioeng 67:1–11
Heap JT, Pennington OJ, Cartman ST, Carter GP, Minton NP (2007) The ClosTron: a universal gene knock-out system for the genus Clostridium. J Microbiol Methods 70:452–464
Herrmann G, Jayamani E, Mai G, Buckel W (2008) Energy conservation via electron-transferring flavoprotein in anaerobic bacteria. J Bacteriol 190:784–791
Hou BK, Kim JS, Jun JH, Lee DY, Kim YW, Chae S, Roh M, In YH, Lee SY (2004) BioSilico: an integrated metabolic database system. Bioinformatics 20:3270–3272
Huang KX, Huang S, Rudolph FB, Bennett GN (2000) Identification and characterization of a second butyrate kinase from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 2:33–38
Huynen MA, Dandekar T, Bork P (1999) Variation and evolution of the citric-acid cycle: a genomic perspective. Trends Microbiol 7:281–291
Inui M, Suda M, Kimura S, Yasuda K, Suzuki H, Toda H, Yamamoto S, Okino S, Suzuki N, Yukawa H (2008) Expression of Clostridium acetobutylicum butanol synthetic genes in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:1305–1316
Jones DT, Woods DR (1986) Acetone–butanol fermentation revisited. Microbiol Rev 50:484–524
Jungermann K, Leimenstoll G, Rupprecht E, Thauer RK (1971) Demonstration of NADH-ferredoxin reductase in two saccharolytic Clostridia. Arch Mikrobiol 80:370–372
Kanehisa M, Goto S, Hattori M, Aoki-Kinoshita KF, Itoh M, Kawashima S, Katayama T, Araki M, Hirakawa M (2006) From genomics to chemical genomics: new developments in KEGG. Nucleic Acids Res 34:D354–D357
Keis S, Shaheen R, Jones DT (2001) Emended descriptions of Clostridium acetobutylicum and Clostridium beijerinckii, and descriptions of Clostridium saccharoperbutylacetonicum sp. nov. and Clostridium saccharobutylicum sp. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 51:2095–2103
Kim BH, Bellows P, Datta R, Zeikus JG (1984) Control of carbon and electron flow in Clostridium acetobutylicum fermentations: utilization of carbon monoxide to inhibit hydrogen production and to enhance butanol yields. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:764–770
Kim TY, Kim HU, Park JM, Song H, Kim JS, Lee SY (2007) Genome-scale analysis of Mannheimia succiniciproducens metabolism. Biotechnol Bioeng 97:657–671
Kotter P, Amore R, Hollenberg CP, Ciriacy M (1990) Isolation and characterization of the Pichia stipitis xylitol dehydrogenase gene, XYL2, and construction of a xylose-utilizing Saccharomyces cerevisiae transformant. Curr Genet 18:493–500
Lee D, Redfern O, Orengo C (2007a) Predicting protein function from sequence and structure. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:995–1005
Lee KH, Park JH, Kim TY, Kim HU, Lee SY (2007b) Systems metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for l-threonine production. Mol Syst Biol 3:149
Lee SH, Park SJ, Lee SY, Hong SH (2008) Biosynthesis of enantiopure (S)-3-hydroxybutyric acid in metabolically engineered Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 79:633–641
Li F, Hinderberger J, Seedorf H, Zhang J, Buckel W, Thauer RK (2008) Coupled ferredoxin and crotonyl coenzyme A (CoA) reduction with NADH catalyzed by the butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase/Etf complex from Clostridium kluyveri. J Bacteriol 190:843–850
Luo RY, Liao S, Tao GY, Li YY, Zeng S, Li YX, Luo Q (2006) Dynamic analysis of optimality in myocardial energy metabolism under normal and ischemic conditions. Mol Syst Biol 2:2006.0031
Mermelstein LD, Welker NE, Bennett GN, Papoutsakis ET (1992) Expression of cloned homologous fermentative genes in Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Biotechnology (NY) 10:190–195
Monot F, Martin JR, Petitdemange H, Gay R (1982) Acetone and butanol production by Clostridium acetobutylicum in a synthetic medium. Appl Environ Microbiol 44:1318–1324
Monot F, Engasser JM, Petitdemange H (1984) Influence of pH and undissociated butyric acid on the production of acetone and butanol in batch cultures of Clostridium acetobutylicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 19:422–426
Nair RV, Bennett GN, Papoutsakis ET (1994) Molecular characterization of an aldehyde/alcohol dehydrogenase gene from Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. J Bacteriol 176:871–885
Nölling J, Breton G, Omelchenko MV, Makarova KS, Zeng Q, Gibson R, Lee HM, Dubois J, Qiu D, Hitti J, Wolf YI, Tatusov RL, Sabathe F, Doucette-Stamm L, Soucaille P, Daly MJ, Bennett GN, Koonin EV, Smith DR (2001) Genome sequence and comparative analysis of the solvent-producing bacterium Clostridium acetobutylicum. J Bacteriol 183:4823–4838
Overheard MA, Puchalka J, Fryer KE, Martins dos Santos VA, Papin JA (2008) Genome-scale metabolic network analysis of the opportunistic pathogen Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1. J Bacteriol 190:2790–2803
Oh YK, Palsson BØ, Park SM, Schilling CH, Mahadevan R (2007) Genome-scale reconstruction of metabolic network in Bacillus subtilis based on high-throughput phenotyping and gene essentiality data. J Biol Chem 282:28791–28799
Ounine K, Petitdemange H, Raval G, Gay R (1983) Acetone–butanol production from pentoses by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Biotechnol Lett 5:605–610
Paredes CJ, Alsaker KV, Papoutsakis ET (2005) A comparative genomic view of clostridial sporulation and physiology. Nat Rev Microbiol 3:969–978
Park JH, Lee KH, Kim TY, Lee SY (2007) Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of l-valine based on transcriptome analysis and in silico gene knockout simulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:7797–7802
Park JH, Lee SY, Kim TY, Kim HU (2008) Application of systems biology for bioprocess development. Trends Biotechnol 26:404–412
Petitdemange H, Cherrier C, Bengone JM, Gay R (1977) Study of the NADH and NADPH-ferredoxin oxidoreductase activities in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Can J Microbiol 23:152–160
Reed JL, Famili I, Thiele I, Palsson BØ (2006a) Towards multidimensional genome annotation. Nat Rev Genet 7:130–141
Reed JL, Patel TR, Chen KH, Joyce AR, Applebee MK, Herring CD, Bui OT, Knight EM, Fong SS, Palsson BO (2006b) Systems approach to refining genome annotation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:17480–17484
Schilling CH, Edwards JS, Palsson BØ (1999) Toward metabolic phenomics: analysis of genomic data using flux balances. Biotechnol Prog 15:288–295
Schilling CH, Edwards JS, Letscher D, Palsson BØ (2000) Combining pathway analysis with flux balance analysis for the comprehensive study of metabolic systems. Biotechnol Bioeng 71:286–306
Segre D, Vitkup D, Church GM (2002) Analysis of optimality in natural and perturbed metabolic networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:15112–15117
Senger RS, Papoutsakis ET (2008a) Genome-scale model for Clostridium acetobutylicum. Part 1: metabolic network resolution and analysis. Biotechnol Bioeng (in press)
Senger RS, Papoutsakis ET (2008b) Genome-scale model for Clostridium acetobutylicum. Part 2: development of specific proton flux states and numerically-determined sub-systems. Biotechnol Bioeng (in press)
Shao L, Hu S, Yang Y, Gu Y, Chen J, Yang Y, Jiang W, Yang S (2007) Targeted gene disruption by use of a group II intron (targetron) vector in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Cell Res 17:963–965
Shinto H, Tashiro Y, Yamashita M, Kobayashi G, Sekiguchi T, Hanai T, Kuriya Y, Okamoto M, Sonomoto K (2007) Kinetic modeling and sensitivity analysis of acetone–butanol–ethanol production. J Biotechnol 131:45–56
Stephanopoulos GN, Aristidou AA, Nielsen J (1998) Metabolic engineering: principles and methodologies. Academic, New York
Tangney M, Mitchell WJ (2000) Analysis of a catabolic operon for sucrose transport and metabolism in Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 2:71–80
Tangney M, Mitchell WJ (2007) Characterisation of a glucose phosphotransferase system in Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 74:398–405
Thiele I, Vo TD, Price ND, Palsson BØ (2005) Expanded metabolic reconstruction of Helicobacter pylori (iIT341 GSM/GPR): an in silico genome-scale characterization of single- and double-deletion mutants. J Bacteriol 187:5818–5830
Varma A, Palsson BØ (1994) Stoichiometric flux balance models quantitatively predict growth and metabolic by-product secretion in wild-type Escherichia coli W3110. Appl Environ Microbiol 60:3724–3731
Wang Q, Wu C, Chen T, Chen X, Zhao X (2006) Expression of galactose permease and pyruvate carboxylase in Escherichia coli ptsG mutant increases the growth rate and succinate yield under anaerobic conditions. Biotechnol Lett 28:89–93
Yu Y, Tangney M, Aass HC, Mitchell WJ (2007) Analysis of the mechanism and regulation of lactose transport and metabolism in Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:1842–1850
Zverlov VV, Berezina O, Velikodvorskaya GA, Schwarz WH (2006) Bacterial acetone and butanol production by industrial fermentation in the Soviet Union: use of hydrolyzed agricultural waste for biorefinery. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:587–597
Acknowledgments
We wish to express thanks to Peter Schumann and Jong-Soon Choi for the determination of cell wall and amino acid composition, respectively. Also, we are grateful to Jin Young Lee and Yu Sin Jang for discussion on cell cultivation and analytical procedure. Finally, we thank Tae Yong Kim and Hyun Uk Kim for discussion on flux balance analysis. This work was supported by the Korea–Australia Collaborative Research Project on the Development of Sucrose-Based Bioprocess Platform (N02071165) from the Korean Ministry of Knowledge Economy. Further support by LG Chem Chair Professorship and Microsoft are appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
J. L. and H. Y. equally contributed to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Data 1
Gene–protein–reaction relationship, metabolite abbreviation, and whole reaction set used in the model. (PDF 548 KB)
Supplementary Data 2
Biomass composition of C. acetobutylicum, ATCC 824 used in the model. (PDF 79.6 KB)
Supplementary Data 3
The list of essential and partially essential genes in synthetic medium from in silico gene deletion analysis. (PDF 60.8 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, J., Yun, H., Feist, A.M. et al. Genome-scale reconstruction and in silico analysis of the Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824 metabolic network. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80, 849–862 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1654-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-008-1654-4